LLM Management
Large Language Models (LLMs) are used for tasks like text generation, summarization, question answering, and supporting MCP server tools.
Agent Factory supports a diverse selection of LLMs from multiple providers. Use the LLM Management screen to set up and manage both generative models and embedding models within the application.
Generative Models
OCI Generative AI
The Agent Factory accepts all generative models available through the OCI Generative AI Service. However, for best results Oracle recommends using the following pre-trained models in combination with the Agent Factory:
-
xai.grok-4 -
xai.grok-4-fast-reasoning -
xai.grok-4-fast-non-reasoning -
llama3.3
Note: Using Google Vertex AI models is not recommended (e.g google.gemini-2.5-pro), as they do not support tool use.
Setup OCI Generative AI Service
Below are the steps to configure xai.grok-4-fast-reasoning pre-trained model from OCI Generative AI Service using a Fingerprint based authentication.
Prerequisites: Setup OCI Generative AI Service. See Getting Started with Generative AI.
Step 1: Click on LLM management on the left side navigation menu.
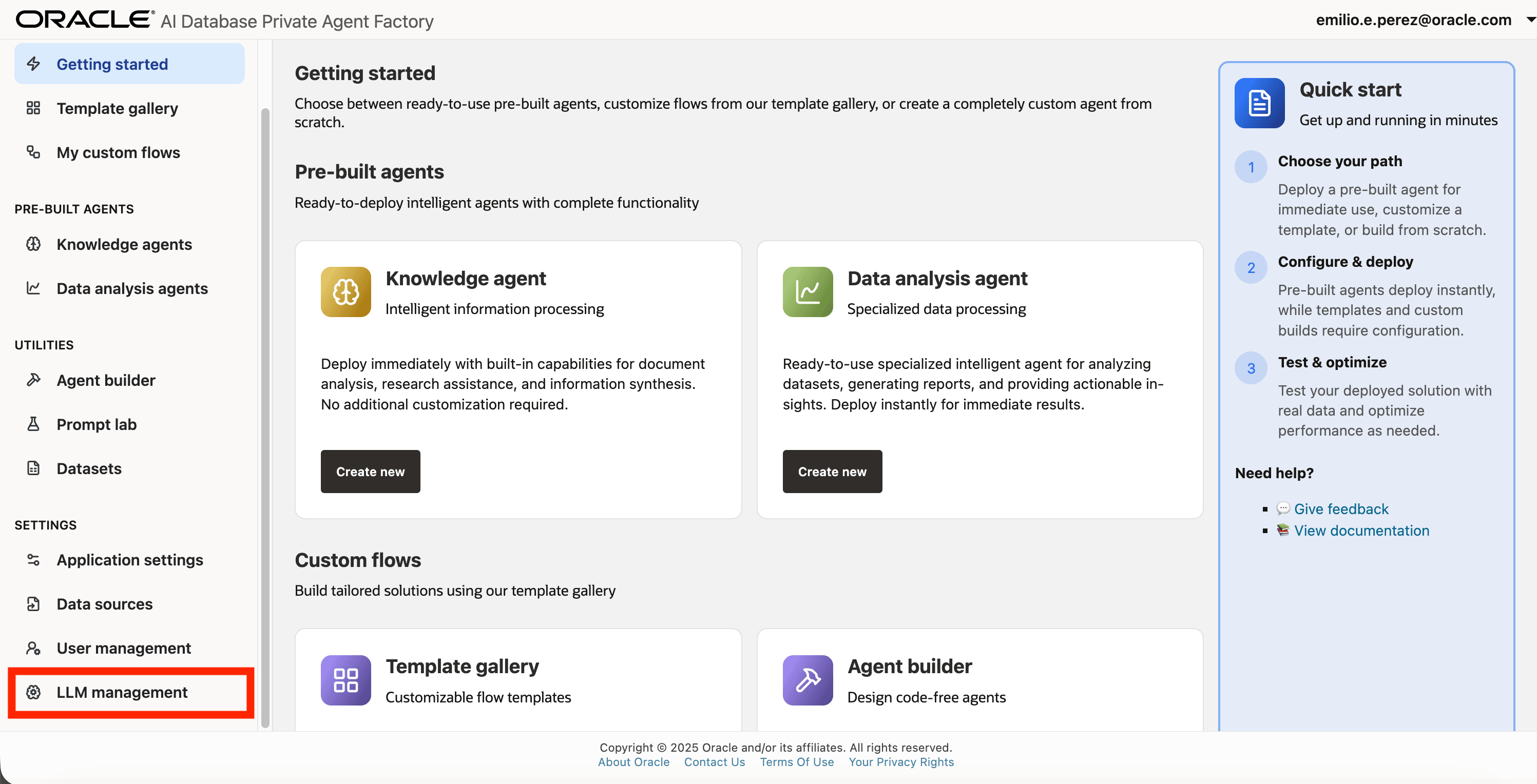
Step 2: Click on Add configuration button placed on the top-right corner.
