ORACLE CONFIDENTIAL. For authorized use only. Do not distribute to third parties.
Pre-General Availability: 2025-12-16
Hosted Box Installation
Follow the below steps to get your Agent Factory environment provisioned, configured, and running on your hosted box.
Caution: Run the installation as a non-root user. Podman must be set up and used in rootless mode for Agent Factory installations. Do not perform the installation or run deployment steps as the root user.
Step 1: Download the Kit and Prepare the Environment
Download the installation kit from artifactory
-
Unset proxy (Oracle internal).
unset https_proxy -
Download the latest version.
-
For AMDx86_64 architecture:
wget http://phoenix120624.dev3sub3phx.databasede3phx.oraclevcn.com:8083/applied_ai.tar.gz -
For ARM64 architecture:
wget http://phoenix120624.dev3sub3phx.databasede3phx.oraclevcn.com:8083/applied_ai_arm64.tar.gz
-
Untar the Zip at the Staging Location
The staging location is a designated directory that:
-
Stores build artifacts like executables and configuration files used to create Podman images for the application
-
Contains a Makefile that allows the user to manage the full deployment lifecycle
Note: While choosing the staging location, make sure it is not on an NFS mount.
Steps:
-
Run the following command to create the staging location.
mkdir <staging_location> -
Copy and extract the downloaded kit to the staging location.
cp <path to applied_ai.tar.gz> <staging_location> tar xzf applied_ai.tar.gz
Automated Installation (Recommended)
The interactive_install.sh script, included in the installation kit, automates nearly all setup tasks, including environment configuration, dependency installation, and application deployment.
This file will be present in the staging location once you extract the kit. Follow the steps below to run the script:
-
Run the Interactive Installer
Now that the kit is unpacked, execute the
interactive_install.shscript from within the same directory.cd <staging_location> bash interactive_install.sh -
Follow the On-Screen Prompts
The script will now guide you through the rest of the process:
Environment Detection: It will detect your operating system (Oracle Linux or macOS) and ask you to confirm your environment type.
Automated Setup: It will automatically configure Podman, set up subuids/subgids, install dependencies like
podman-compose, and enable user linger mode.Guided Steps: It will prompt you for necessary inputs, such as your username, passwords, and confirmation for key steps.
Database Preparation: If you opt for a production setup, the script will display the exact SQL commands you need to run on your database.
Application Build & Launch: Finally, the script will run the
make buildandmake upcommands to build the container images and launch the application. -
Proceed to UI Setup
Once the script completes the
make upstep, the application will be running athttps://<hostname>:8080/studio/installation. You can now proceed to the installation steps to be done from UI to finalize the configuration through your web browser.
Manual Installation
Follow the steps below for manual installation.
Note: Oracle recommends running the interactive installer included in the installation kit to automate the setup tasks instead of performing a manual installation.
-
Podman setup for your user on your hosted box
Note: Follow these steps if you are facing issues running Podman as your user. This can happen when the Podman storage locations point to your home directory.
-
Create
graphrootandrunroot.mkdir -p /scratch/podman_storage/storage/graphroot mkdir -p /scratch/podman_storage/storage/runroot -
Create
~/.config/containersif not already present.mkdir -p ~/.config/containers -
Run
vi ~/.config/containers/storage.confand paste below contents.[storage] driver = "overlay" graphroot = "/scratch/podman_storage/storage/graphroot" runroot = "/scratch/podman_storage/storage/runroot" -
Replace the
<USERNAME>with the username of the VM and run the commands below.sudo /sbin/usermod --add-subgids 10000-75535 <USERNAME> sudo /sbin/usermod --add-subuids 10000-75535 <USERNAME> podman system migrate
Note
During container setup, you may encounter the following error when running
podman system migrateor logging into the container registry:Error: invalid configuration: the specified mapping 10000:65536 in "/etc/subuid" includes the user UIDThis typically occurs when the subuid/subgid range assigned in /etc/subuid or /etc/subgid overlaps with your actual UID or GID. For example, this can occur if your UID falls within the allocated subuid range. Run the following setup to resolve any Podman UID/GID mapping conflicts during installation:
-
Check your actual UID with:
id -u <your_username> -
Open
/etc/subuidand/etc/subgidand verify that none of the assigned ranges include your real UID or GID. -
If they do, remove or comment out the conflicting lines.
