EVS Codec Transcoding Support
Enhanced Voice Services (EVS) is a super-wideband speech audio codec developed by 3GPP and documented in TS 26.441. EVS supports source-controlled variable bit rate, sampling rates of 8, 16, 32, or 48 kHz, dynamic payload type, and an interoperability mode for AMR-WB. The Oracle Communications Session Border Controller (SBC) supports typical transcoding features. EVS can also analyze traffic signaling, allowing it to change to the correct core EVS codec when necessary. These changes can occur at every 20ms frame boundary. The SBC also supports transcoding EVS to and from all supported transcodable codecs unless the EVS mode is using super-wideband or fullband EVS bandwidths. Note that, by configuration, you can set the SBC to recognize EVS-WB as transcodable, which is useful for scenarios such as supporting SRVCC handovers.
Before configuring the SBC to transcode EVS, you must enable it with the setup entitlements command. EVS codec feature support includes:
- transrating
- transcoding
- pooled transcoding
- RTCP generation
- AMR-WB interoperability and payload-type mapping
Note:
See the Release Notes for any platform-based EVS transcoding limitations.Bitrate support per bandwidth includes:
- Narrowband (NB) — 5.9, 7.2, 8, 9.6, 13.2, 16.4, 24.4
- Wideband (WB) — 5.9, 7.2, 8, 9.6, 13.2, 13.2 channel-aware, 16.4, 24.4, 32, 48, 64, 96, 128 (6.6 ~ 23.85 for AMR-WB IO)
- Super-wideband (SWB) — 9.6, 13.2, 13.2 channel-aware, 16.4, 24.4, 32, 48, 64, 96, 128
- Fullband (FB) — 16.4, 24.4, 32, 48, 64, 96, 128
EVS data is always octet-aligned in both Primary and AMR-WB interoperability mode.
Interoperation with AMR-WB
EVS' AMR-WB interoperable (IO) mode provides backwards compatibility with endpoints that support AMR-WB, but don't support EVS. Based on user configuration and SDP offers, AMR-WB IO mode allows the SBC to deliver media between such endpoints without using trancoding resources.
EVS Supported Options
There are no required SDP Parameters for EVS. Some EVS parameters may have values that the SBC's DSP does not support. Supported values must be verified before the SBC makes transcoding decisions. if any of these parameter checks fail, the SBC marks the codec as non-transcodable
Unless noted otherwise, see 3GPP TS 26.445 and related specifications for complete parameter documentation. Optional SDP parameters include:- ptime—The length of
time in milliseconds represented by the media in a packet. See RFC 4566 for
more details.
For both EVS Primary mode and EVS AMR-WB IO mode, the supported ptimes are 20, 40, and 60 ms.
- maxptime—The maximum
amount of media that can be encapsulated in each packet, expressed as time in
milliseconds. See RFC 4566 for more details.
For both EVS Primary mode and EVS AMR-WB IO mode, the supported maxptimes are 20, 40, and 60 ms.
- evs-mode-switch—Specifies whether Primary mode or EVS AMR-WB IO mode should be used at the start or update of the session. The default of 0 specifies the use of primary mode.
- hf-only—Specifies whether to limit the session to header-full format. The default of 0 allows both compact and header-full format in both directions.
- dtx—Specifies whether or not to support discontinuous transmission. The default of 1 specifies that DTX is enabled.
- dtx-recv—This parameter enables (dtx-recv=1) or disables (dtx-recv=0) the receiver's DTX functionality towards the sender.
- max-red—Specifies the maximum number of milliseconds allowed between the first transmission of a frame, a redundant transmission and the corresponding redundant transmission. See RFC 4867 for more details.
- channels—Specifies the number of audio channels, with a default of 1. The SBC supports only 1 channel for transcoding.
- cmr—Specifies whether codec mode request (CMR) is supported for the session. The default of 0 enables all CMR values.
The following parameters apply only to EVS Primary mode:
- br—Specifies, in
kilobits per second, the range of source codec bit-rate for EVS Primary mode in
the session for both send and receive directions.
Source codec bit-rates for the EVS codec
Source codec bit-rate (kbit/s) Audio bandwidths supported Source Controlled Operation Available 5.9 (SC-VBR)
NB, WB
Yes (Always On)
7.2
NB, WB
Yes
8.0
NB, WB
Yes
9.6
NB, WB, SWB
Yes
13.2
NB, WB, SWB
Yes
13.2 (channel aware)
WB, SWB
Yes
16.4
NB, WB, SWB, FB
Yes
24.4
NB, WB, SWB, FB
Yes
32
WB, SWB, FB
Yes
48
WB, SWB, FB
Yes
64
WB, SWB, FB
Yes
96
WB, SWB, FB
Yes
128
WB, SWB, FB
Yes
If the given br value conflicts with the given bw value, the SBC DSP marks the codec as non-transcodable.