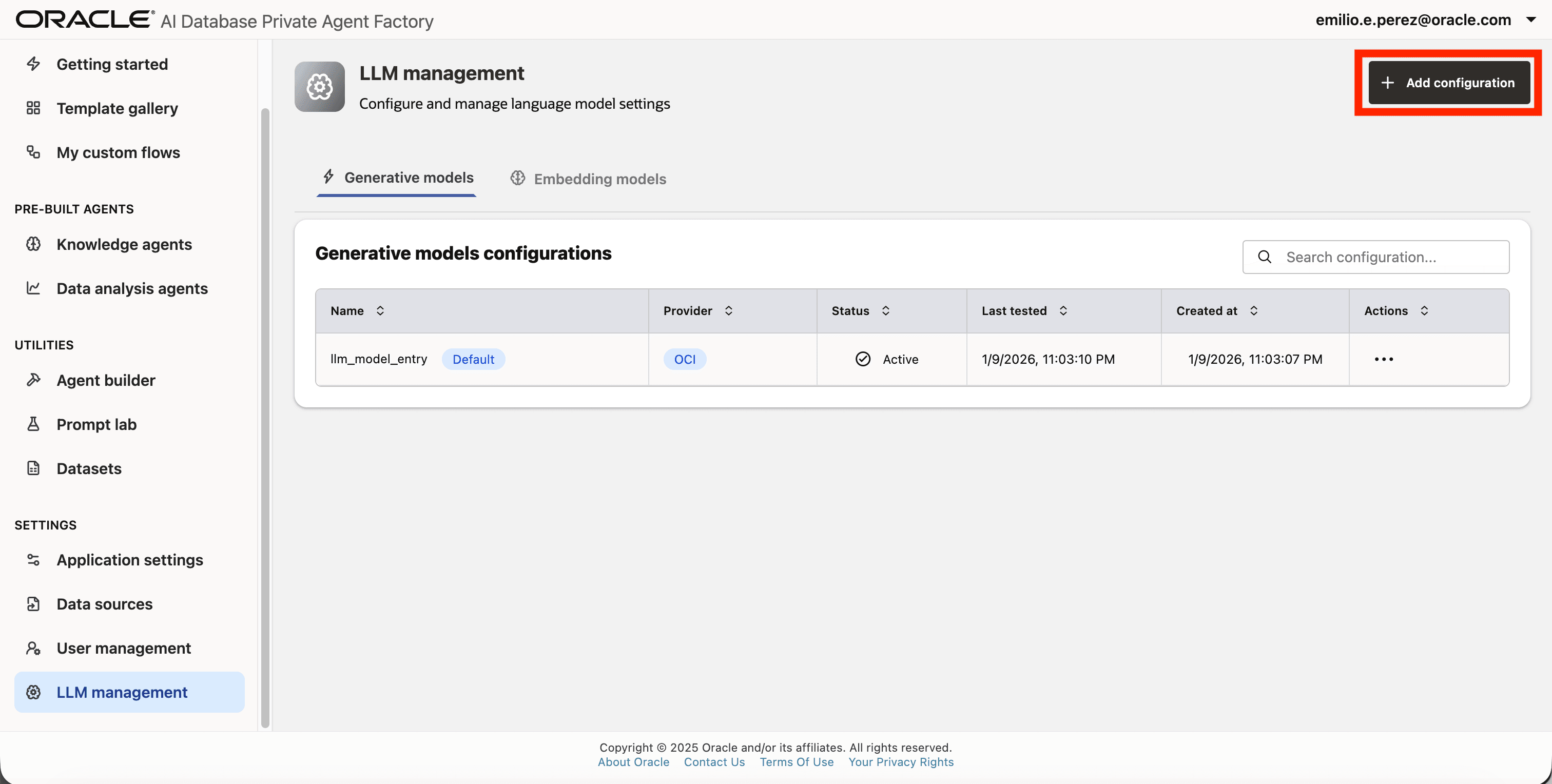
Step 3: A form will open, under Model type pick Generative model.