-
Assign a new, non-overlapping range using:
sudo /sbin/usermod --add-subuids 165536-231071 <your_username> sudo /sbin/usermod --add-subgids 165536-231071 <your_username> -
Resume installation steps.
This issue can also occur due to conflicting or leftover configuration from previous Podman installations. Always verify current mappings and adjust as needed.
Attention
The default
tmpdirectory on dev machines often does not have sufficient space. In such cases, run the following setup.Problem:
Error: copying system image from manifest list: writing blob: storing blob to file “/var/tmp/container_images_storage1158655352/7”: write /var/tmp/container_images_storage1158655352/7: no space left on device.Solution:
- Run the following command:
mkdir /scratch/podman_tmp-
Edit your
~/.config/containers/containers.confpointing podman to aTMPDIRwith enough free space. For example, if your/scratchdirectory has enough memory (~100GB), then create the directory/scratch/podman_tmpand change contents of~/.config/containers/containers.confto:[engine] env = ["TMPDIR=/scratch/podman_tmp"]
-
-
Set up Podman Compose for your user on your hosted box
-
Set proxy (oracle internal).
export https_proxy=http://www-proxy.us.oracle.com:80 -
To install
podman-composeon your OL8 system, run the following command. If it fails try step 3.sudo yum install podman-compose -
If yum is unable to locate the EPEL repo, create
/etc/yum.repos.d/oracle-epel-ol8.repoassudowith the following content and try again.sudo vi /etc/yum.repos.d/oracle-epel-ol8.repoContent:
[ol8_developer_EPEL] name=Oracle Linux $releasever EPEL Packages for Development ($basearch) baseurl=https://yum$ociregion.$ocidomain/repo/OracleLinux/OL8/developer/EPEL/$basearch/ gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-oracle gpgcheck=1 enabled=1 [ol8_developer_EPEL_modular] name=Oracle Linux $releasever EPEL Modular Packages for Development ($basearch) baseurl=https://yum$ociregion.$ocidomain/repo/OracleLinux/OL8/developer/EPEL/modular/$basearch/ gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-oracle gpgcheck=1 enabled=1
-
-
Get access to Oracle Container Registry
-
Go to https://container-registry.oracle.com/.
-
Login and generate auth token.
Description of the illustration oracle-container-registry.png
-
Set proxy (oracle internal).
export https_proxy=http://www-proxy.us.oracle.com:80 -
Log in using key and username (email) from Oracle Container Registry.
podman login container-registry.oracle.com -
Test it out by running the following command:
podman pull container-registry.oracle.com/database/free:latest
-
-
Create a database user
Note: This step is only required for a production installation and can be skipped for quickstart mode.
You will need an Oracle AI Database 26ai instance available for the Agent Factory.
-
Log in as the
SYSDBAuser to your Pluggable Database (PDB) using SQL*Plus or your preferred tool. -
Create the database user. “Replace
and with your desired username and password, then run the commands below.” CREATE USER <DB_USER> IDENTIFIED BY <DB_PASSWORD> DEFAULT TABLESPACE USERS QUOTA unlimited ON USERS; GRANT CONNECT, RESOURCE, CREATE TABLE, CREATE SYNONYM, CREATE DATABASE LINK, CREATE ANY INDEX, INSERT ANY TABLE, CREATE SEQUENCE, CREATE TRIGGER, CREATE USER, DROP USER TO <DB_USER>; GRANT CREATE SESSION TO <DB_USER> WITH ADMIN OPTION; GRANT READ, WRITE ON DIRECTORY DATA_PUMP_DIR TO <DB_USER>; GRANT SELECT ON V_$PARAMETER TO <DB_USER>; exit;
-
-
Extend VARCHAR2 for self-managed Oracle AI Database
The
max_string_sizedatabase parameter must be set toEXTENDEDbefore running the application. Themax_string_sizeparameter for the DB should be extended to 32K before running the application.-
Log in as the
SYSDBAuser to your Pluggable Database (PDB) using SQL*Plus or your preferred tool. -
Check the current value of the parameter:
SELECT value FROM v$parameter WHERE name = 'max_string_size'; -
If the output is already EXTENDED, no further action is needed. Otherwise, run the following script as the
SYSDBAuser. This sequence will restart the database.ALTER SYSTEM SET max_string_size=extended SCOPE=SPFILE; SHUTDOWN NORMAL; STARTUP UPGRADE; @$ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/admin/utl32k.sql SHUTDOWN IMMEDIATE; STARTUP; @$ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/admin/utlrp.sql -
If you are using a multitenant CDB or PDB architecture, repeat the following for the PDB where the application schema will be installed:
-
From the CDB root, open the PDB in UPGRADE mode.
