4 Deploying Authorization Service
This chapter describes how to optionally deploy and manage the Authorization service.
Overview
The Authorization service defines a simplified and centralized approach for managing the authorization configurations for services.
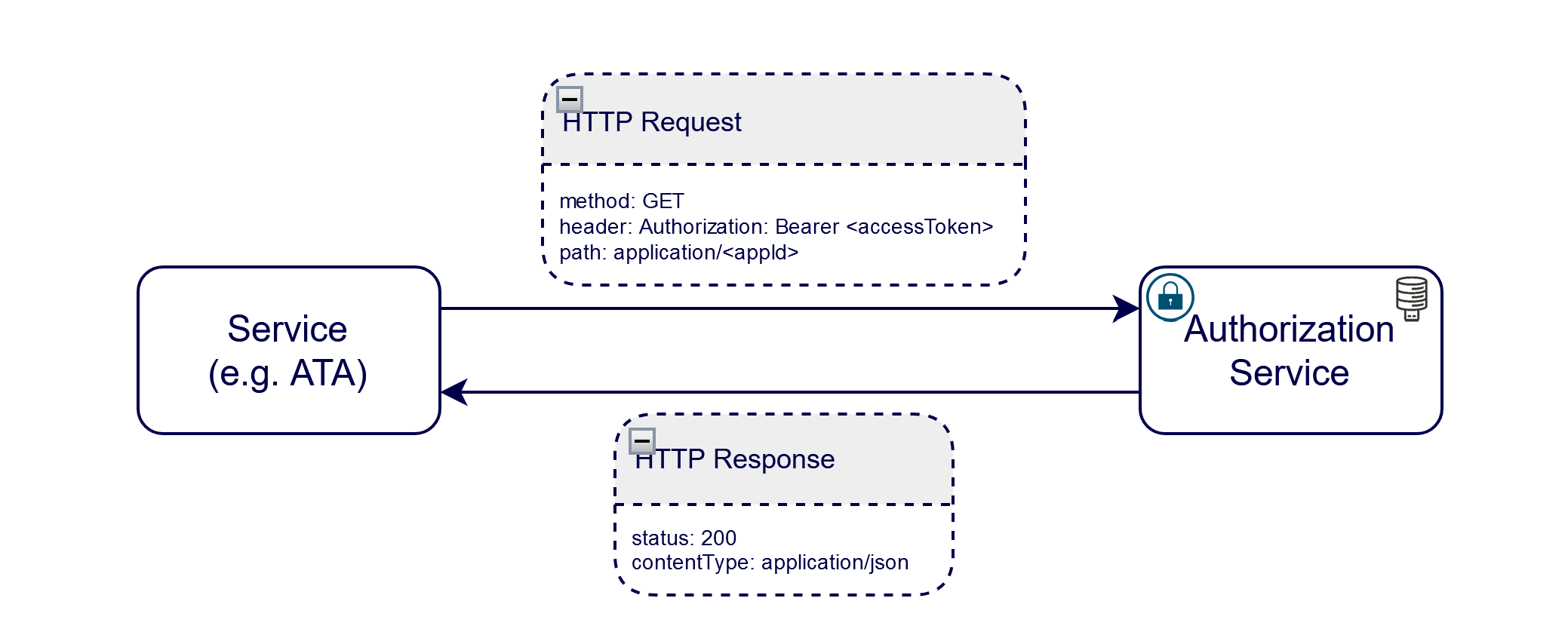
The consuming service (for example, ATA) sends an HTTP request with access token (from IdP) as Authorization Header to get the allowed resources for the authenticated users. Based on the response, users are allowed to perform certain actions on the consuming service.
For example, users with AtaAdministrator
role are allowed to customize the icons and colors on the ATA canvas.
The users with AtaAdvancedUser role are
allowed to access the advance settings of ATA canvas, but are not allowed to
customize the icons and colors on the ATA canvas.
The architecture diagram of Authorization service is as follows:
Creating Authorization Images
You must install the prerequisite software and tools for creating the Authorization images.
Prerequisites for Creating Authorization Images
You require the following prerequisites for creating the Authorization images:
- Podman on the build machine (if Linux version is greater than or equal to 8).
- Docker on the build machine (if Linux version is lesser than 8).
- Authorization Builder Toolkit. For the toolkit, see "Unified Inventory and Topology Toolkit".
- Install Maven and update the path variable with Maven Home as
follows:
set PATH variable export PATH=$PATH:$MAVEN_HOME/bin - Install Java with JAVA_HOME set in the environment as
follows:
Set PATH variable export PATH=$PATH:$JAVA_HOME/bin - Bash, to enable the
<tab>command.
Note:
See UIM Software Compatibility for software versions.Configuring Authorization Images
The corresponding manifest file describes the input that goes into the Authorization images. The default configuration in the latest manifest file provides the necessary components for creating the Authorization images. See "About the Manifest File" for more information.
Creating Authorization and Schema Images
To create the Authorization and schema images:
- Set the JAVA_HOME variable in your environment to match the
location of your Java installation as
follows:
export JAVA_HOME=<location of jdk-21> - Go to WORKSPACEDIR.
