About Thread-Based Architecture
Oracle Database instance or an Oracle Automatic Storage Management instance architecture is thread-based.
Threads allow concurrent operations within an operating system process so that a process can run different parts of its program simultaneously on different processors. A thread-based architecture provides the following advantages:
-
Faster context switching
-
Shared memory segments
-
Faster spawning of new connections, because threads are created more quickly than processes
-
Decreased memory usage, because threads share more data structures than processes
Internally, the code to implement the thread model is compact and separate from the main body of Oracle Database code. Exception handlers are used to deallocate resources. They add robustness, with no downtime because of resource leaks or program that does not function as expected.
Oracle Database is not a typical Windows process. On Windows, an Oracle Database instance or an Oracle Automatic Storage Management instance (threads and memory structures) is a Windows service: a background process registered with the operating system. The service is started by Windows and requires no user interaction to start. This enables the database to open automatically at computer startup.
When running multiple Oracle Database or Oracle Automatic Storage Management instances on Windows, each instance runs its own Windows service with multiple component threads. The background processes read and write from various data files, depending on your configuration. Oracle Database architecture on Windows is illustrated in Figure 1-1. Examples of Oracle Database required threads on Windows are listed in Table 1-1 .
Figure 1-1 Oracle Database Architecture on Windows
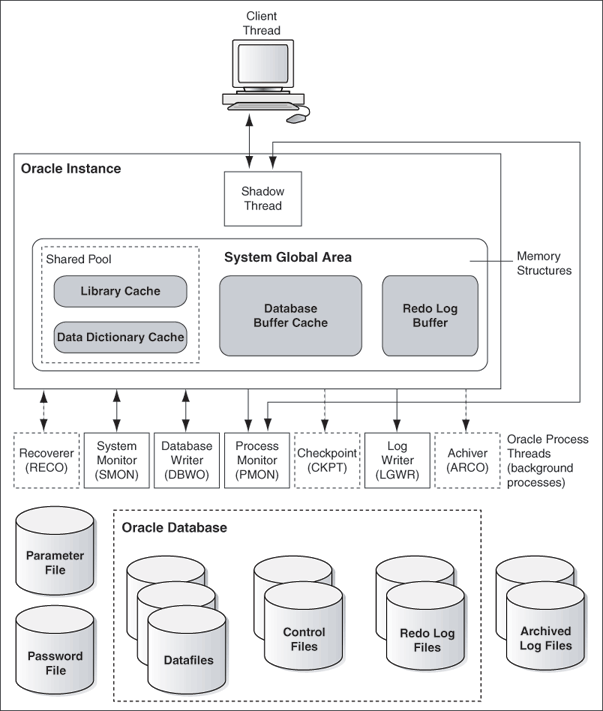
Description of "Figure 1-1 Oracle Database Architecture on Windows"
Table 1-1 Oracle Database Threads
| Oracle Database Thread | Description | Required/Optional |
|---|---|---|
|
|
database writer |
Required |
|
|
log writer |
Required |
|
|
memory manager process |
Required |
|
|
process monitor |
Required |
|
|
process spawner process |
Required |
|
|
system monitor |
Required |
|
|
checkpoint process (thread on Windows) that runs by default on Windows |
Required |
|
|
archive process (or thread on Windows) |
Required |
|
|
distributed recovery background process |
Required |
Note:
You can view running background processes by executing the following query:
SQL> select * from v$bgprocess where paddr <> '00';
Oracle Database instance or an Oracle Automatic Storage Management instance runs as a Windows Service. On Microsoft Windows, the entire instance runs as a single operating system process. Oracle Database instance contains two types of Oracle processes: background and foreground Oracle processes. Each of these Oracle processes is spawned as an operating system thread within in the Oracle Database instance.
Oracle Database for Microsoft Windows is supplied as a set of executables and
dynamic link libraries (DLLs). Executable images can be modified using
ORASTACK to change the size of the stack used by the threads of the
Oracle Database process. Oracle recommends that you use this tool only under the
guidance of Oracle Support Services.
- About Enabling Support for threaded_execution Initialization Parameter
Starting with Oracle Database 21c, Oracle Database supports thethreaded_executioninitialization parameter.
Parent topic: Thread-Based Architecture