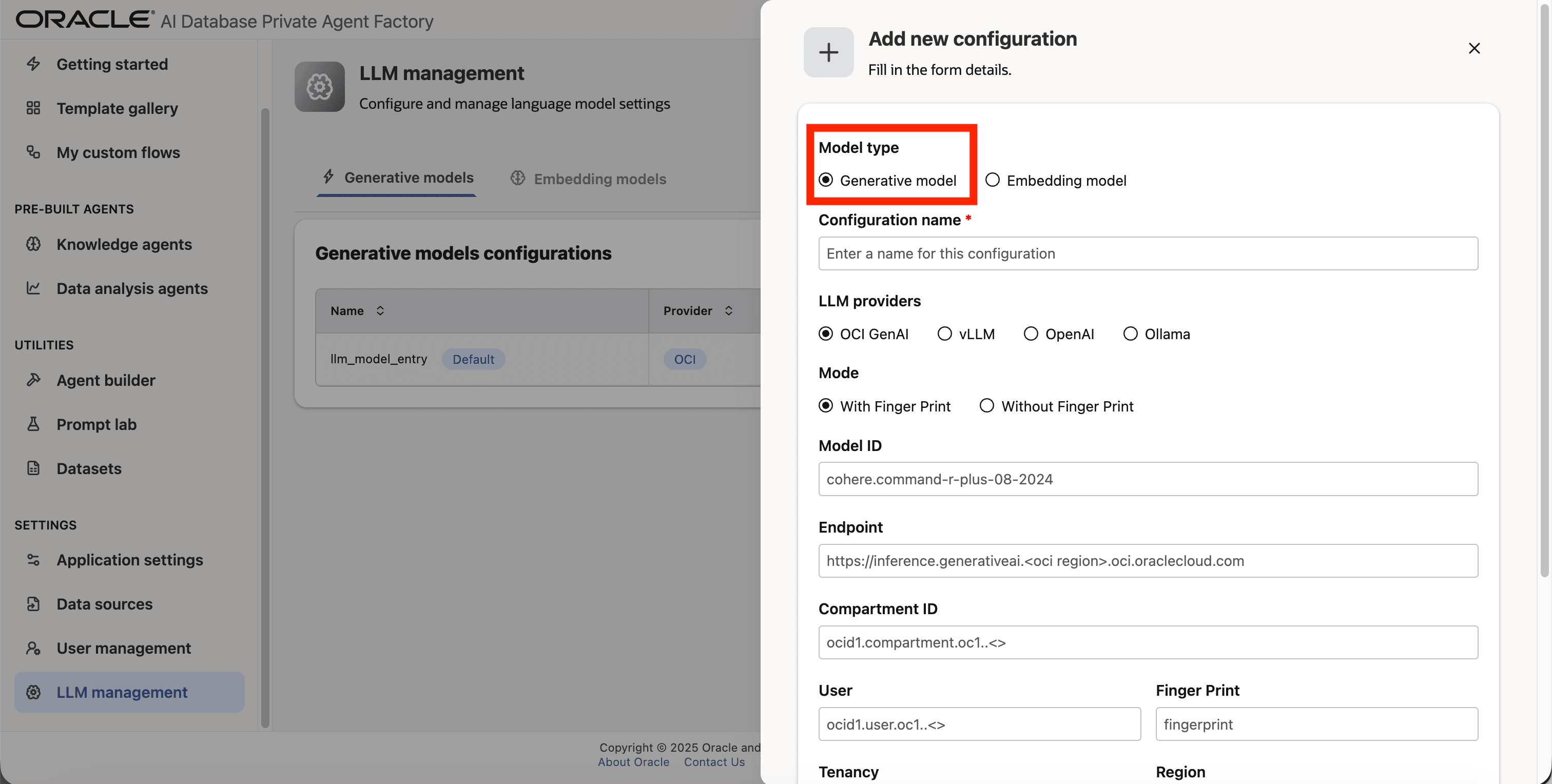
Step 4: Give your LLM configuration a preferred name under Configuration name, avoid whitespaces since they are not allowed.