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE <PDB_NAME> OPEN UPGRADE; -
Switch your session to the PDB.
ALTER SESSION SET CONTAINER=<PDB_NAME>; -
Run the migration script in the PDB.
@$ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/admin/utl32k.sql -
Switch back to CDB root.
ALTER SESSION SET CONTAINER=CDB$ROOT; -
Close and then open the PDB.
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE <PDB_NAME> CLOSE IMMEDIATE; ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE <PDB_NAME> OPEN;
-
-
Switch to the PDB, and verify that the change was successful. The output of this query must be EXTENDED.
SELECT value FROM v$parameter WHERE name = 'max_string_size';
-
-
Enable linger mode
Run the following command to enable linger mode for your Oracle Linux session user. Replace
<USERNAME>with the specific user’s login name.loginctl enable-linger <USERNAME>Note: Linger mode allows a user’s background processes to continue running even after they log out of the system.
Step 2: Install and Launch Agent Factory
Installation from Source
Installation from source can be performed in two modes: prod and quickstart. For installation using the prod mode, you need your own 26ai database user, while the quickstart mode brings up the containerised form of Oracle AI database 26ai.
Note: Refer to the Installation Modes if you are unsure which installation mode to choose.
Follow these steps to perform the installation in prod mode.
-
Go to the staging location where you have copied the kit in Step 1.
cd <staging_location> -
Untar kit.
tar xzf applied_ai.tar.gz -
Set proxies.
export https_proxy=http://www-proxy.us.oracle.com:80 export NO_PROXY=.oracle.com -
Create the images required to run the application.
Note: This step can be skipped by checking if you have the latest Private AI image already present using the command
podman imagesmake build -
For deployment in
prodmode, type 1 when prompted to choose the install mode.Select installation mode: 1) prod 2) quickstart Enter choice (1 or 2): 1 Building the images necessary in Production mode You selected Production mode. Confirm? (yes/no) [yes]: yes Building Applied AI Image... -
Bring the containers up.
make upThe following is the output for the
prodinstallation. You can see that theollama-server-labelwas not built.Oracle Agent Factory Starting deployment mode determination... [checkmark] Image 'localhost/applied-ai-label:latest' found. [checkmark] Image 'localhost/applied-ai-label:latest' found. Only Production mode deployment is possible. Deploying Agent Factory in Production mode... Initiating startup for oracle-applied-ai-label container... [checkmark] oracle-applied-ai-label container is UP and RUNNING. -Please wait while the application is being set up within oracle-applied-ai-label container... Application setup successfully within the container 'oracle-applied-ai-label'. -Configuring application container: oracle-applied-ai-label... [checkmark] Application container oracle-applied-ai-label configured successfully. [checkmark] Production deployment complete.Note: The user can monitor Agent Factory installation logs by running:
make logsaai -
Once installation is complete, you can access the application at:
https://<hostname>:8080/studio/installation
Installation Steps from the User Interface
Accessing the application URL for the first time in prod mode would bring up the UI based installation flow.
