1 SD-WAN Edge Service Chaining UI
Overview
Oracle SD-WAN Edge supports Service Chaining on the E100 platforms. This capability allows the installation of the Guest VM from the web UI. This guide covers the installation of the Guest VM. Each Guest VM has a different configuration method that is not included in this guide, however, gaining access to the console interface of the Guest VM will be included as a first step to configuring the Guest VM. Once console access is provided, the user can configure access to the Guest VM for further configuration through the Guest VM web interface.
Currently, the supported Guest VMs include pfSense.
Oracle SD-WAN Edge operates in native mode while the Guest VM will run in the KVM Linux space. Understanding the supported topologies is important prior to installing the Guest VM. The next section will provide an overview of the topologies and recommendations on deployment scenarios.
The supported Guest VMs will require an image for the KVM environment (qcow, qcow2) which you will need to obtain from the vendor. You then need an XML configuration file for the Guest VM. The XML file provided by Oracle is available in this release's software zip file. The XML configuration file will include the RAM, disk, and VCPU required for the Guest VM. The properties of this file should not be changed without consulting a support representative.
Supported Topologies and Recommendations
The supported topologies of the Guest VM include the options to install the Guest VM on the LAN or WAN side of an SD-WAN Edge instance. There are design considerations and recommendations that pertain to each design which are outlined below:
- What services is the Guest VM providing?
- Does the Guest VM need to see the user native traffic prior to the Oracle Talari Application?
- If the Oracle Talari Application receives the traffic first and the destination is another site with an Oracle Talari, the traffic will be Oracle Talari encapsulated.
- Oracle Talari topologies - Router Mode (L3) or Inline Mode (L2).
- Router Mode is Fail-To-Block (FTB):
- Traffic is blocked if the Oracle Talari Service or Guest VM is down.
- More secure solution when using a Firewall as the Guest VM.
- Inline Mode is Fail-To-Wire (FTW):
- Traffic will flow through the Oracle Talari Appliance.
- This may pose a potential security issue for certain users.
- Router Mode is Fail-To-Block (FTB):
Note:
Traffic flowing through the Appliance while in FTW mode is still being tested as of the time this document was compiled.- Guest VM configuration is supported on the E100 bypass segments only.
- Guest VM configuration is independent of the Oracle Talari configuration.
- If the VM is WAN side – Oracle Talari would use the Guest VM IP as a gateway.
- When using Internet Explorer, the image size cannot exceed 4GB (use sparse image).
- After installation of the image and XML files, the system will need to restart the networking process to configure the network interfaces and routing table properly (Management Interface and Management bridge group).
- The user should have a console connected to the E100 when enabling the Service Chaining feature.
- The Oracle Talari Service must be disabled to install the Guest VM.
Oracle Talari E100 with WAN side Guest VM (Firewall)
This topology has the Oracle Talari E100 with the Guest VM on the WAN side of the
Oracle Talari Application. The topology will be similar to the image below, depending on
the selected configuration within the Oracle Talari installation page.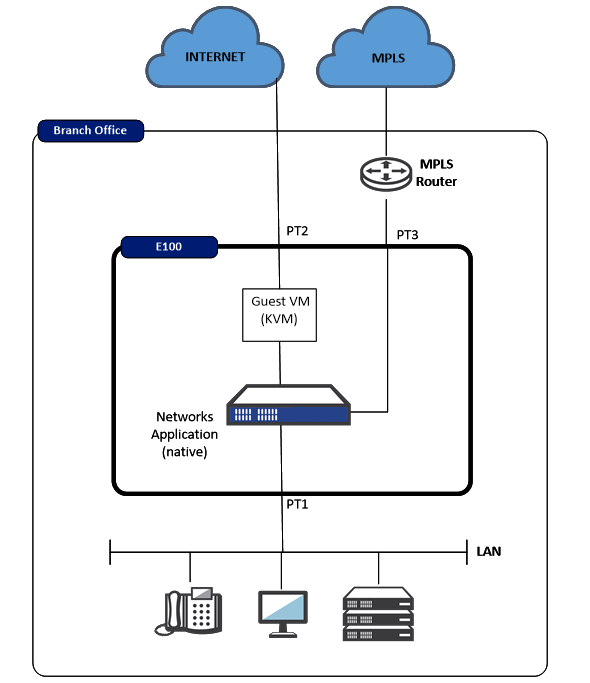
In this topology example, traffic from the physical LAN port 1 is received by the Oracle Talari Application prior to the Guest VM. The user must understand what function the Guest VM is performing, as the Oracle Talari Application will encapsulate any traffic destined for another SD-WAN Edge site. Because the Oracle Talari Application encapsulates Oracle Talari site-to-site traffic, the Guest VM can provide Firewall services. This may include security for Internet traffic, as well as Firewall services for Oracle Talari Conduit traffic. The traffic is then mapped out port 2 of the Oracle Talari Appliance.
