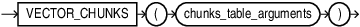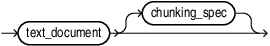VECTOR_CHUNKS
Use VECTOR_CHUNKS to split plain text into smaller chunks to generate vector embeddings that can be used with vector indexes or hybrid vector indexes.
chunks_table_arguments::=
chunking_spec::=
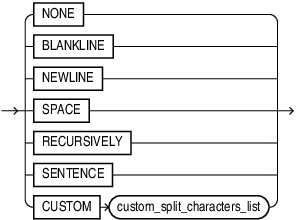
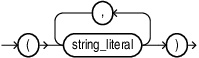
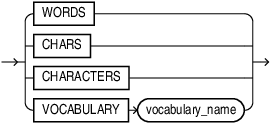
split_characters_list::=
custom_split_characters_list
normalization_spec
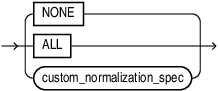
custom_normalization_spec
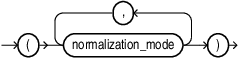
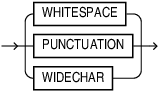
normalization_mode
chunking_mode::=
Purpose
VECTOR_CHUNKS takes a character value as the text_document argument and splits it into chunks using a process controlled by the chunking parameters given in the optional chunking_spec. The chunks are returned as rows of a virtual relational table. Therefore, VECTOR_CHUNKS can only appear in the FROM clause of a subquery.
The returned virtual table has the following columns:
-
CHUNK_OFFSETof data typeNUMBERis the position of each chunk in the source document, relative to the start of the document, which has a position of 1. -
CHUNK_LENGTHof data typeNUMBERis the length of each chunk. -
CHUNK_TEXTis a segment of text that has been split off fromtext_document.
The data type of the CHUNK_TEXT column and the length unit used by the values of CHUNK_OFFSET and CHUNK_LENGTH depend on the data type of text_document as listed in the following table:
Table 7-1 Input and Output Data Type Details
| Input Data Type | Output Data Type | Offset and Length Unit |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
byte |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note:
-
For more information about data types, see Data Types in the SQL Reference Manual.
-
The
VARCHAR2input data type is limited to4000bytes unless theMAX_STRING_SIZEparameter is set toEXTENDED, which increases the limit to32767.
Parameters
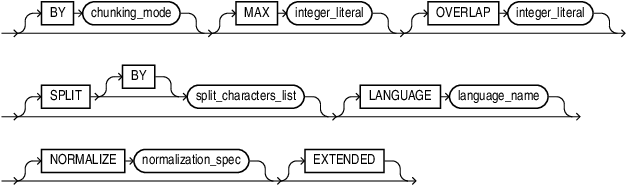
All chunking parameters are optional, and the default chunking specifications are automatically applied to your chunk data.
When specifying chunking parameters for this API, ensure that you provide these parameters only in the listed order.
Table 7-2 Chunking Parameters Table
| Parameter | Description and Acceptable Values |
|---|---|
|
|
Specifies the mode for splitting your data, that is, to split by counting the number of characters, words, or vocabulary tokens. Valid values:
Default value: |
|
|
Specifies a limit on the maximum size of each chunk. This setting splits the input text at a fixed point where the maximum limit occurs in the larger text. The units of Valid values:
Default value: |
|
|
Specifies where to split the input text when it reaches the maximum size limit. This helps to keep related data together by defining appropriate boundaries for chunks. Valid values:
Default value: |
|
|
Specifies the amount (as a positive integer literal or zero) of the preceding text that the chunk should contain, if any. This helps in logically splitting up related text (such as a sentence) by including some amount of the preceding chunk text. The amount of overlap depends on how the maximum size of the chunk is measured (in characters, words, or vocabulary tokens). The overlap begins at the specified Valid value: Default value: |
|
|
Specifies the language of your input data. This clause is important, especially when your text contains certain characters (for example, punctuations or abbreviations) that may be interpreted differently in another language. Valid values:
You must use double quotation marks (
For one-word language names, quotation marks are not needed. For example:
Default value: |
|
|
Automatically pre-processes or post-processes issues (such as multiple consecutive spaces and smart quotes) that may arise when documents are converted into text. Oracle recommends you to use a normalization mode to extract high-quality chunks. Valid values:
Default value: |
|
|
Increases the output limit of a If |
Examples
VECTOR_CHUNKS can be called for a single character value provided in a character literal or a bind variable as shown in the following example:
COLUMN chunk_offset HEADING Offset FORMAT 999
COLUMN chunk_length HEADING Len FORMAT 999
COLUMN chunk_text HEADING Text FORMAT a60
VARIABLE txt VARCHAR2(4000)
EXECUTE :txt := 'An example text value to split with VECTOR_CHUNKS, having over 10 words because the minimum MAX value is 10';
SELECT * FROM VECTOR_CHUNKS(:txt BY WORDS MAX 10);
SELECT * FROM VECTOR_CHUNKS('Another example text value to split with VECTOR_CHUNKS, having over 10 words because the minimum MAX value is 10' BY WORDS MAX 10);To chunk values of a table column, the table needs to be joined with the VECTOR_CHUNKS call using left correlation as shown in the following example:
CREATE TABLE documentation_tab (
id NUMBER,
text VARCHAR2(2000));
INSERT INTO documentation_tab
VALUES(1, 'sample');
COMMIT;
SET LINESIZE 100;
SET PAGESIZE 20;
COLUMN pos FORMAT 999;
COLUMN siz FORMAT 999;
COLUMN txt FORMAT a60;
PROMPT SQL VECTOR_CHUNKS
SELECT D.id id, C.chunk_offset pos, C.chunk_length siz, C.chunk_text txt
FROM documentation_tab D, VECTOR_CHUNKS(D.text
BY words
MAX 200
OVERLAP 10
SPLIT BY recursively
LANGUAGE american
NORMALIZE all) C; See Also:
-
For a complete set of examples on each of the chunking parameters listed in the preceding table, see Explore Chunking Techniques and Examples of the AI Vector Search User's Guide.
-
To run an end-to-end example scenario using this function, see Convert Text to Chunks With Custom Chunking Specifications of the AI Vector Search User's Guide.
Parent topic: Chunking and Vector Generation Functions