1 Multi Entity Implementation
This topic describes the information about Multi Entity Implementation.
Banks can have multiple implementations across different geographies or can have multiple brands within the same legal entity.
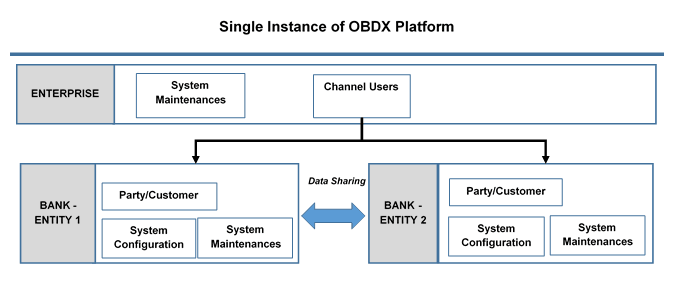
Multi Entity is a mechanism through which the banks can deploy a single instance of platform and onboard multiple entities onto the platform.
The same platform can host data of multiple entities on a single instance that runs on a set of resources. The banks can have data sharing enabled across multiple entities so that users from one entity can have access to data of other entities if required.
As part of the OBAPIS Cloud Service Installer, there will always be default entity created along with a system administrator.
If the implementation of the bank is multi entity enabled, system administrator can create new entities with their details as part of system configuration and also edit details of the default entity.
The system administrator by default gets access to all the created as well as the default entities.
There is a parameter for multi entity enabled implementation wherein the bank can decide if data sharing across entities is required.
Note:
Currently in the system, data sharing across entities is always enabled and the same cannot be disabled by the user.Users can be mapped to more than one entity depending on the implementation requirements. User always has a default/home entity to which he/she is mapped to and can also have accessible entities to access details of other entities.
If there is a need by the bank wherein some of the users i.e. bank administrator or corporate/retail users should not get access to all of the created entities then the same can be controlled through User Management by not giving access to the required entities.
For users who have access to multiple entities, there will be an entity switcher as part of the transaction/inquiry screen wherein the user can switch the entity to the home/accessible entity and inquire details of that entity.
The system maintenance can be at an enterprise level i.e. the same maintenance/configuration being applicable for all the created entities and certain maintenance are specific to an entity i.e. each entity can have a different setup or configuration.
Figure 1-1 Single Instance of OBDX Platform
The classification of administrative maintenance being at an enterprise or an entity level is present below:
Table 1-1 Classification of Administrative
| Sr No. | Transactions | Entity/Enterprise | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | System Configuration | Entity | - |
| 2 | Transaction Aspects | Enterprise | - |
| 3 | Limits Definition | Entity | - |
| 4 | Limits Package | Entity | - |
| 5 | Spend Category Maintenance | Entity | - |
| 6 | Goal Category Maintenance | Entity | - |
| 7 | System Rules | Enterprise | Role level limits will be defined for each entity |
| 8 | Role Transaction Mapping | Enterprise | - |
| 9 | Payment Purpose Mapping | Entity | - |
| 10 | Payee Restrictions | Entity | - |
| 11 | Biller Category Mapping | Entity | - |
| 12 | Authentication | Entity | - |
| 13 | Manage Security Questions | Enterprise | - |
| 14 | Password Policy Maintenance | Enterprise | - |
| 15 | User Group Subject Mapping | Entity | - |
| 16 | Alerts Maintenance | Enterprise | Alerts message template are at entity level |
| 17 | Mailers | Entity | - |
| 18 | Mailbox | Entity | - |
| 19 | User Print Information | Enterprise | - |
| 20 | User Onboarding | Entity | - |
| 21 | Merchant Onboarding | Entity | - |
| 22 | Transaction Blackout | Entity | - |
| 23 | Working Window | Entity | - |
| 24 | Manage Brand | Entity | - |
| 25 | Audit Log | Entity | - |
| 26 | ATM/ Branch Maintenance | Entity | - |
| 27 | Product Mapping | Entity | - |
| 28 | Party Preferences | Entity | - |
| 29 | Party to Party Linkage | Entity | - |
| 30 | Workflow Management | Entity | - |
| 31 | Rules Management | Entity | - |
| 32 | Party Account Access | Entity | - |
| 33 | User Account Access | Entity | - |
| 34 | Service Request | Entity | - |
| 35 | File Identifier Maintenance | Entity | - |
| 36 | User File Identifier Mapping | Entity | - |
| 37 | Reports | Enterprise | - |
| 38 | User Report Mapping | Entity | - |
| 39 | User Group Management | Entity | - |
| 40 | Alert Subscription | Enterprise | - |
| 41 | Session Summary | Entity | - |
| 42 | ATM/ Branch Locator | Entity | - |
| 43 | Manage Alerts | Enterprise | - |
Once the OBAPIS Cloud Service installation is complete, system administrator logs in and starts with the system configuration.
There will always be a default entity available in OBAPIS Cloud Service i.e. one created as part of installer irrespective of whether the implementation is multi entity enabled.