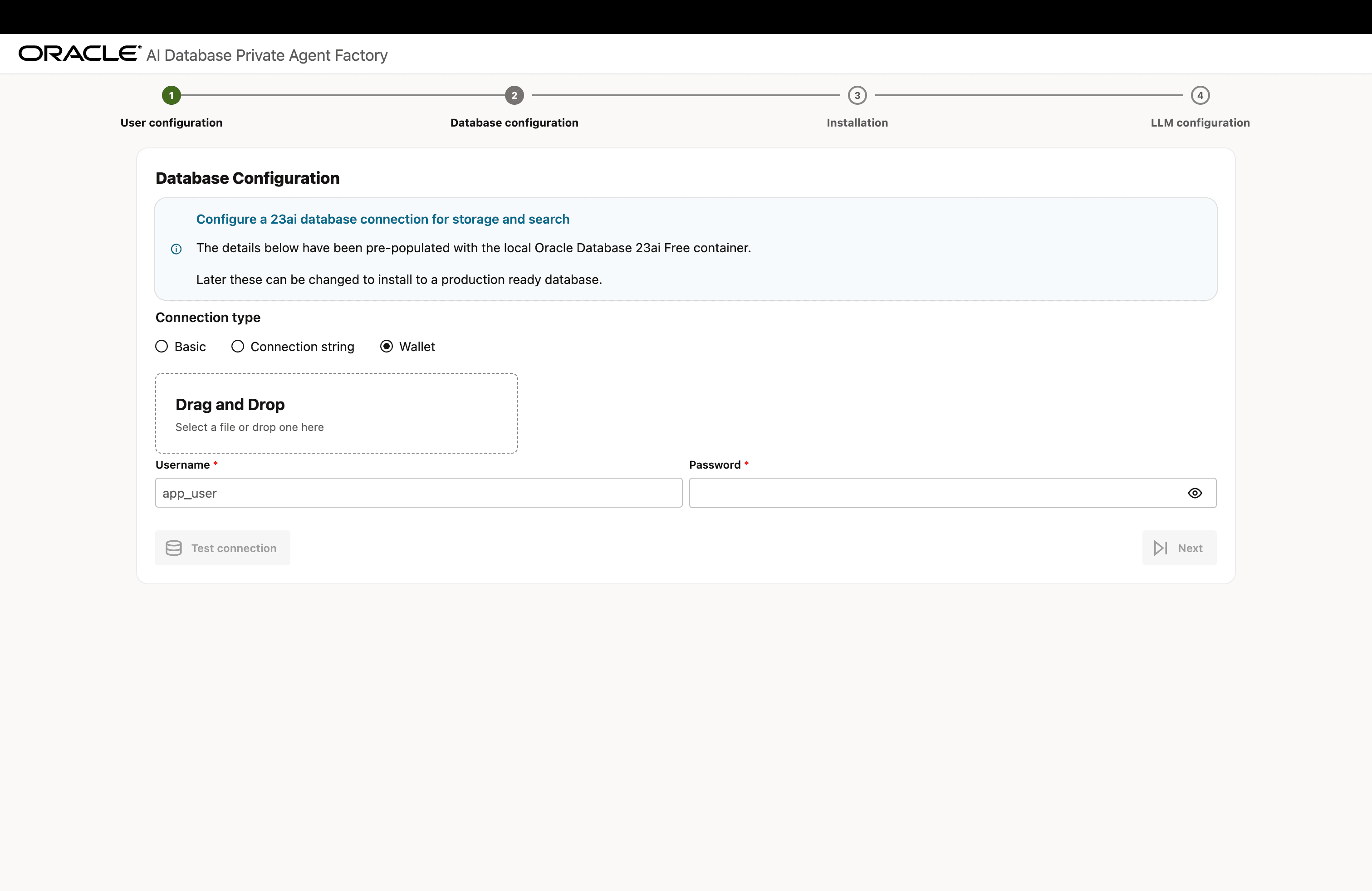
Database Configuration Options
Provide your database connection details in either of the three formats and click Test Connection to verify that the information entered is correct. Upon a successful connection, you will see a Database connection successful notification.