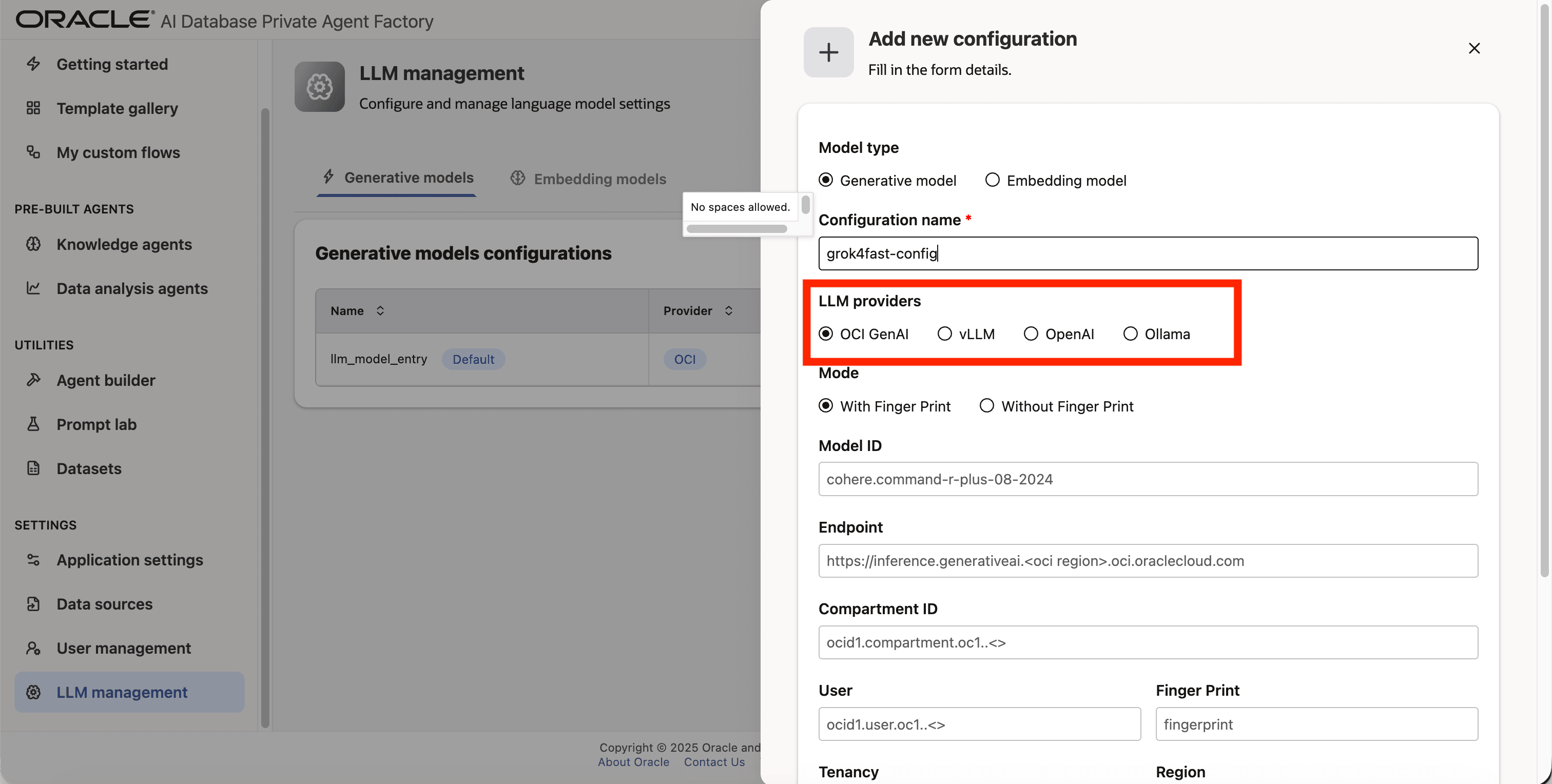
Step 5: From list of LLM providers pick OCI GenAI.
