SIP and H.323
The Oracle Communications Session Border Controller supports interworking between SIP and H.323 for H.323 Slow Start and Fast Start calls. In addition to describing IWF sessions when initiated from the H.323 side and from the SIP side (with sample call flows), this section provides information you will need when you configure SIP and H.323.
SIP H.323 Negotiation H.323 Fast Start
The Oracle Communications Session Border Controller can perform protocol translations for SIP and H.323 Fast Start, where media capabilities are sent with the Setup request for an H.323 session.
This section’s call flow diagrams show how SIP and H.323 messages flow between SIP and H.323 devices, with the Oracle Communications Session Border Controller positioned between the two entities so it can perform translations. The following two sample scenarios with Fast Start appear in the diagrams below, although other scenarios are possible:
- Calls originating in SIP being translated to H.323 Fast Start
- Calls originating in H.323 Fast Start translated to SIP
SIP to Fast Start H.323
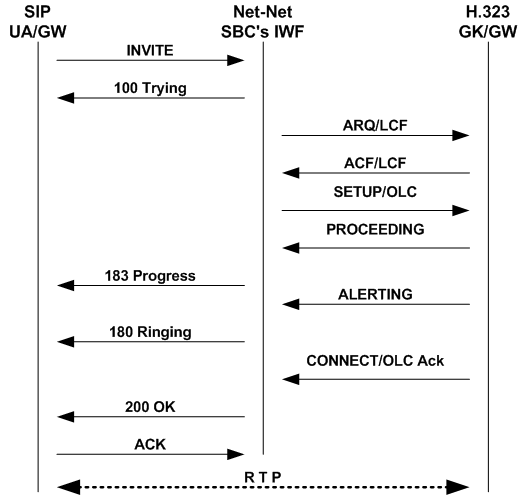
In the following diagram below, a SIP endpoint (such as a UA or a SIP Gateway) initiates a session by sending an INVITE message destined for an H.323 endpoint (a GK or GW). Between these entities, the system is positioned to perform interworking. The Oracle Communications Session Border Controller recognizes that the INVITE message is destined for an H.323 device, and returns a 100 Trying message to the SIP endpoint as it attempts to negotiate the H.323 side of the session. This negotiation starts when the Oracle Communications Session Border Controller initiates the RAS process with the H.323 endpoint by sending either an ARQ or an LRQ, allowing the Oracle Communications Session Border Controller to determine if the H.323 endpoint will accept the session.
Once the H.323 endpoint responds with an ACF or LCF, the Oracle Communications Session Border Controller reissues the SIP INVITE on the H.323 side as an H.225 Setup, which is sent with the OLC. Then the H.323 endpoint responds with Proceeding and Alerting messages (which correspond respectively to SIP 183 Progress and 180 Ringing messages). At that point, the H.323 endpoint sends a Connect message that includes the OpenLogicalChannel message (OLC), announcing the logical channel for media flows has been set up. The Oracle Communications Session Border Controller converts the H.323 OLC to a SIP 200 OK. After receiving the 200 OK, the SIP endpoint sends an ACK, confirming that the session has been established. Because there is no H.323 equivalent for the SIP ACK, the Oracle Communications Session Border Controller does not generate a corresponding message on the H.323 side. At this point, the session is fully established and RTP flows between the endpoints.
H.323 Fast Start to SIP
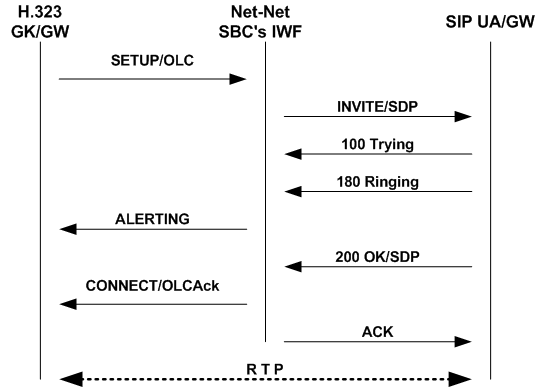
In the diagram below, an H.323 endpoint (a GK or GW) initiates a session by sending a Setup request destined for a SIP endpoint (such as a UA or a SIP Gateway). Between these entities, the Oracle Communications Session Border Controller is positioned to perform interworking. The H.323 endpoint has completed the RAS process prior to sending the SETUP message.
The Oracle Communications Session Border Controller receives the Setup message and then sends a SIP INVITE on the SIP side. The SIP endpoint responds with a 100 Trying; the Oracle Communications Session Border Controller does not resend this message on the H.323 side. Next, the SIP endpoint issues a 180 Ringing message, which the Oracle Communications Session Border Controller reissues to the H.323 endpoint as an Alerting message. The SIP endpoint then sends a 200 OK, retransmitted by the Oracle Communications Session Border Controller as a Connect message that includes an OLC. Once the Oracle Communications Session Border Controller sends an ACK to the SIP endpoint, RTP flows between the endpoints.