Format 1: Enter all the connection details manually
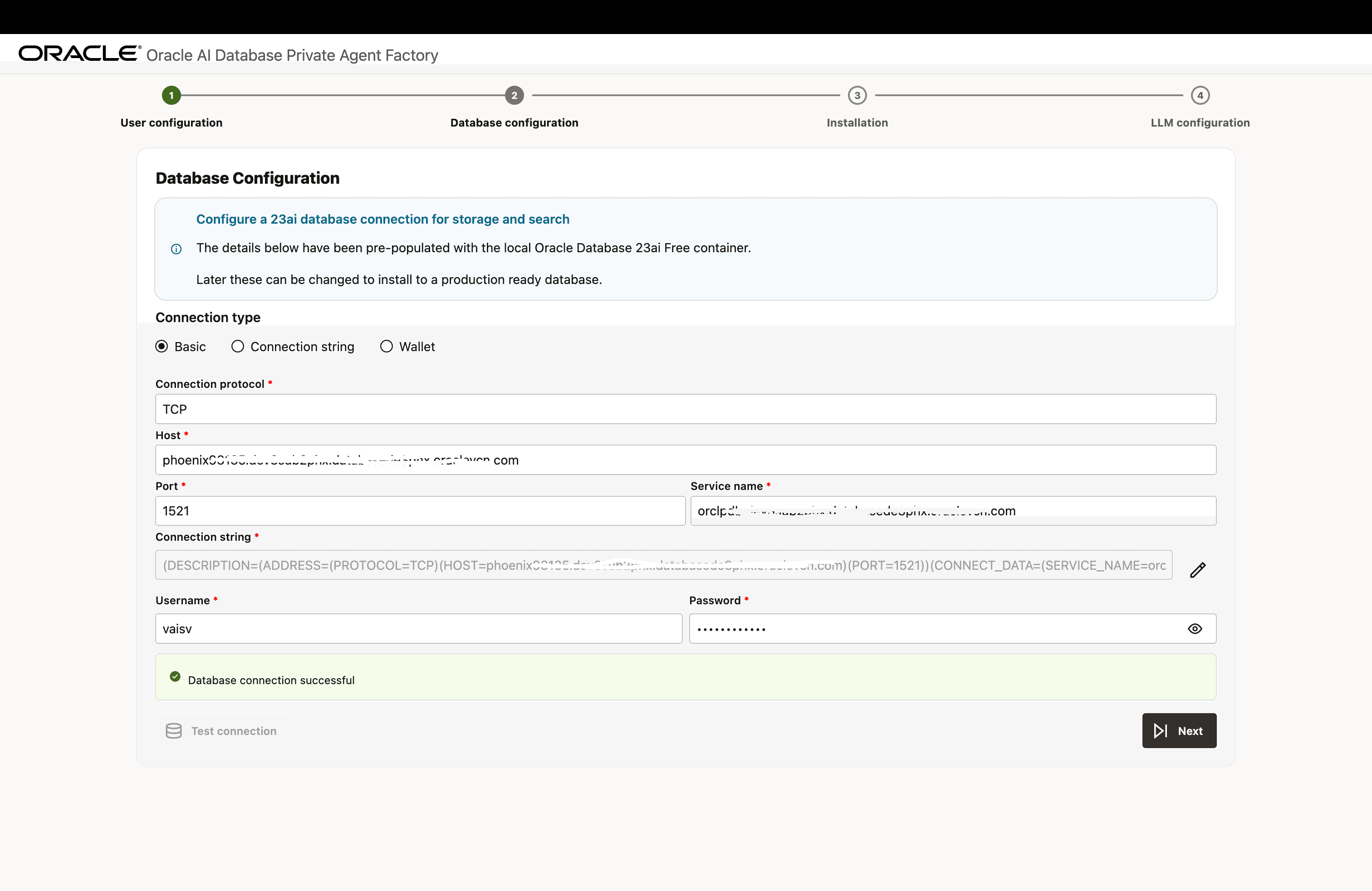
Description of the illustration install-step-2-db-config-1.png
Format 2: Enter the Database Connection String
Description of the illustration install-step-2-db-config-2.png
Format 3: Upload a Database Wallet File
