3.2.3.9 RPM List
The RPM List dashboard offers a comprehensive matrix view of installed RPM packages and their versions across multiple nodes and clusters. It serves as a critical tool for verifying software consistency and quickly identifying discrepancies across systems.
Figure 3-25 RPM List
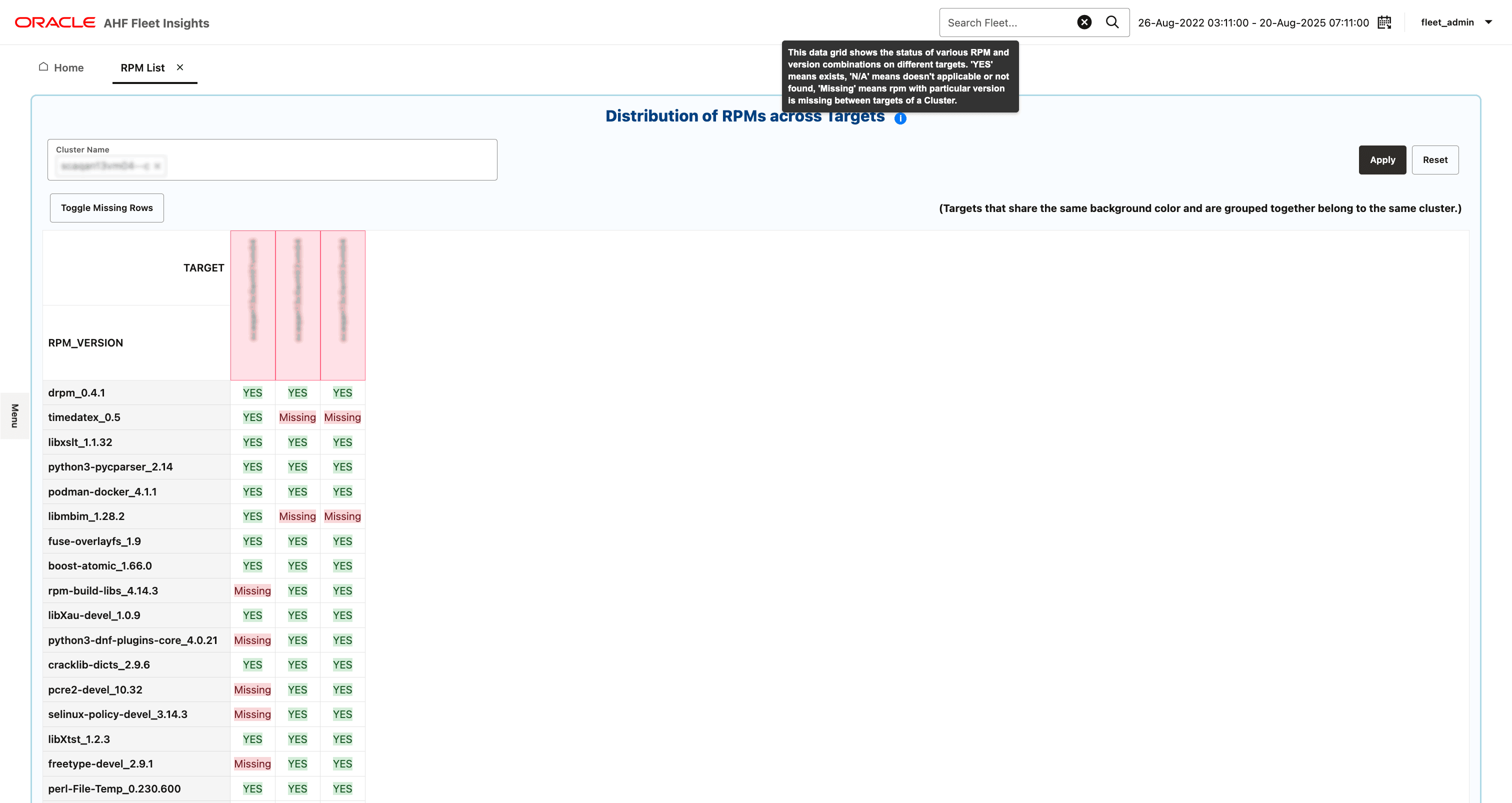
- Identifying missing, inconsistent, or outdated RPMs across servers
- Enforcing standardization and compliance across environments
- Supporting patch readiness and troubleshooting by pinpointing package gaps
- Cluster selection
Cluster Name Filter: Users can select one or more clusters to analyze and compare RPM package status.
- Supports multi-cluster comparison
- Allows side-by-side validation of package presence and versions across nodes
- Ideal for reviewing fleet-wide consistency
Use this to:- Isolate specific clusters for focused audits
- Compare development, staging, and production environments
- Toggle missing rows
Toggle Missing Rows: This button filters the matrix to only show RPMs that are missing on one or more nodes.
- Helps quickly narrow down inconsistencies
- Eliminates noise by hiding fully consistent rows
- Essential for preparing clean, focused patch plans
Use cases- Patch planning
Identify which RPMs need to be installed or upgraded before applying a patch to ensure smooth execution.
- Compliance checks
Verify that critical RPMs are installed consistently across nodes and clusters to meet organizational or regulatory standards.
- Cluster health review
Spot RPM mismatches within a cluster that could lead to unpredictable behavior, software failures, or drift from configuration baselines.
Parent topic: Insights