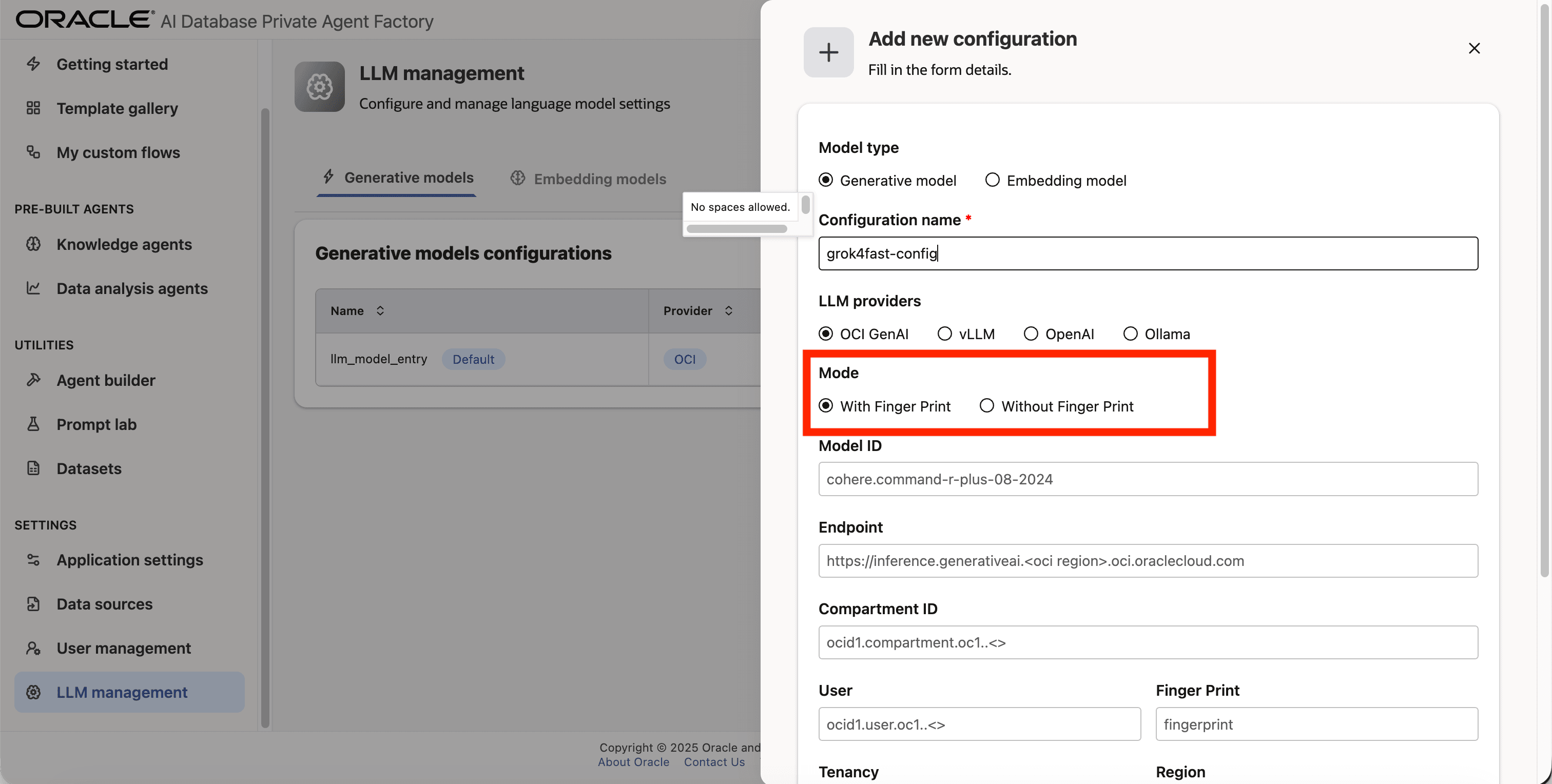
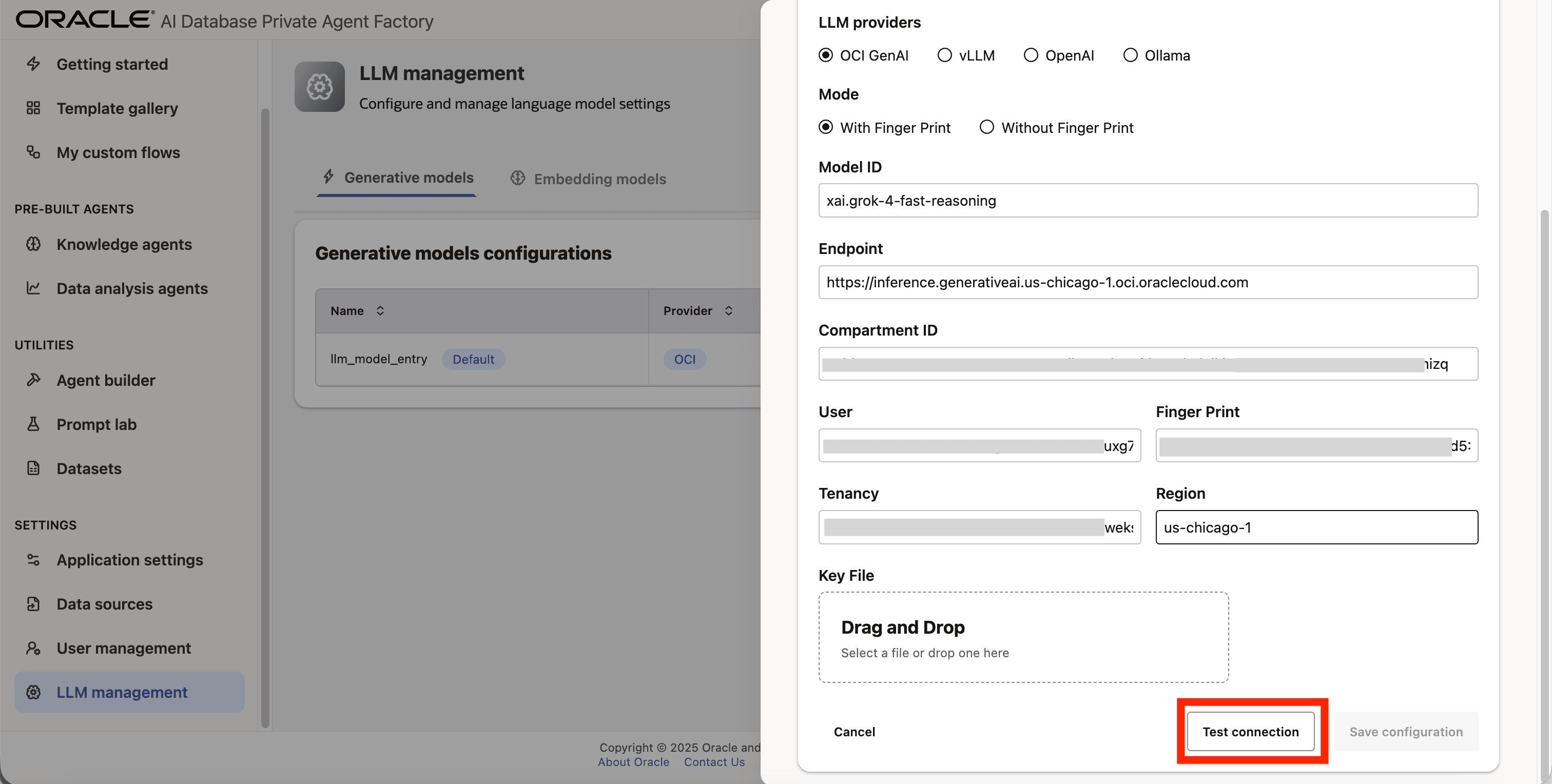
Step 6: On **Mode_ click on With Finger Print.