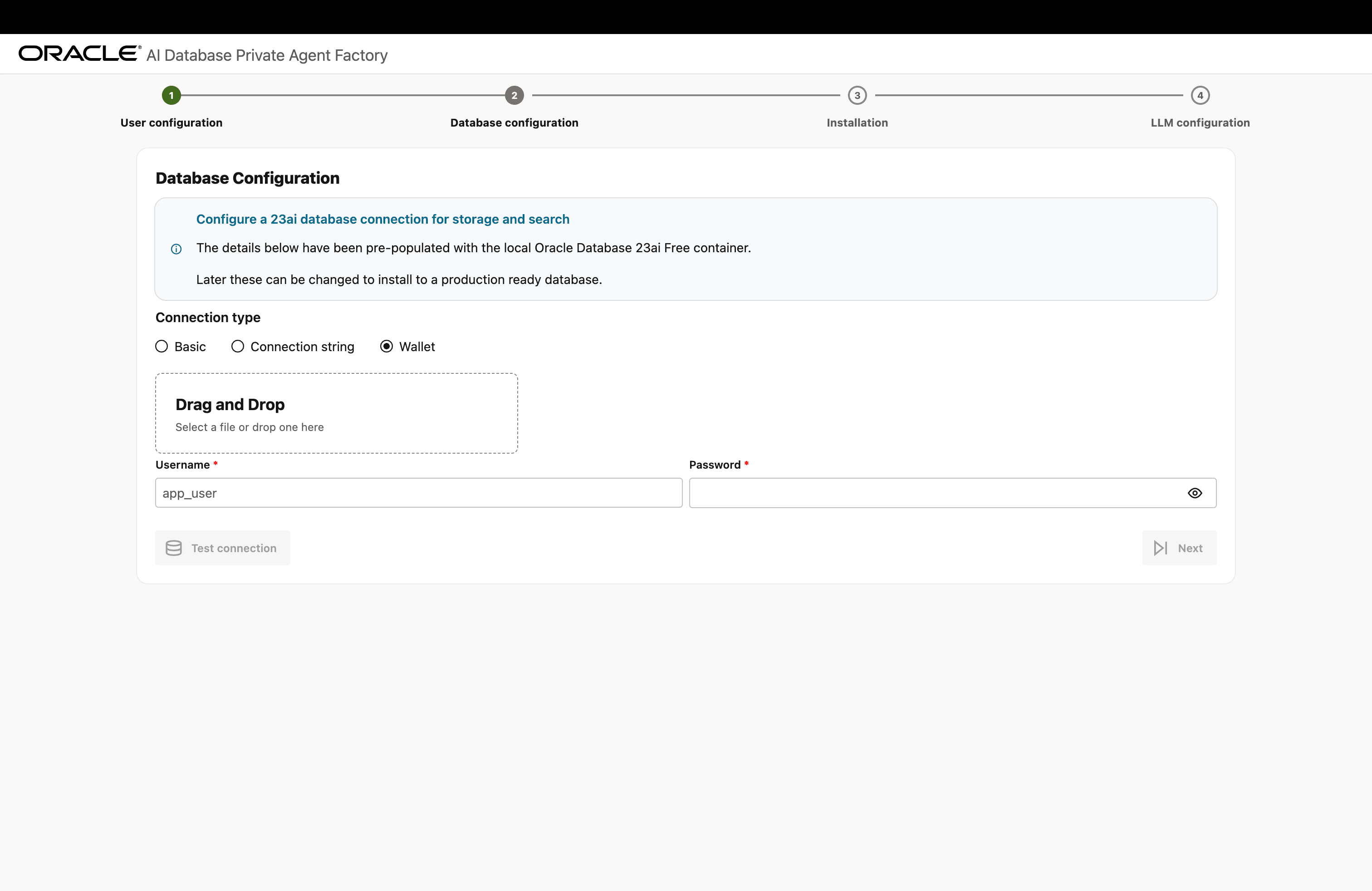
Description of the illustration install-step-2-db-config-3.png
LLM Configuration Options
Choose an LLM - Ollama, vLLM, OpenAI, or OCI GenAI to configure a generative model. See Configure LLM for more details on the LLM configurations.