Oracle Talari E100 with LAN side Guest VM (Firewall)
This topology has the Oracle Talari E100 with the Guest VM on the LAN side
of the Oracle Talari Application. The topology will be similar to Figure 2, depending on
the selected configuration within the Oracle Talari installation page.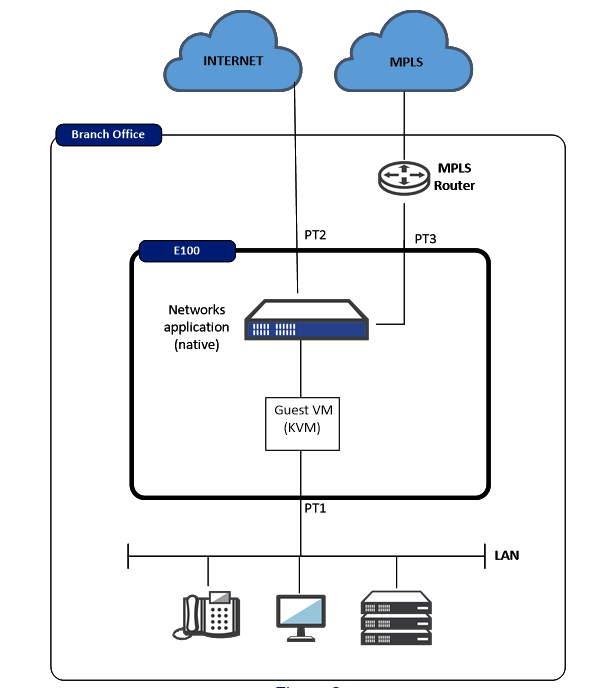
In this topology example, traffic from the physical LAN port 1 is received by the Guest VM prior to the Oracle Talari Application. The user must understand what function the Guest VM is performing, and configure the Guest VM appropriately. Once the Oracle Talari Application receives the user traffic, it will encapsulate any traffic destined for another Oracle Talari site into the Oracle Talari Conduit. The user may then also use other Oracle Talari services for non-Conduit traffic, such as Internet, Intranet, etc. The traffic is then mapped out port 2 of the Oracle Talari Appliance.
Guest VM Installation Process
The process to install the Guest VM is defined by the following steps once a topology decision has been made.
- Log into the Oracle SD-WAN Edge Controller appliance and ensure the Talari service has been disabled. If not, disable the Oracle Talari service through Manage SD-WAN Edge, Enable/Disable Services.
- Proceed to Configuration, Service Chaining.
- Select the VM type to be used.
- Select WAN or LAN side topology and physical Oracle Talari interface to be used to communicate with the Guest VM.
- Upload the qcow or qcow2 image.
- Upload the XML configuration file.
- Select Install.
- The Guest VM should now be installed and running. Proceed to the next section for directions on establishing Guest VM console access in order to configure the Guest VM.
Note:
The XML file is provided by Oracle Talari Networks and can be downloaded. The file has basic properties that are proven to work with the supported Guest VMs. The MAC addresses used are locally administered addresses. The CPU and memory are configured per Guest VM requirements. Please consult a support representative for any required changes to these properties.Once the VM has been successfully installed, the user will see a row
resembling the figure below in the VM Management section and the status should say
“running”. At this point, the user has the option to Restart, Shutdown, or Uninstall the
VM. The installation process will also notify the user that connectivity to the
management interface maybe lost while the Guest VM is being activated. 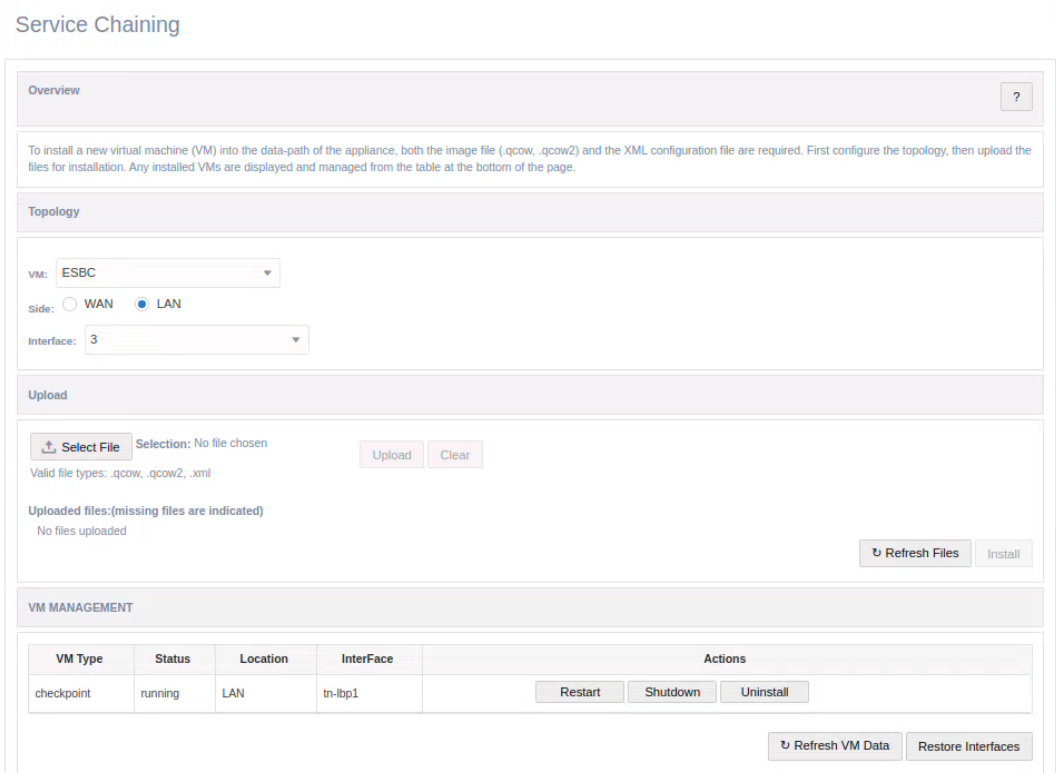
The user may now enable the Oracle Service under Manage SD-WAN Edge, Enable/Disable Services.
Guest VM Configuration
Now that the Guest VM is up and operational, the user must configure it. Steps to gain access to the console interface are as follows.
- SSH into the E100 using an X Windows interface, such as X11 forwarding, with the talariuser username.
- Issue the command vncviewer
Note:
Note: The Guest VM must be running for this step to work as expected.- The VNC Viewer popup window will now appear. Hit enter. The user should now have a terminal window for the Guest VM.
The user may now configure the Guest VM based on the instruction provided by the specific vendor.