SIP H.323 Negotiation H.323 Slow Start
The Oracle Communications Session Border Controller can also perform protocol translations for SIP and H.323 Slow Start, where—unlike the cases with Fast Start described above—media information is not sent with the Setup request for an H.323 session. For H.323 Slow Start, media is negotiated after the session is established.
This section’s call flow diagrams show how SIP and H.323 messages flow between SIP UA/GW and an H.323 GK/GW, with the Oracle Communications Session Border Controller positioned between the two entities so it can perform translations. Two sample scenarios with Slow Start appear in the diagrams below:
- SIP being interworked to Slow Start H.323
- Slow Start H.323 being interworked to SIP
H.323 SIP to Slow Start
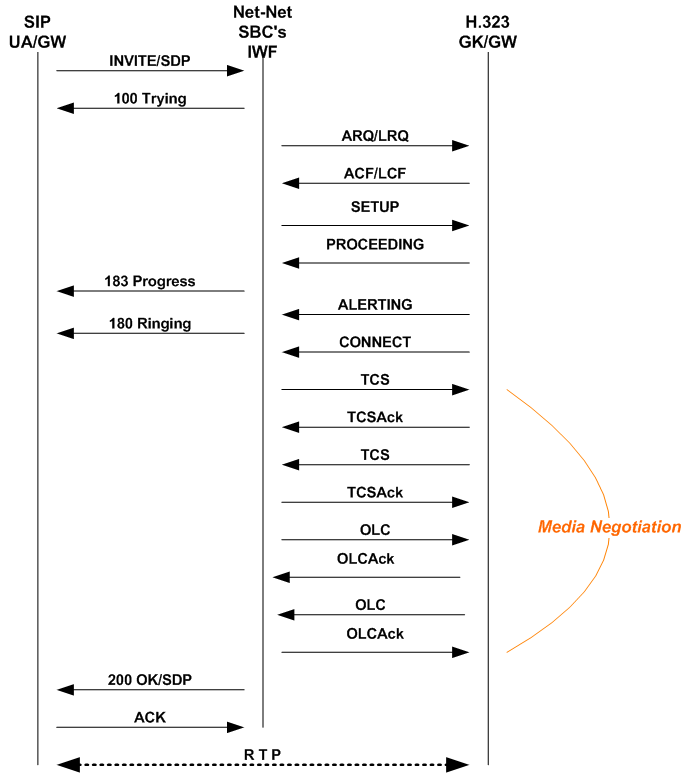
In the following diagram below, a SIP endpoint (such as a UA or a SIP Gateway) initiates a session by sending an INVITE request destined for an H.323 Slow Start endpoint (a GK or GW). Between these entities, the Oracle Communications Session Border Controller is positioned to perform interworking.
The call flow for this type of translation works fundamentally the same way that the translation does for SIP to Fast Start H.323, with the exception of how the media is established. Media is negotiated through the exchange of TCS and OLC messages after the H.323 Connect and SIP 180 Ringing messages have been sent. The first TCS message is sent from the Oracle Communications Session Border Controller to the H.323 endpoint, and it contains information about media capabilities in SDP. The H.323 endpoint accepts and acknowledges this information with a TCS Ack message. Then the H.323 endpoint sends a second TCS, carrying information about the Gateway’s capabilities, that the Oracle Communications Session Border Controller accepts and acknowledges. The H.323 endpoint and the Oracle Communications Session Border Controller then exchange OLC and OLC Ack messages that establish the operating mode and Gateway capability. Finally, the Oracle Communications Session Border Controller completes the 200 OK/ACK sequence on the SIP side, and RTP flows between the two endpoints.