- br-send—Specifies,
in kilobits per second, the range of source codec bit-rate for EVS Primary mode
in the session for the send direction.
If the given br-send value conflicts with the given bw value, the SBC DSP marks the codec as non-transcodable.
- br-recv—Specifies, in kilobits per second, the range of source
codec bit-rate for EVS Primary mode in the session for the receive direction.
The SBC can independently decode an EVS packet with any bit rate that is received. Thus, br-recv is not used in determining whether the codec is transcodable or not.
- bw—Specifies the
audio bandwidth for EVS Primary mode to be used in the session for the send and
the receive directions.
For transcoding, the SBC DSP only supports nb, wb, and nb-wb.
- bw-send—Specifies
the bandwidth to be used in the session for the send direction.
For transcoding, the SBC DSP only supports nb, wb, and nb-wb.
- bw-recv—Specifies
the bandwidth to be used in the session for the receive direction.
For transcoding, the SBC DSP only supports nb, wb, and nb-wb.
- ch-send—Specifies the number of audio channels for the send direction. The default is 1.
- ch-recv—Specifies the number of audio channels for the receive direction. The default is 1.
- ch-aw-recv—Enumerated setting for channel-aware mode. The default of 0 specifies that partial redundancy mode is not used for the receive direction at the start of the session.
The following parameters apply only to EVS AMR-WB IO mode. Optional parameters of AMR-WB not defined below may not be used in the EVS AMR-WB IO mode.
- mode-set—Restricts
the active codec mode set to a subset of all modes when the EVS codec operates
in AMR-WB IO.
Source codec bit-rates for the AMR-WB Interoperable Modes of the EVS codec
Mode Indicator Source codec bit-rate (kbit/s) 0
6.6
1
8.85
2
12.65
3
14.25
4
15.85
5
18.25
6
19.85
7
23.05
8
23.85
Note:
The SBC supports only mode-sets 0-7 for both AMR and AMR-WB. - mode-change-period—Specifies a number of frame-blocks, N (1 or 2). This is the frame-block period at which codec mode changes are allowed for the sender. See RFC 4867 for more details.
- mode-change-capability—Specifies if the client is capable of transmitting with a restricted mode change period. See RFC 4867. The default, and only allowed value is 2 in EVS AMR-WB IO.
- mode-change-neighbor—Permissible values are 0 and 1. If 1, the sender SHOULD only perform mode changes to the neighboring modes in the active codec mode set. See RFC 4867 for more details.
Default EVS Media Profile
By default, the SBC uses the following parameters for EVS, referenced in the configuration as EVS.
media-profile
name EVS
subname
media-type audio
payload-type
transport RTP/AVP
clock-rate 16000
req-bandwidth 0
frames-per-packet 0
parameters
average-rate-limit 6000
peak-rate-limit 0
max-burst-size 0
sdp-rate-limit-headroom 0
sdp-bandwidth disabled
police-rate 0
standard-pkt-rate 0
as-bandwidth 0
CLI Commands
CLI command changes made to support EVS include:
- The show sipd codecs command includes EVS Count.
- The show sipd transcode command includes EVS.
- The show xcode codecs command includes EVS-AMR-WB sessions.
SNMP
This section presents SNMP OID detail the SBC uses to support EVS.
ap-codec.mib
| Object Name/OID | Description |
|---|---|
| apCodecRealmCountEVS
1.3.6.1.4.1.9148.3.7.1.1.1.33 |
The count of SDP media streams received in the realm that negotiated to the EVS codec. |
The EVS realm statistic apCodecRealmCountEVS is available in the apCodecRealmStatsEntry.
ap-smgmt.mib
| Object Name/OID | Description |
|---|---|
| apSysXCodeEVSCapacity
1.3.6.1.4.1.9148.3.2.1.1.49 |
The percentage of licensed EVS transcoding utilization (non pollable). |
| apSysMgmtXCodeEVSUtilGroup
1.3.6.1.4.1.9148.3.2.4.2.35 |
Object to monitor licensed EVS transcoding utilization. |
New Traps—The new SNMP OID apSysXCodeEVSCapacity is added to transcoding utilization statistics, as reported in the apSysMgmtGroupTrap. When utilization falls below 80%, the system sends the apSysMgmtGroupClearTrap.