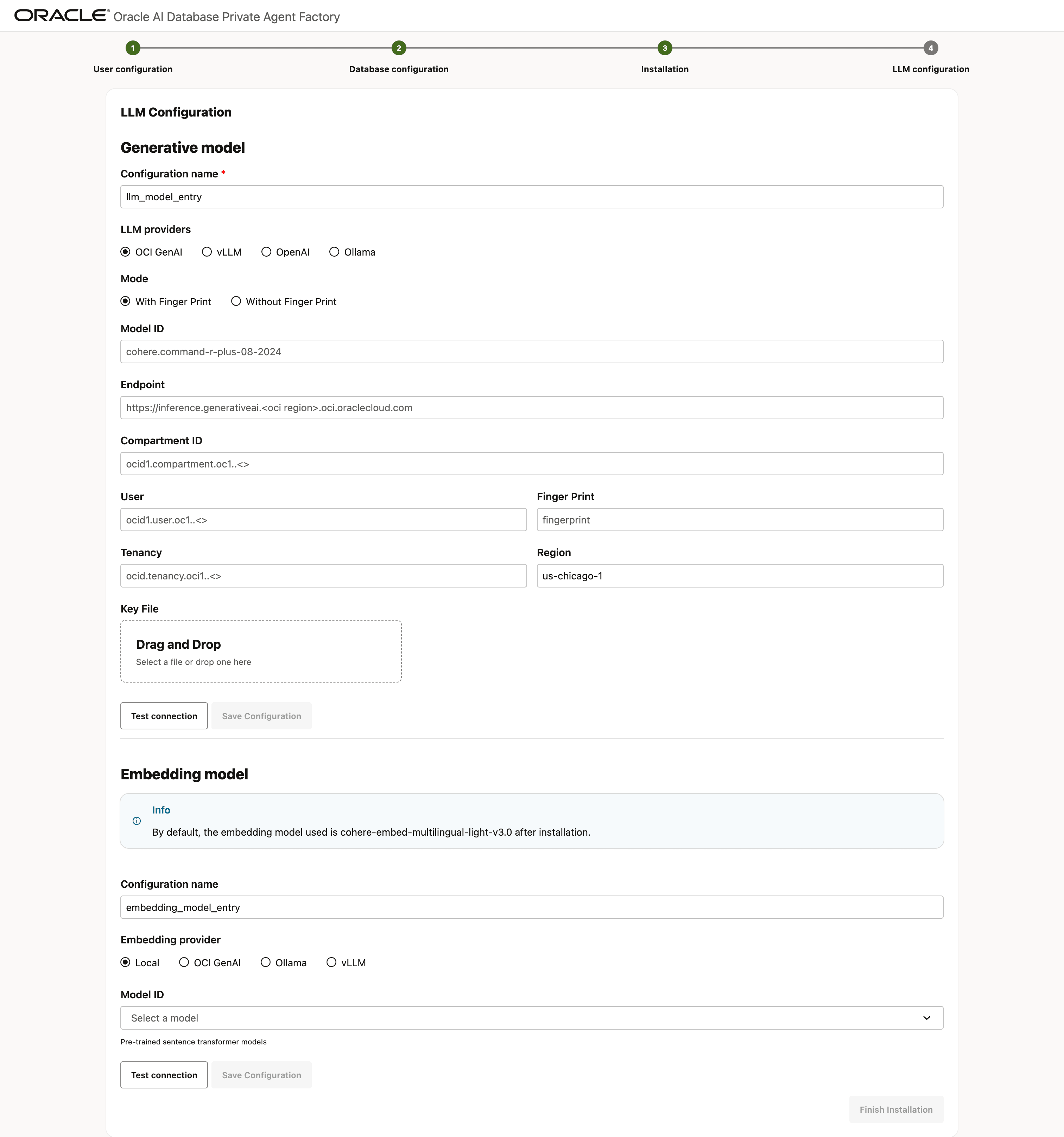
Description of the illustration install-step-llm-config.png
Enter the required details in the selected LLM configuration and select Test Connection. Once you see the Connection successful message, select Save Configuration.
Optionally, configure an embedding model to use for data ingestion and retrieval. By default, cohere-embed-multilingual-light-v3.0 model is used to generate embeddings and is also the local embedding model included with the service.
Pre-built Knowledge Assistants currently support only Large Language Models (LLMs) from the OCI Generative AI Service. To ensure proper functionality of the pre-built knowledge agents, select from the following embedding models.
- cohere.embed-multilingual-light-v3.0
- cohere.embed-english-v3.0
- cohere.embed-multilingual-v3.0
Finally, select Finish Installation to complete the setup and be redirected to the login page.
Import Certificates into the Container (Optional)
Follow the steps below to import certificates into the oracle-applied-ai-label container.
-
Copy certificate and key files into the container.
podman cp <cert_file> oracle-applied-ai-label:/tmp podman cp <key_file> oracle-applied-ai-label:/tmp -
Enter the container.
podman exec -it oracle-applied-ai-label bash -
Run the import command.
cd /home/aaiuser/install ./aai importcert -cert /tmp/<cert_file> -key /tmp/<key_file>