H.323 Slow Start to SIP
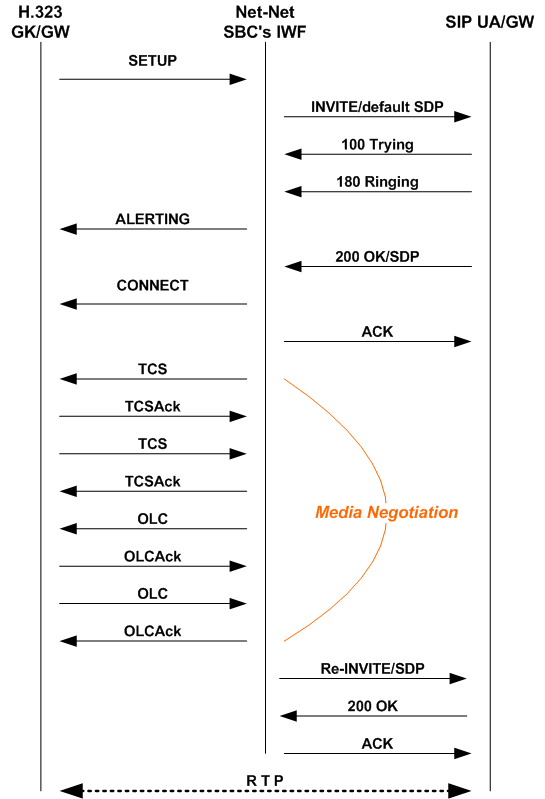
In the following diagram below, an H.323 endpoint (GW or GK) initiates a session by sending a Setup request destined for a SIP endpoint (such as a UA or a SIP Gateway). Between these entities, the Oracle Communications Session Border Controller is positioned to perform interworking. The H.323 endpoint has completed the RAS process prior to sending the SETUP message.
The call flow for this type of translation works fundamentally the same way that the translation does for H.323 Fast Start to SIP, with the exception of how the media is established. When the Oracle Communications Session Border Controller receives an H.323 message destined for a SIP endpoint, it sends a SIP INVITE message that includes default SDP to that SIP endpoint. The default SDP is constructed using information in the media profiles listed for the IWF configuration; if necessary, this media information is amended later in the sequence. Once the call is set up, the Oracle Communications Session Border Controller negotiates media with the H.323 endpoint through a series of TCS/TCS Ack and OLC/OLC Ack messages that establish the operating mode and Gateway capability.
When the Oracle Communications Session Border Controller completes media negotiation with the H.323 endpoint, it issues a re-INVITE to the SIP endpoint that contains the updated information needed for media transmission. In response, the SIP endpoint sends a 200 OK message that the Oracle Communications Session Border Controller answers with an ACK. Then RTP can flow between the two endpoints.
Status and Codec Mapping
The Oracle Communications Session Border Controller maps SIP and H.323 status codes as described in this section. Status and codec mapping do not require configuration; they occur transparently.
IWF Termination from H.323
When a call that requires the IWF terminates from the H.323 side, the Oracle Communications Session Border Controller uses the mapping scheme in the following table to determine the appropriate SIP status.
| H.323 Disconnect Reason | SIP Status |
|---|---|
| No Bandwidth | 480 Temporarily Unavailable |
| Gatekeeper Resource | 404 Not Found |
| Unreachable Destination | 404 Not Found |
| Destination Rejection | 603 Decline |
| Invalid Revision | 505 Version Not Supported |
| No Permission | 401 Unauthorized |
| Unreachable Gatekeeper | 503 Service Unavailable |
| Gateway Resource | 480 Temporarily Unavailable |
| Bad Format Request | 400 Bad Request |
| Adaptive Busy | 486 Busy Here |
| In Conference | 486 Busy Here |
| Undefined Reason | 500 Internal Server Error |
| Facility Call Deflection | 486 Busy Here |
| Security Denied | 401 Unauthorized |
| Called Party Not Registered | 404 Not Found |
| Caller Not Registered | 401 Unauthorized |
IWF Termination During H.323 RAS
When a call that requires the IWF terminates from the H.323 side during RAS and generates an error, the Oracle Communications Session Border Controller uses the mapping scheme in the following table to determine the appropriate SIP status.
| H.323 RAS Error | SIP Status |
|---|---|
| Called Party Not Registered | 404 Not Found |
| Invalid Permission | 401 Unauthorized |
| Request Denied | 503 Service Unavailable |
| Undefined | 500 Internal Server Error |
| Caller Not Registered | 401 Unauthorized |
| Route Call To Gatekeeper | 305 User Proxy |
| Invalid Endpoint ID | 500 Internal Server Error |
| Resource Unavailable | 503 Service Unavailable |
| Security Denial | 401 Unauthorized |
| QoS Control Not Supported | 501 Not Implemented |
| Incomplete Address | 484 Address Incomplete |
| Route Call to SCN | 302 Moved Temporarily |
| Aliases Inconsistent | 485 Ambiguous |
| Not Currently Registered | 401 Unauthorized |
IWF RAS Registration Failure Code Mapping
For calls that require interworking between H.323 and SIP, the Oracle Communications Session Border Controller supports IWF response code mapping. This feature enables the Oracle Communications Session Border Controller to support configurable SIP response codes for IWF calls that fail during RAS, when the Oracle Communications Session Border Controller has been unable to register with a gatekeeper; this allows a wider range of more accurate response codes to be communicated.
When this feature is not enabled, the Oracle Communications Session Border Controller generates a 404 Not Found when a SIP-to-H.323 call fails as a result of the stack’s failure to register with a gatekeeper.
