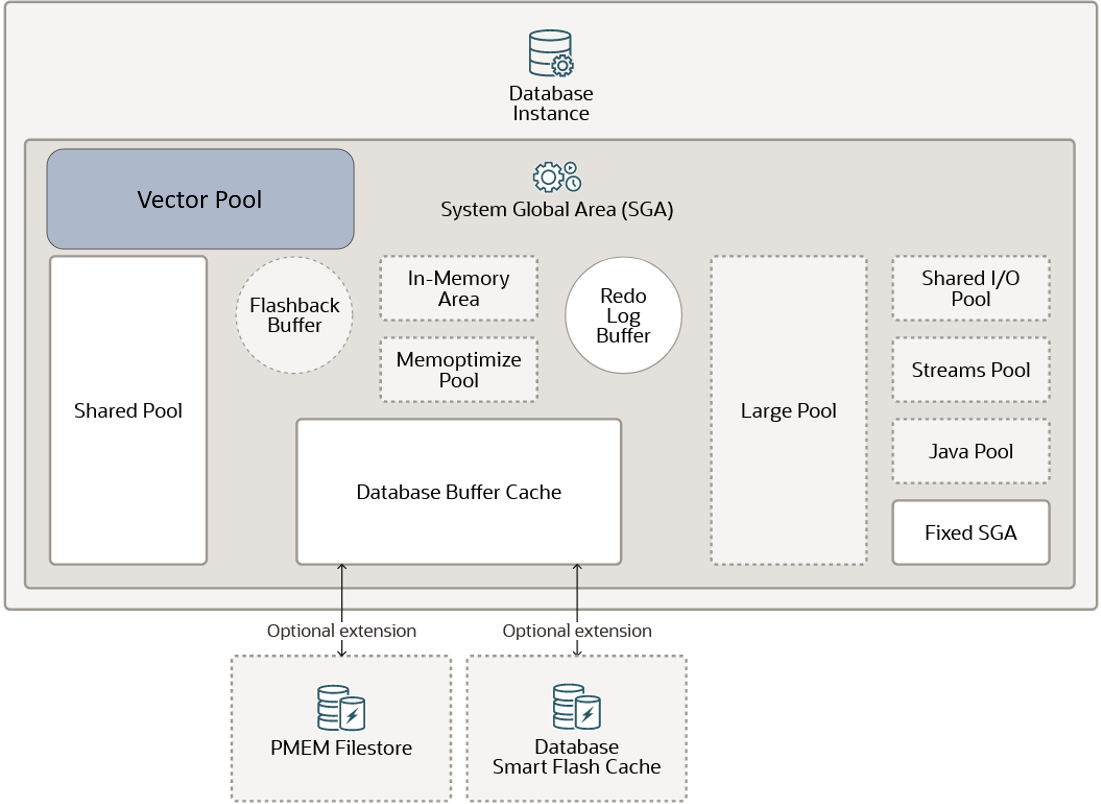
Size the Vector Pool
To allow vector index creation, you must enable a new memory area stored in the SGA called the Vector Pool.
The Vector Pool is a memory allocated in SGA to store Hierarchical Navigable Small World (HNSW) vector indexes and all associated metadata. It is also used to speed up Inverted File Flat (IVF) index creation as well as DML operations on base tables with IVF indexes.
Note:
IVF centroid vectors are stored in the vector pool to improve IVF index creation and index maintenance performance. If space runs out in the vector pool, the centroid vectors are cached in the large pool. If space runs out in the large pool, the centroid vectors are not cached inmemory. This rule applies to both unpartitioned and partitioned local and global IVF indexes.
Enabling a Vector Pool is illustrated in the following diagram:
To size the Vector Pool in an on-premises environment, use the VECTOR_MEMORY_SIZE initialization parameter. You can dynamically modify this parameter at the following levels:
- At the CDB level VECTOR_MEMORY_SIZE specifies the current size of the Vector Pool. Reducing the parameter value will fail if there is current vector usage.