| Trap Name (and Clear Trap Name) | Description |
|---|---|
| apSysMgmtCPULoadAvgTrap
(apSysMgmtCPULoadAvgClearTrap) |
The system generates the trap when the CPU Load Average Alarm exceeds its minor alarm threshold. The system sends the clear trap when the CPU load average recedes to the minor alarm level. |
Capability MIB IODs
| Object Name/OID | MIB file |
|---|---|
| apSmgmtXCodeEVSUtilCap
1.3.6.1.4.1.9148.2.1.8.59 |
ap-smgmt.mib |
| apCodecRealmCodecCap9
1.3.6.1.4.1.9148.2.1.13.11 |
ap-codec.mib |
Alarms
The Licensed EVS Transcoding Capacity Threshold Alarm is a warning triggered when the EVS transcoding utilization exceeds 95% of licensed capacity. This alarm does not affect the system's health score. The system clears this alarm when the EVS transcoding utilization falls below 80% of licensed capacity.
RADIUS
The Acme-FlowType_FS{1,2}_{F,R} AVPs reflect the use of the EVS codec.
EVS Configuration Detail
This section discusses aspects of SBC configuration that you must consider in addition to typical transcoding configuration for EVS.
Payload Type Mapping
The user enables EVS AMR-WB IO payload type mapping using the media-manager-config option audio-payload-type-mapping=yes. If the option is not present, EVS AMR-WB IO payload type mapping is disabled.
media-manager
…
options
audio-payload-type-mapping=yesFurthermore, the payload-type is not critical as long as the audio-payload-type-mapping=yes option is configured. Normally the PT used in the network is configured in the payload-type field. But the SBC matches against codec name/string instead of payload-type.
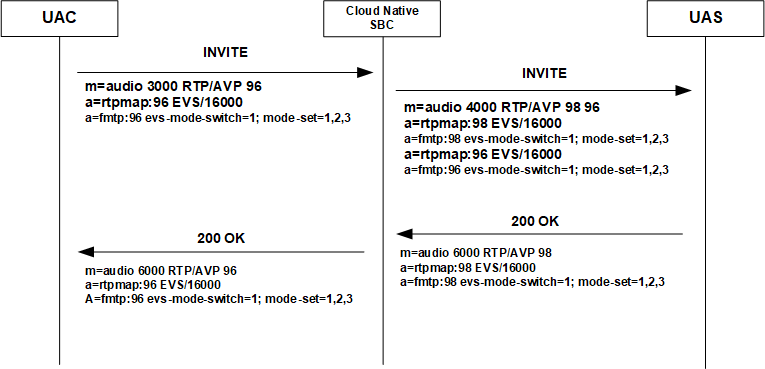
EVS Call Flow Example
The flow depicted below provides an example that uses the audio-payload-type-mapping=yes to enable payload type mapping. In addition, the flow uses add-codecs-on-egress configuration in the egress codec policy configured as EVS::PT98. The offer contains EVS in AMR-WB IO mode and the SBC adds a separate EVS AMR-WB IO with a different payload type. The answerer selects PT 98 and since audio-payload-type-mapping=yes, so transcoding is not required, and payload type mapping is used. The offer and answer are both octet-aligned and they have intersecting mode-sets, so transcoding is not required and payload type mapping is used.
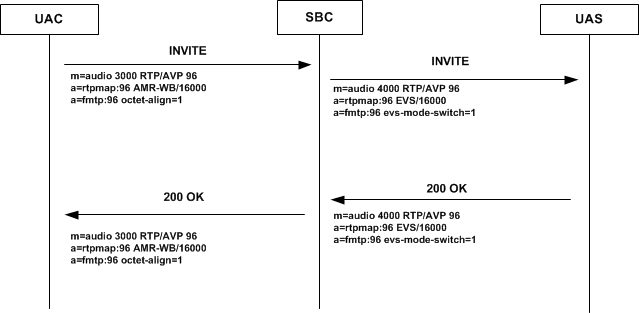
AMR-WB to EVS AMR-WB IO Transparent Call Example
This example explains how you can configure the SBC and applicable resources to support calls between EVS and AMR-WB endpoints without requiring transcoding, and therefore not consuming SBC transcoding resources. This use case, established by logic within the SBC, can accommodate calls in either direction.
