Configuring SSH
This section describes how to configure SSH and test your Cygwin setup after installing Cygwin on a host.
Note:
While configuring SSH, you may need to run the cygwin.bat script. While running cygwin.bat, ensure that you invoke it in administrator mode. To do this, right-click the cygwin.bat file and select Run as administrator.
To configure SSH and test your Cygwin setup, follow these steps:
- After you install Cygwin, navigate to the
C:\cygwindirectory, open theCygwin.batfile in edit mode using any editor, and add the following line before invoking the bash shell.set CYGWIN=binmode ntsecFor example, here are the contents for the
Cygwin.batfile after adding the above line:@echo off C: chdir C:\cygwin\bin set CYGWIN=binmode ntsec bash --login -i - To verify if Cygwin
(cygrunsrv)is installed properly, runC:\cygwin\Cygwin.bat, and execute the following command:cygrunsrv -hIf Cygwin is installed properly, then all the Cygwin help options are displayed on the screen. However, if this command returns an error message, then you may have to reinstall Cygwin.
- To configure the SSHD service, run
C:\cygwin\Cygwin.bat,and execute the following command:ssh-host-configAfter running the command, you are prompted the following questions:
*** Info: StrictModes is set to 'yes' by default. *** Info: This is the recommended setting, but it requires that the POSIX *** Info: permissions of the user's home directory, the user's .ssh *** Info: directory, and the user's ssh key files are tight so that *** Info: only the user has write permissions. *** Info: On the other hand, StrictModes don't work well with default *** Info: Windows permissions of a home directory mounted with the *** Info: 'noacl' option, and they don't work at all if the home *** Info: directory is on a FAT or FAT32 partition. *** Query: Should StrictModes be used? (yes/no) no *** Query: Should privilege separation be used? <yes/no>: yes *** Query: New local account 'sshd'? <yes/no>: yes *** Query: Do you want to install sshd as a service? *** Query: <Say "no" if it is already installed as a service> <yes/no>: yes *** Query: Enter the value of CYGWIN for the deamon: [] binmode ntsec *** Query: Do you want to use a different name? (yes/no) yes/noAt this point, if you want to use the same name, that is
cyg_server,enterno. You are then prompted the following questions:*** Query: Create new privileged user account 'cyg_server'? (yes/no) yes *** Query: Please enter the password: *** Query: Renter:However, if you want to use a different name, enter
yes. You are then prompted the following questions:*** Query: Enter the new user name: cyg_server1 *** Query: Reenter: cyg_server1 *** Query: Create new privileged user account 'cyg_server1'? (yes/no) yes *** Query: Please enter the password: *** Query: Reenter:If the configuration is successful, you will see the following message:
Host configuration finished. Have fun! - Backup the
c:\cygwin\etc\passwdfile and then use any editor to open the file in edit mode. Remove only those entries of the user that you will use to connect to the host on which you want to install a Management Agent. Ask the user to make a backup of thec:\cygwin\etc\passwdfile before editing.-
If the user that you are employing to connect to the host on which you want to install the Management Agent is a local user, run
C:\cygwin\Cygwin.batand execute the following:/bin/mkpasswd -l –u <USER> >> /etc/passwd (for example, /bin/mkpasswd -l -u pjohn >> /etc/passwd) -
If the user you are employing to connect to the host on which you want to install the Management Agent running is a domain user, run
C:\cygwin\Cygwin.batand execute the following:/bin/mkpasswd -d -u <USER> >> /etc/passwd (for example, /bin/mkpasswd -d -u pjohn >> /etc/passwd) mkdir -p /home/<USER> (for example, mkdir -p /home/pjohn) chown <USER> /home/<USER> (for example, chown pjohn /home/pjohn)
-
- (For a domain user only) If the user you are employing to connect to the host on which you want to install the Management Agent is a domain user, do the following to start the SSH daemon:
- Right-click on My Computer, and select Manage.
- In the Computer Management dialog box that appears, go to Services and Applications, and select CYGWIN sshd.
- Right-click CYGWIN sshd and select Properties.
- In the Properties dialog box, go to the Log On tab.
- Here, specify the domain/user name and password. Click Apply.
- Run
C:\cygwin\Cygwin.bat,and execute the following:chown <USERNAME> /var/log/sshd.log chown -R <USERNAME> /var/empty chown <USERNAME> /etc/ssh* chmod 755 /var/empty chmod 644 /var/log/sshd.logNote:
If
/var/log/sshd.logdoes not exist, you do not have to execute the following commands:chown <USERNAME> /var/log/sshd.log chmod 644 /var/log/sshd.log
- Perform one of the following steps to start the SSH daemon:
Run
C:\cygwin\Cygwin.batand execute the following command:/usr/sbin/sshdOR
Run
C:\cygwin\Cygwin.batand execute the following command:cygrunsrv -S sshdOR
Perform these steps:
-
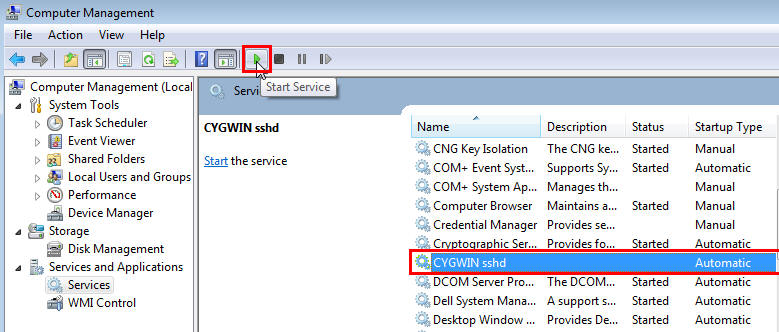
Right-click on My Computer, and select Manage.
-
In the Computer Management dialog box that appears, go to Services and Applications, and select CYGWIN sshd.
-
Click CYGWIN sshd, then click the Start button.
Note:
If the SSH daemon does not start up, view the
c:\cygwin\var\log\sshd.logfile for information on why the start up failed. -
- You can now test your Cygwin setup. To do this, go to a different machine (that has the
sshclient running), and execute the following command:ssh -l <USERNAME> <localhost> 'date' OR ssh -l <USERNAME> <this node> 'date'For example,
ssh -l pjohn example.com 'date'This command will prompt you to specify the password. When you specify the correct password, the command should return the accurate date.
Note:
If you experience a process fork failure, memory leak error, or a file access error after configuring SSH, view the following website for a workaround:
If you are unable to find a workaround for your problem, report your problem to the Cygwin community using the following website: