ACR Event Records
The OCSBC supports ACR [Event] records, according to 3GPP TS 32.260. This is in addition to start, stop and interim records. These records reflect a preset type of SIP event. The ACRs are then sent to the CCF.
The OCSBC can create Event ACR messages on REGISTER and/or local-re-REGISTER requests. A local re-register is when registration caching is enabled and the REGISTER from an currently registered endpoint occurs before half of the registration expiration time. In such cases the OCSBC sends a 200 OK to the re-registering endpoint and does not forward the re-REGISTER to the registrar.
Event record creation is enabled with the generate-event parameter in the account config. This parameter can be set to register, local-register or both values. The configured value indicates the type of message that initiates an event ACR message sent to a CCF. Register only prompts the OCSBC to create Event ACRs at a REGISTER, local-register prompts the OCSBC to create Event ACRs on a re-REGISTER that was replied to by the OCSBC.
Event messages are created when the OCSBC receives a SIP Final Response 2xx or SIP Final Response (4xx or 5xx), that indicates an unsuccessful REGISTER.
Event ACR messages are also generated to indicate there has been an unsuccessful session attempt. Upon receiving a 4xx, 5xx or 6xx response to a SIP Invite, an Event message is created.
ACR Event Message Construction
An Event ACR is generated according to the tables that describe the AVPs present in the OCSBC’s ACR message. Refer to the checked items in the Event column to see all included AVPs. Note that the Accounting-Record-Type AVP (480) is set to Event_Record (1).
Event-Type AVP
The Event-Type AVP (AVP code 823) is a Grouped AVP and contains information about the type of chargeable telecommunication service/event for which the accounting-request and/or credit control request message(s) is generated.
It is used in an AAR Event record. In this context, refer to the following:
| AVP | Number | Acme # | Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
| [ SIP-Method ] | 824 | 173 | Contains the name of the SIP Method (this will be REGISTER) causing a accounting request to be sent to the CCF. |
| [ Event ] | 825 | 245 | Holds the content of the "Event:" header.
This is not present in a REGISTER or re-REGISTER message |
| [ Expires ] | 888 | 246 | Holds the content of the "Expires" header.
Upon a re-REGISTER this value is the time remaining until the endpoint’s registration expires. |
Expires Value
A refresher on the expires value: If the Contacts: header does not contain an expires parameter, the OCSBC adds one with the value in the Expires: header in the 200 OK returned to the UA who sent the INVITE. If there is no Expires: header, the OCSBC adds expires parameter with a value of 3600 and an Expires header with a value of 3600 to the 200 OK.
As the OCSBC forwards the final 200 OK to the initiating endpoint, the Expires (888) AVP contains the largest expires value of all expires parameters in Contact: headers.
When registration caching is enabled and the OCSBC receives a reREGISTER from an endpoint before the halftime of the local registration has expired, the OCSBC inserts the maximum of all associates contacts’ remaing time until expiry in the Expires AVP.
Event ACRs Generated for Unsuccessful Session Attempts
When any of the following responses are received in response to a SIP Invite, an Event ACR message is created to indicate there has been an unsuccessful session attempt:
- 4xx Request Failure Code — this code is used when the SIP transaction is terminated due to an IMS node receiving a 4xx error response.
- 5xx Server Failure Code — this code is used when the SIP transaction is terminated due to an IMS node receiving a 5xx error response.
- 6xx Global Failure Code — this code is used when the SIP transaction is terminated due to an IMS node receiving a 6xx error response.
This example call flow shows how a 5xx server failure results in the sending of an Event ACR.
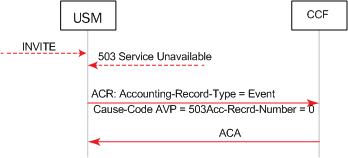
Call Flow Example Showing Event ACR Generation Due to 5xx Server Failure
The following call flow example shows two session agents. The first session agent replies with 503, which results in an Event ACR with cause code 503. The second session agent replies with 200OK that causes the sending of a Start ACR. The generate-start parameter is OK.
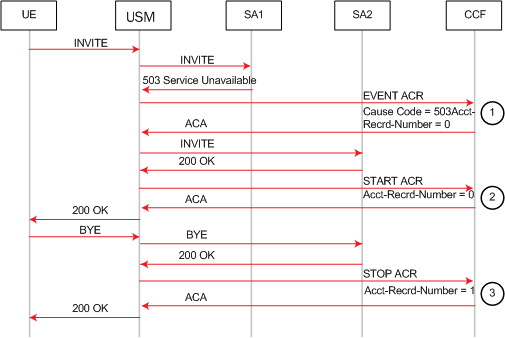
Call Flow Example Showing Sending of an Event and Start ACR
This example call flow illustrates the same call flow when generate-start are equal to Invite. In this case, Start, Interim and Stop ACRs are sent. The generate-start parameter is OK.
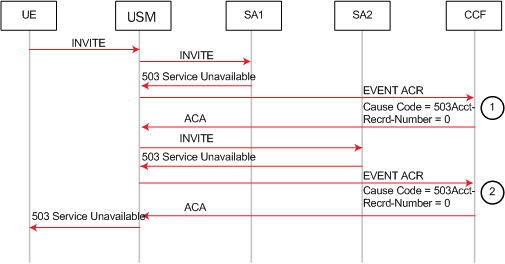
Call Flow Example Showing Generation of Event ACRs Due to 5xx Server Failures
This example call flow shows how a session is created and a Start ACR is sent but then a 5xx server failure occurs that results in sending an Interim ACR. The generate-start parameter is Invite.