In this call flow a codec policy is set on the egress realm to not allow AMR-WB and to add EVS AMR-WB IO on egress. The offer contains AMR-WB. The SBC recognizes that the incoming AMR-WB codec matches the EVS codec to be added:
- They have the same octet-align
- EVS codec is in interoperable mode (evs-mode-switch=1)
- You have a media-profile configured that matches the parameters presented in the AMR-WB offer
The SBC strips AMR-WB and adds EVS with the same payload type as AMR-WB even though EVS is not configured with that payload type.
codec-policy
name Transparent-AMR-WB-IO
allow-codecs * AMR-WB:no
add-codecs-on-egress EVS::WBIO
force-ptime disabled The call proceeds transparently between AMR-WB and EVS.
EVS and SRVCC
The SBC includes support and requirements that you must consider when handling call flows that include the EVS codec and Single Radio Voice Call Continuity (SRVCC) handovers. This support includes basic functionality as well as transcoding considerations when EVS is in super-wideband mode.
Media Management
Enable mm-in-realm in the core realm to support transcoding EVS within environments that include SRVCC. Oracle also recommends that you enable codec-manip-in-realm for these deployments.
Transcoding Free Operation
You can configure the SBC to handle scenarios that cannot use transcoding, but still support super-wideband end stations. Examples of such scenarios include SRVCC handovers wherein super-wideband is established before the handover. The srvcc-trfo parameter in the realm-config allows you to establish this functionality on a per-realm basis for the EVS codec. This behavior is compliant with TS24-237 (proxy mode) for EVS calls.
For example, assume a call established from the IMS core towards a VoLTE leg is using EVS-SWB and the codec needs to change because of an SRVCC event. With this configuration in place, the SBC forces codec renegotiation with the far end in the event of a SRVCC handover from a packet to a circuit switching environment. The codec change on the VoLTE leg needs to match what the Mobile Switching Center (MSC) server offers to establish transcoder free operation. Assume the MSC offers AMR-WB to follow the process.
- The SBC recognizes AMR-WB being presented to the VoLTE UE and refrains from sending the 200 OK as an answer to the INVITE (proxy mode).
- Instead, the SBC sends it own INVITE towards the SRVCC UE, replacing EVS SWB in the SDP to force a renegotiation. Instead of EVS SWB, this INVITE contains the SDP from the SRVCC UE (AMR-WB).
- The IMS core receives the SBC INVITE and propagates it towards the SRVCC UE.
- Ultimately the SRVCC UE accepts AMR-WB as codec and replies towards the SBC with a 200 OK.
- The IMS core sends this 200 OK to the SBC (ATU-STI).
- The SBC replies with its own 200 OK to the MSC (STN-SR).
- RTP restarts using AMR-WB between the VoLTE UE and the SRVCC UE.
This codec renegotiation happens end-to-end with the ATGW in the media path.
Navigate to the core realm-config and configure this parameter using the syntax below.
ORACLE(realm-config)# srvcc-trfo evsThis 'manual' trigger by the SBC to force SDP re-negotiation prevents the call from requiring transcoding to EVS-SWB after the handover to the circuit switching environment.
Circumventing EVS SWB Transcoding Scenarios
You can configure SBC to maintain a call that may otherwise fail when an SRVCC event puts the SBC in the position of having to transcode from EVS SWB. When configured, the SBC can recognize the requirement to transcode EVS SWB, and present EVS WB to the SRVCC UE. The SBC supports transcoding EVS WB so there is no need to drop the call. This configuration also allows the SBC to continue to use EVS SWB for the opposing UE.
You can configure the SBC to support these scenarions using the realm-config option, srvcc-evs-swb-to-wb.
For example, assume a call has been established with EVS SWB when an SRVCC handover occurs. EVS SWB is not available within an MSC/3G network. By default, the call would fail. But when configured with the srvcc-evs-swb-to-wb option, the SBC internally changes the presented codec from EVS SWB to EVS WB on ingress, while continuing to present EVS SWB back to the egress. This allows the SBC to present this transcodable codec and support the SRVCC handover, while continuing to use EVS SWB on the other side.
Configure this option using the syntax below.
ORACLE(realm-config)# options +srvcc-evs-swb-to-wbIf you type options and then the option value without the plus sign, you overwrite any previously configured options. To add a new option to an options list, pre-pend the new option with a plus sign as shown in the previous example.
In addition, this function requires that you have an EVS media profile name as an allowed codec on both sides of the call. The default EVS profile can serve this purpose.