Call Flow Examples
The call flows in this topic demonstrate how the ESBC identifies the surrogate-agent for an incoming call for the purpose of authentication. Your surrogate-agent, session-agent, and sip-interface configuration are key to processing these calls.
Call Flow 1
This first call flow depicts the ESBC successfully handling the end station authentication. In this case, the ESBC identifies the surrogate-agent by matching the FROM header with the register-user and register-host parameters in the surrogate-agent configuration.
surrogate-agent:
register-host: oracle.com
register-user: 123
source-ip-prefix: 192.168.0.0/16Next, the ESBC matches the source IP of the INVITE request with the source-ip-prefix parameter in the surrogate-agent configuration to determine if it should perform surrogate authentication. Note the source IP address, 192.168.1.1 falls in the range of the setting, 192.168.0.0/16.
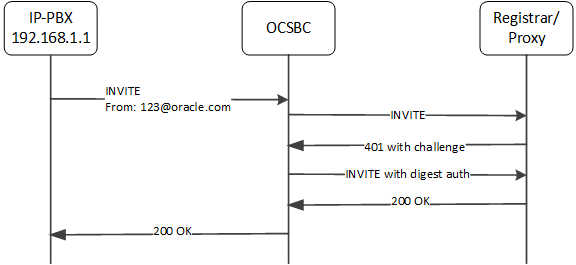
The ESBC does not reference the customer-next-hop parameter because you have configured the source-ip-prefix with some value.
Call Flow 2
This next call flow depicts the ESBC not handling an end station authentication. In this case, the source-ip-prefix, configured to 172.16.0.0/16, does not match the source IP address.
surrogate-agent:
register-host: oracle.com
register-user: 123
source-ip-prefix: 172.16.0.0/16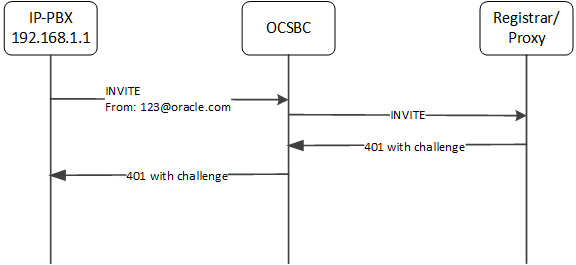
Again, the ESBC does not reference the customer-next-hop parameter.
Call Flow 3
Consider this next case, wherein the source-ip-prefix is not configured. But the relevant configuration, shown below, includes a customer-next-hop configuration that provides a match.
surrogate-agent:
register-host: oracle.com
register-user: 123
customer-next-hop: SA1
source-ip-prefix: <empty>
session-agent:
hostname: SA1
ip-address: 192.168.1.1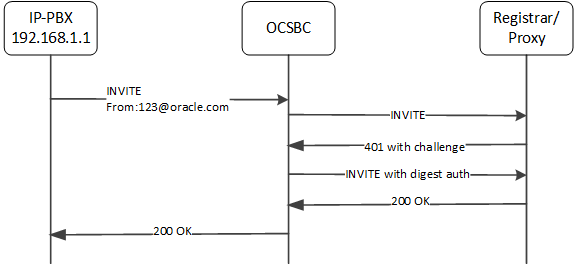
Call Flow 4
Consider this next case, wherein the surrogate-agent configuration fails to identify the source correctly. Because the register-host and register-user values do not match either the FROM presented in the INVITE, the ESBC does not have a means of forwarding the INVITE, so it replies with '480 - No Routes Found' message.
surrogate-agent:
register-host: acmepacket.com
register-user: 486
customer-next-hop: <any value>
source-ip-prefix: <any value>
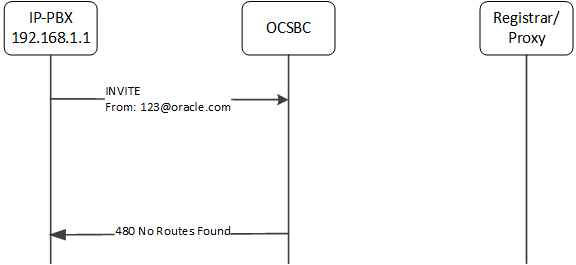
Separate from the surrogate agent feature, the ESBC could use a local-policy or other routing configuration, to route this call.