- Download the JDK 21 (jdk-<version>_linux-x64_bin.tar.gz) for linux and copy it to $WORKSPACEDIR/authorization-builder/staging/downloads/java.
- (Optional) If there is a change in the JDK version or in the file
name, update the version and path accordingly in the manifest file as
follows:
$vi $WORKSPACEDIR/authorization-builder/bin/authorization_manifest.yaml jdk: vendor: Oracle version: <JDK Version> path: $CN_BUILDER_STAGING/downloads/java/jdk-<version>_linux-x64_bin.tar.gz - Set the proxy environment variables for running Gradle. For
example:
#The eth0 is sample. replace "etho" with your specific interface name. export ip_addr=`ip -f inet addr show eth0|egrep inet|awk '{print $2}'|awk -F/ '{print $1}'` export http_proxy= export https_proxy=$http_proxy export no_proxy=localhost,$ip_addr export HTTP_PROXY= export HTTPS_PROXY=$HTTP_PROXY export NO_PROXY=localhost,$ip_addr - Update
$WORKSPACEDIR/authorization-builder/bin/gradle.properties with
required
proxies:
systemProp.http.proxyHost= systemProp.http.proxyPort= systemProp.https.proxyHost= systemProp.https.proxyPort= systemProp.http.nonProxyHosts=localhost|127.0.0.1 systemProp.https.nonProxyHosts=localhost|127.0.0.1 - Run
build-all-images.shin bin to build all the images (authorization, authorization-schema):cd $WORKSPACEDIR/authorization-builder/bin ./build-all-images.sh
Note:
You can include the above procedure into your CI pipeline as long as the required components are already downloaded to the staging area.
Creating an Authorization Service Instance
This section describes how to create an Authorization service instance in your cloud native environment using the operational scripts and the configuration provided in the common cloud native toolkit.
Before you can create an Authorization service instance, you must validate cloud native environment. See "Planning UIM Installation" for details on prerequisites.
In this section, while creating a basic instance, the project name is considered as sr and instance name is considered as quick.
Note:
Project and instance names cannot contain any special characters.
Installing Authorization Cloud Native Artifacts and Toolkit
Build container images for the following using the Authorization cloud native image builder:
- Authorization application
- Authorization schema installer
See "Deployment Toolkits" to download the Common cloud native toolkit archive file. Set the variable for the installation directory by running the following command, where $WORKSPACEDIR is the installation directory of the COMMON cloud native toolkit:
export COMMON_CNTK=$WORKSPACEDIR/common-cntkSetting up Environment Variables
The Authorization service relies on access to certain environment variables to run seamlessly. Ensure the following variables are set in your environment:
- Path to your common cloud native toolkit
- Traefik namespace
To set the environment variables:
- Set the COMMON_CNTK variable to the path of directory where the Common
cloud native toolkit is extracted as
follows:
$ export COMMON_CNTK=$WORKSPACEDIR/common-cntk - Set SPEC_PATH variable to the location where application and database
YAML files are copied. See "Assembling the Specifications" to copy specification files if
not already
copied.
$ export SPEC_PATH=$WORKSPACEDIR/spec_dirFor example:
$ mkdir -p $SPEC_PATH/$PROJECT/$INSTANCE/common $ cp $COMMON_CNTK/samples/applications.yaml $SPEC_PATH/$PROJECT/$INSTANCE/applications.yaml $ cp $COMMON_CNTK/samples/database.yaml $SPEC_PATH/$PROJECT/$INSTANCE/database.yaml $ cp $COMMON_CNTK/samples/credentials/common-config.yaml $SPEC_PATH/$PROJECT/$INSTANCE/common/common-config.yaml
Creating Secrets
You must store sensitive data and credential information in the form of Kubernetes Secrets that the scripts and Helm charts in the toolkit consume. Managing secrets is out of the scope of the toolkit and must be implemented while adhering to your organization's corporate policies. Additionally, ATA service does not establish password policies.
Creating Secrets for Authorization Database Credentials
The database secret specifies the connectivity details and the credentials for connecting to the Authorization PDB (Authorization schema). This is consumed by the Authorization DB installer and Authorization runtime.
To create secrets for authorization database credentials:
- Run the following script to create the required
secrets:
$COMMON_CNTK/scripts/manage-app-credentials.sh -p <project-name> -i <instance-name> -a authorization -f $SPEC_PATH/$PROJECT/$INSTANCE/applications.yaml create database <project-name> -> This value should match with the namespace in which you want to run the helm install. <instance-name> -> This value should be matching with the instance that you are going to specify while doing the helm install.For example:
$COMMON_CNTK/scripts/manage-app-credentials.sh -p sr -i quick -f $SPEC_PATH/sr/quick/applications.yaml -a authorization create database - Enter the corresponding values as prompted:
Authorization DB Admin(sys) Username: Provide Authorization Database admin usernameAuthorization DB Admin(sys) Password: Provide Authorization Database admin passwordAuthorization Schema Username: Provide username for Authorization schema to be createdAuthorization Schema Password: Provide Authorization schema passwordAuthorization DB Host: Provide Authorization Database HostnameAuthorization DB Port: Provide Authorization Database PortAuthorization DB Service Name: Provide Authorization Database Service Name
- Verify that the following secret is
created:
$ kubectl get secret -n <namespace> <project-name>-<instance-name>-authorization-db-credentials
Creating Secrets for Common Identity Provider Credentials
The OAuth (common identity provider) secret specifies the OIDC details of your identity provider. It is used by the Authorization service to protect the admin endpoints and for fetching the user profile information (subject, roles or groups, and so on) from access token. If authentication is enabled, ensure that you create an oauthConfig secret with the appropriate OIDC details of your identity provider.