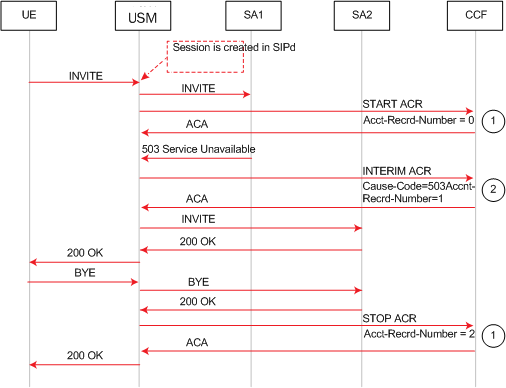
Call Flow Example Showing Sending of Start and Interim ACRs
This example call flow shows how the SD rejects a call before a session is created. When the enhanced-cdr option is not set, an Event ACR is then sent.
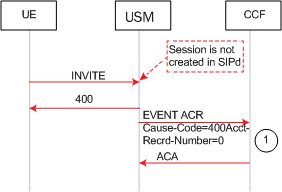
Call Flow Example Showing Unsuccessful Session Creation and Sending of a Event ACR
Event ACRs Generated for Receipt of SIP Messages
An Event ACR is issued when the following SIP messages are received:
- 200 OK message for a SIP Register from the IMS core.
- SIP Final/Redirection Response 3xx
- SIP Final Response (4xx, 5xx or 6xx) — this indicates an unsuccessful session-unrelated procedure.
- SIP Final Response (4xx, 5xx or 6xx) — this indicates an unsuccessful SIP session set-up.
This example call flow shows an Event ACR that is created due to the reception of a 3xx SIP message. In this example the call fails after being redirected.
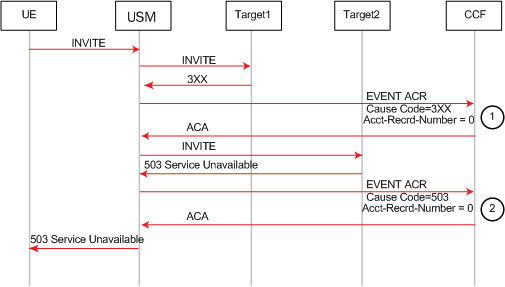
Event ACR Created Upon Reception of a 3xx Message Followed by Call Failure After Redirect
This example call flow shows an Event ACR that is created due to the reception of a 3xx SIP message. Then it shows a Start ACR upon reception of a 200OK. In this example the call succeeds after being redirected. The generate-start is OK.
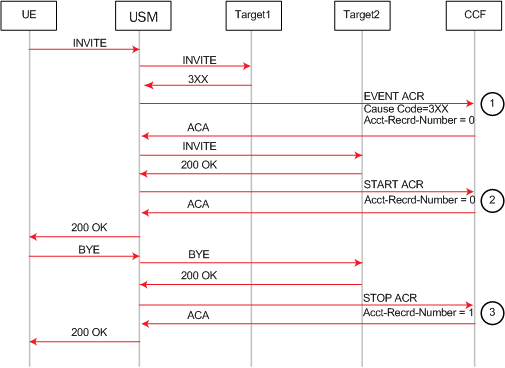
Event ACR Created Upon Reception of a 3xx Message Followed by Call Success After Redirect
This example call flow shows a Start ACR being sent when an Invite is received and an Interim ACR that is created due to the reception of a 3xx SIP message. In this example the call succeeds after being redirected. The generate-start is Invite.
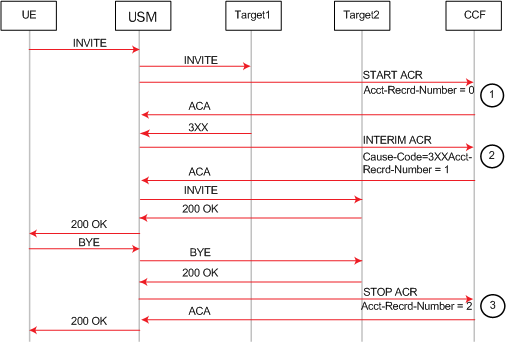
Event Local CSV File
This feature also creates an Event CSV file when the generate-event parameter is enabled. The following table describes the inclusive CSV element order:
| CSV Placement | Attribute Name | AVP Number |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Record Type | 480 |
| 2 | NAS IP Address | |
| 3 | NAS Port | 16 |
| 4 | Calling Station ID | |
| 5 | Called Station ID | |
| 6 | Diameter Session ID | 263 |
| 7 | SIP Method | 824 |
| 8 | Event Time | 55 |
| 9 | User Name | 1 |
| 10 | Node Function | 862 |
| 11 | Application ID | 259 |
| 12 | Role Node | 829 |
| 13 | Event | 825 |
| 14 | Expires | 888 |
| 15 | Associated URI | 856 |
| 16 | Cause Code | 861 |
| 17 | CDR Sequence Number | |
| 18 | Origin Realm | 296 |
| 19 | Origin Host | 264 |
| 20 | Destination Realm | 283 |
| 21 | Destination Host |