9.2.1.2 Sparse Disk Groups
Exadata Snapshots utilize Oracle ASM sparse disk groups.
Sparse data files can be created only in Oracle Automatic Storage Management (Oracle ASM) sparse disk groups. The following figure shows a sparse disk group containing three Exadata Snapshots.
Figure 9-5 Sparse Disk Group Contains Exadata Snapshots
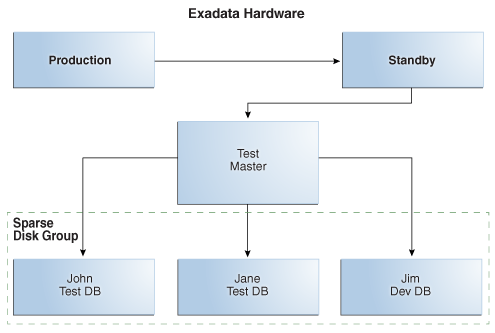
Description of "Figure 9-5 Sparse Disk Group Contains Exadata Snapshots"
A sparse disk group has the following attributes:
compatible.asmmust be set to12.1.0.2or higher.compatible.rdbmsmust be set to12.1.0.2or higher.cell.smart_scan_capablemust be set totrue.cell.sparse_dgmust be set toallsparse. This attribute identifies the disk group to Oracle ASM as being made up of sparse grid disks.- As is the case for all Oracle ASM disk groups on
Exadata, the recommended allocation unit (AU) size is
4M.
For example, the following SQL command creates a sparse disk group:
SQL> CREATE DISKGROUP SPARSE
NORMAL REDUNDANCY
DISK 'o/*/SPARSE_*'
ATTRIBUTE
'compatible.asm' = '12.1.0.2',
'compatible.rdbms' = '12.1.0.2',
'cell.smart_scan_capable' = 'true',
'cell.sparse_dg' = 'allsparse',
'au_size' = '4M';
A sparse Oracle ASM disk group can store both sparse and non-sparse files, which makes it possible to store a test master database and Exadata Snapshots in the same disk group. However, because sparse grid disks are limited in size (to a maximum of 4 TB on a cell disk) and because there is no benefit in placing non-sparse files in a sparse disk group, you should reserve space in sparse disk groups for the sparse files associated with Exadata Snapshots and place the test master database in a regular (non-sparse) disk group.
Parent topic: Exadata Snapshot Concepts