When the condition noted above takes place, the response code can be any of the ones listed in this table. The code values listed in the table are used to specify the code to which you want to map.
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 403 | Forbidden |
| 406 | Not Acceptable |
| 408 | Request Timeout |
| 410 | Gone |
| 420 | Bad Extension |
| 480 | Temporarily Unavailable |
| 486 | Busy Here |
| 487 | Request Terminated |
| 500 | Server Internal Error |
| 503 | Service Unavailable |
| 504 | Server Time-out |
| 600 | Busy Everywhere |
| 603 | Decline |
To enable IWF RAS registration failure code mapping:
IWF Termination from SIP
When a call that requires the IWF terminates from the SIP side, the Oracle Communications Session Border Controller uses the mapping scheme in the following table to determine the appropriate H.323 Release Complete Reason code.
| SIP Status | H.323 Release Complete Reason |
|---|---|
| 300 Multiple Choices | Undefined Reason |
| 401 Unauthorized | Security Denied |
| 402 Payment Required | Undefined Reason |
| 403 Forbidden | No Permission |
| 404 Not Found | Unreachable Destination |
| 405 Method Not Allowed | Undefined Reason |
| 406 Not Acceptable | Undefined Reason |
| 407 Proxy Authentication Required | Security Denied |
| 408 Request Timeout | Adaptive Busy |
| 409 Conflict | Undefined Reason |
| 410 Gone | Unreachable Destination |
| 411 Length Required | Undefined Reason |
| 414 Request-URI Too Large | Bad Format Address |
| 415 Unsupported Media Type | Undefined Reason |
| 420 Bad Extension | Bad Format Address |
| 480 Temporarily Unavailable | Adaptive Busy |
| 481 Call/Transaction Does Not Exist | Undefined Reason |
| 482 Loop Detected | Undefined Reason |
| 483 Too Many Hops | Undefined Reason |
| 484 Address Incomplete | Bad Format Address |
| 485 Ambiguous | Undefined Reason |
| 486 Busy Here | In Conference |
| 487 Request Terminated | Undefined Reason |
| 488 Not Acceptable Here | Undefined Reason |
| 500 Internal Server Error | Undefined Reason |
| 501 Not Implemented | Undefined Reason |
| 502 Bad Gateway | Gateway Resource |
| 503 Service Unavailable | Gateway Resource |
| 504 Gateway Timeout | Adaptive Busy |
| 505 Version Not Supported | Invalid Revision |
| 600 Busy Everywhere | Adaptive Busy |
| 603 Decline | Destination Rejection |
| 604 Does Not Exist Anywhere | Unreachable Destination |
| 606 Not Acceptable | Undefined Reason |
Q.850 Cause to H.323 Release Complete Reason
When a call that requires the IWF terminates from the H.323 side and no H.323 Release Complete Reason is specified, the Oracle Communications Session Border Controller maps the Q.850 cause to an H.323 Release Complete Reason using the mapping scheme in the following table. This new H.323 status is then mapped to a SIP status as described in the IWF Termination from SIP table.
| Q.850 Cause | H.323 Release Complete Reason |
|---|---|
| No Route To Destination | Unreachable Destination |
| Normal Call Clearing | Destination Rejection |
| User Busy | In Conference |
| Subscriber Absent | Called Party Not Registered |
| Invalid Number Format | Bad Format Address |
| Normal Unspecified | Undefined Reason |
| No Circuit/Channel Available | No Bandwidth |
| Network Out Of Order | Unreachable Gatekeeper |
| Temporary Failure | Adaptive Busy |
| Switching Equipment Congestion | Gateway Resource |
| Resource Unavailable | Gatekeeper Resource |
| Incompatible Destination | Invalid Revision |
| Interworking Unspecified | No Permission |
Codec Mapping
The Oracle Communications Session Border Controller uses the following mapping scheme when converting media specifications between H.245 (used in H.323) and SDP (used in SIP).
Media coming into the Oracle Communications Session Border Controller one way exits the system in the corresponding way as specified in the following table. For example, media coming into the Oracle Communications Session Border Controller as H.245 type g711Ulaw64k exits the system as media type PCMU.
| H.245 Type | SDP Media Type |
|---|---|
| g711Ulaw64k | PCMU |
| g711Ulaw56k | PCMU |
| g711Alaw64k | PCMA |
| g711Alaw56k | PCMA |
| g726 | G726-32 |
| g7231 | G723 |
| g722 | G722 |
| g728 | G728 |
| g729wAnnexB | G729 |
| g729 | G729
fmtp:18 annexb=no |
| h261VideoCapability | H261 |
| h263VideoCapability | H263 |