To create secrets for common identity provider credentials, see "Adding Common OAuth Secret and ConfigMap" and "Common Configuration Options For all Services".
Installing Authorization Service Schema
To install the Authorization service schema:
- Update values under authorization-schema in $SPEC_PATH/sr/quick/database.yaml
file with values required for authorization schema creation.
Note:
- The YAML formatting is case-sensitive. Use a YAML editor to ensure that you do not make any syntax errors while editing. Follow the indentation guidelines for YAML.
- Before changing the default values provided in the specification file, verify that they align with the values used during PDB creation. For example, the default tablespace name should match the value that you used while creating PDB.
- Edit the database.yaml file and update the Authorization schema installer
image to point to the location of your image as
follows:
authorization-schema: #imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent schema: image: name: "authorization-schema-1.0.0.0.0" tag: latest db: defaultTablespace: SYSTEM tempTablespace: TEMP - If your environment requires a password to download the container
images from your repository, create a Kubernetes secret with the Docker pull
credentials. See "Kubernetes documentation" for
details. Refer the secret name in the database.yaml. Provide the image pull
secret and image pull policy
details.
authorization-schema: imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent # The image pull access credentials for the "docker login" into Docker repository, as a Kubernetes secret. # Uncomment and set if required. # imagePullSecret: "" - Run the following script to start the Authorization Schema installer, which
instantiates a Kubernetes pod resource. The pod resource lives until the Schema
installation operation
completes.
$COMMON_CNTK/scripts/install-database.sh -p <project-name> -i <instance-name> -f $SPEC_PATH/<project-name>/<instance-name>/database.yaml -a authorization -c 1 <project-name> -> This value should match with the namespace in which you are running the helm install. <instance-name> -> This value should be matching with the instance that you specified while creating the secret.For Example:
$COMMON_CNTK/scripts/install-database.sh -p sr -i quick -f $SPEC_PATH/sr/quick/database.yaml -a authorization -c 1 - Check the console to see if the Schema installer is installed successfully.
- If the installation has failed, run the following command to review the error
message in the
log:
kubectl logs -n sr sr-quick-authorization-schema - Clear the failed pod by running the following
command:
helm uninstall sr-quick-authorization-schema -n sr - Run the install-database script again to install the Authorization schema installer.
Creating an Authorization Service Instance in Your Environment
To create an Authorization service instance in your environment using the scripts that are provided with the toolkit:
- Run the following command to create an Authorization service
instance:
$COMMON_CNTK/scripts/create-applications.sh -p sr -i quick -f $SPEC_PATH/sr/quick/applications.yaml -a authorizationThe create-applications script uses the helm chart located in $COMMON_CNTK/charts/authorization-app to create and deploy an authorization service.
- If the scripts fail, run the following command to review the error message in the
log:
kubectl logs -n sr sr-quick-authorization - Clear the failed pod by running the following
command:
helm uninstall sr-quick-authorization -n sr - Fix the issues, if any, and run the script again to deploy the Authorization service.
Upgrading the Authorization Instance
Upgrading Authorization is required when there are updates made to applications.yaml or other configuration files.
To upgrade the Authorization instance:
-
Run the following command:
$COMMON_CNTK/scripts/upgrade-applications.sh -p sr -i quick -f $COMMON_CNTK/sr/quick/applications.yaml -a authorization -
After running the script, validate the Authorization service by running the
application-statusscript.
Restarting the Authorization Instance
To restart the Authorization instance:
- Run the following command to restart Authorization
service:
$COMMON_CNTK/scripts/restart-applications.sh -p sr -i quick -f $SPEC_PATH/sr/quick/applications.yaml -a authorization - After running the script, validate the Authorization service by running the
application-statusscript.
Deleting the Authorization Service Instance and Authorization Schema
To delete the Authorization instance:
- Run the following command to delete the Authorization service
instance:
$COMMON_CNTK/scripts/delete-applications.sh -p <project-name> -i <instance-name> -f $COMMON_CNTK/<project-name>/<instance-name>/applications.yaml -a authorization - Run the following script to delete the Authorization Schema installed, which
instantiates a Kubernetes pod resource. The pod resource stays until the Schema
deletion
completes:
$COMMON_CNTK/scripts/install-database.sh -p <project-name> -i <instance-name> -f $COMMON_CNTK/<project-name>/<instance-name>/database.yaml -a authorization -c 2