- At the PDB level VECTOR_MEMORY_SIZE specifies the maximum Vector Pool usage allowed by a PDB. Reducing the parameter value will be allowed even if current vector usage exceeds the new quota.
You can change the value of a parameter in a parameter file in the following ways:
- By editing an initialization parameter file. In most cases, the new value takes effect the next time you start an instance of the database.
- By issuing an
ALTER SYSTEM SET ... SCOPE=SPFILEstatement to update a server parameter file. - By issuing an
ALTER SYSTEM RESETstatement to clear an initialization parameter value and set it back to its default value.
Here is an example of how to change the value for
VECTOR_MEMORY_SIZE at the PDB level if you are using an SPFILE:
SQL> show con_name
CON_NAME
------------------------------
MYPDB1
SQL> show user
USER is "SYS"
SQL> show parameter vector_memory_size
NAME TYPE VALUE
------------------ ----------- -----
vector_memory_size big integer 500M
SQL> SELECT ISPDB_MODIFIABLE
2 FROM V$SYSTEM_PARAMETER
3* WHERE NAME='vector_memory_size';
ISPDB_MODIFIABLE
___________________
TRUE
SQL> ALTER SYSTEM SET vector_memory_size=1G SCOPE=BOTH;
System altered.
SQL> show parameter vector_memory_size
NAME TYPE VALUE
------------------- ----------- -------
vector_memory_size big integer 1G
SQL>For more information about changing initialization parameter values, see Managing Initialization Parameters Using a Server Parameter File.
If VECTOR_MEMORY_SIZE is set to 1 and the
sga_target is greater than 0 at CDB initialization, HNSW index creation
will automatically grow the vector memory pool to satisfy the new index. The maximum PDB
VECTOR_MEMORY_SIZE value is limited to 70% of the PDB
sga_target. Dropping an HNSW index shrinks the vector memory pool
accordingly.
In this configuration, where the vector memory pool grows automatically, the PDB
VECTOR_MEMORY_SIZE value will default to 0 and cannot be changed using the
ALTER SYSTEM command. Changes in vector pool size as a result of automatic
growth are not persisted to the spfile, so when the database is restarted, the vector pool
size is reset.
You can query the V$VECTOR_MEMORY_POOL view to monitor the
Vector Pool.
Note:
To roughly determine the memory size needed to store an HNSW index, use the following formula: 1.3 * number of vectors * number of dimensions * size of your vector dimension type (for example, aFLOAT32
is equivalent to BINARY_FLOAT and is 4 bytes in size).
See Also:
Vector Pool Size with Autonomous Database Serverless Services
When using Autonomous Database Serverless services (ADB-S), you cannot explicitly set any SGA-related memory parameters. This includes direct modification of the Vector Pool size.
With ADB-S, the Vector Pool can dynamically grow and shrink:
- An increase to the Vector Pool size is automatically triggered by HNSW index creation and when reopening a PDB containing HNSW indexes.
- A reduction to the Vector Pool size is automatically triggered by an HNSW index drop, PDB close, and CPU reduction.
Note:
Vector Pool size is limited to a maximum of 70% of the PDB SGA size. The SGA size can be retrieved by using the following query:
SELECT value FROM V$PARAMETER WHERE name='sga_target';Note:
Changing instance configuration can cause a previously created HNSW index to be evicted due to insufficient Vector Pool memory. For example, this could be the case if one instance with 15 OCPUs is split into two instances, each with 8 OCPUs.
You can check how much memory is allocated to the Vector Pool after HNSW
index creation using a SELECT statement similar to the following:
SELECT sum(alloc_bytes) FROM V$VECTOR_MEMORY_POOL;Note:
Until an HNSW index is created, V$VECTOR_MEMORY_POOL shows
0 in the ALLOC_BYTES column.
Parent topic: Create Vector Indexes and Hybrid Vector Indexes