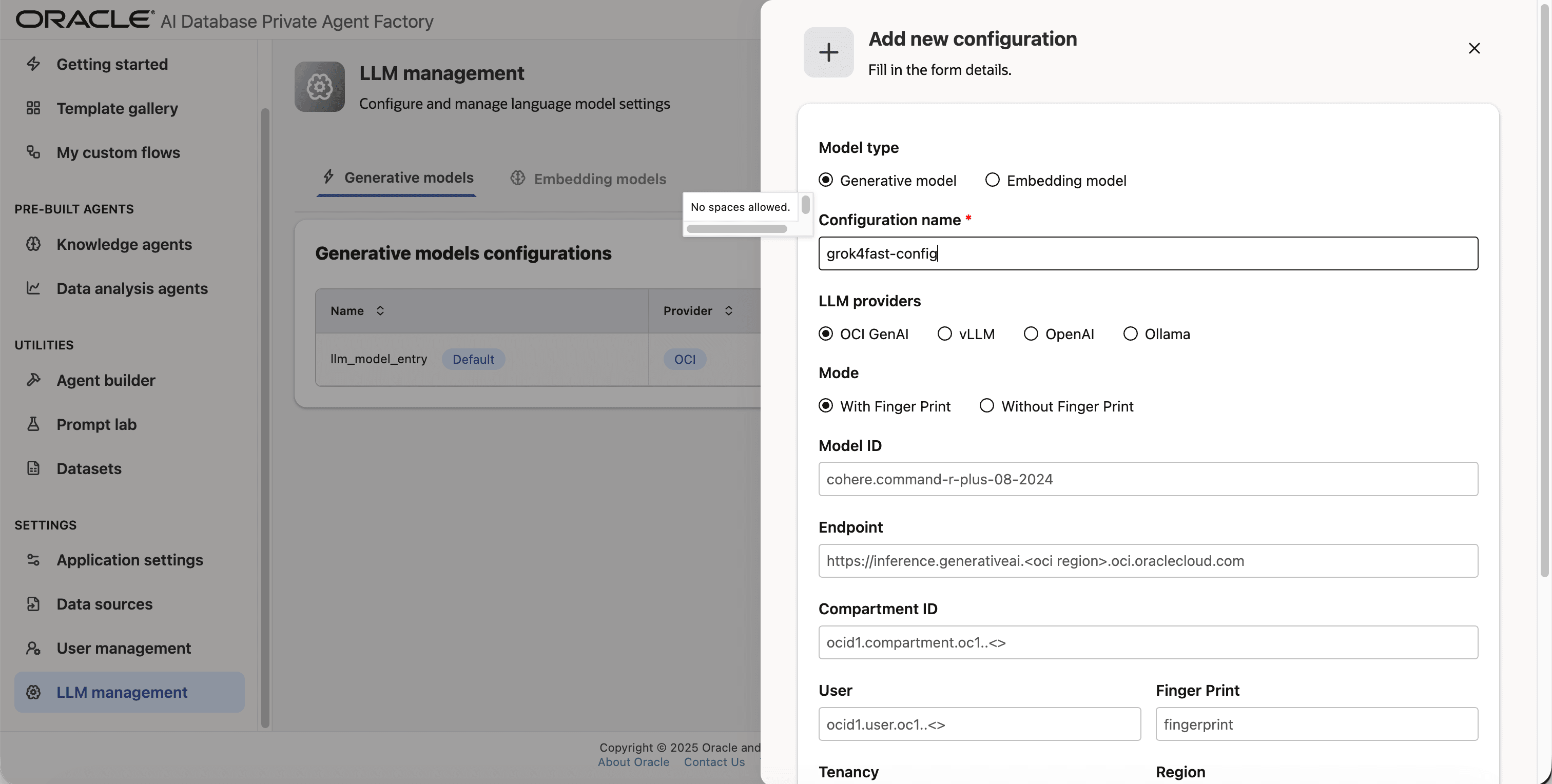
Step 7: On Model ID enter xai.grok-4-fast-reasoning
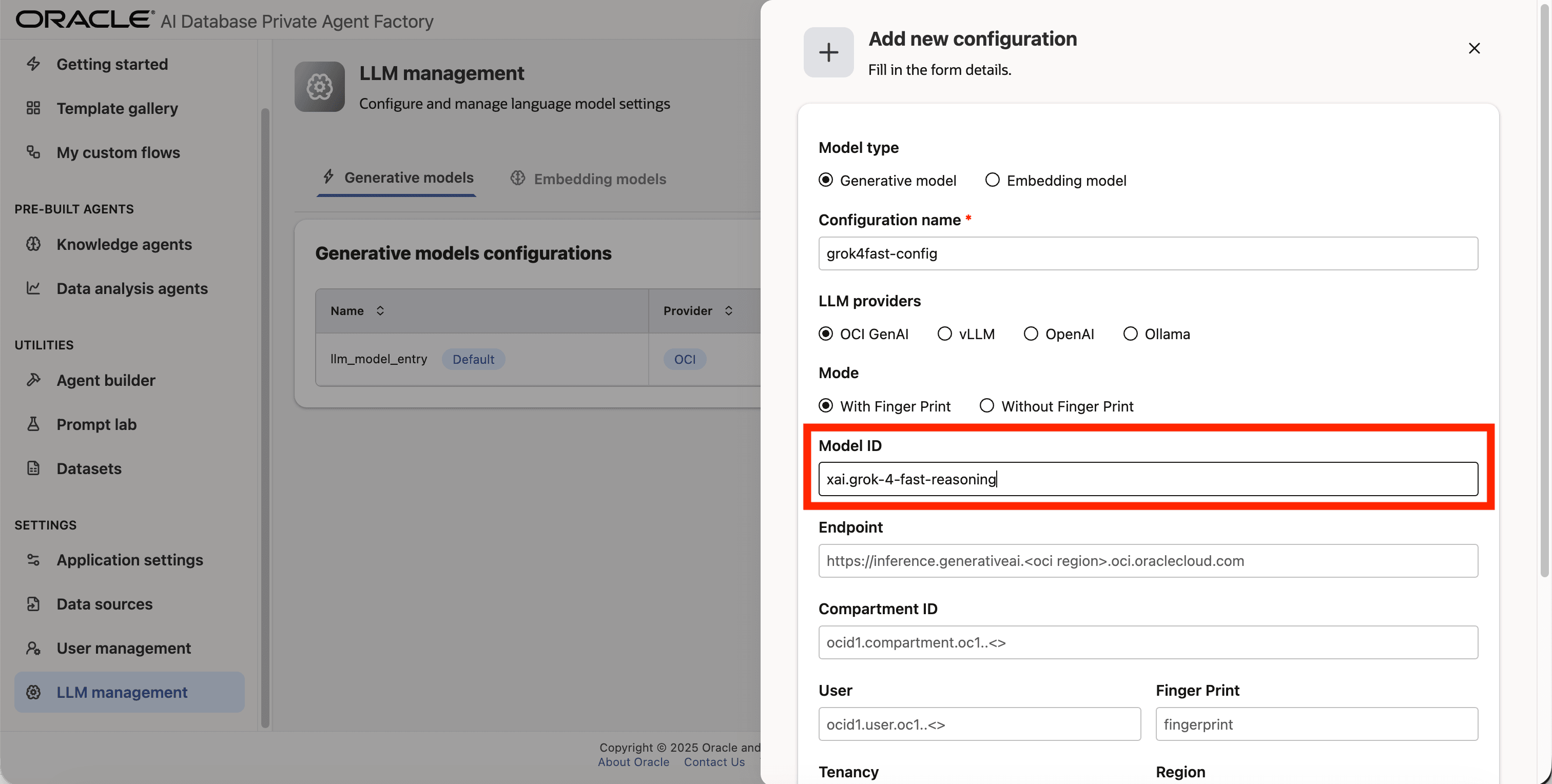
Step 8: Fill Endpoint, Compartment ID, User, Tenancy, Finger Print & Region fields with your own credentials from OCI Generative AI Service.
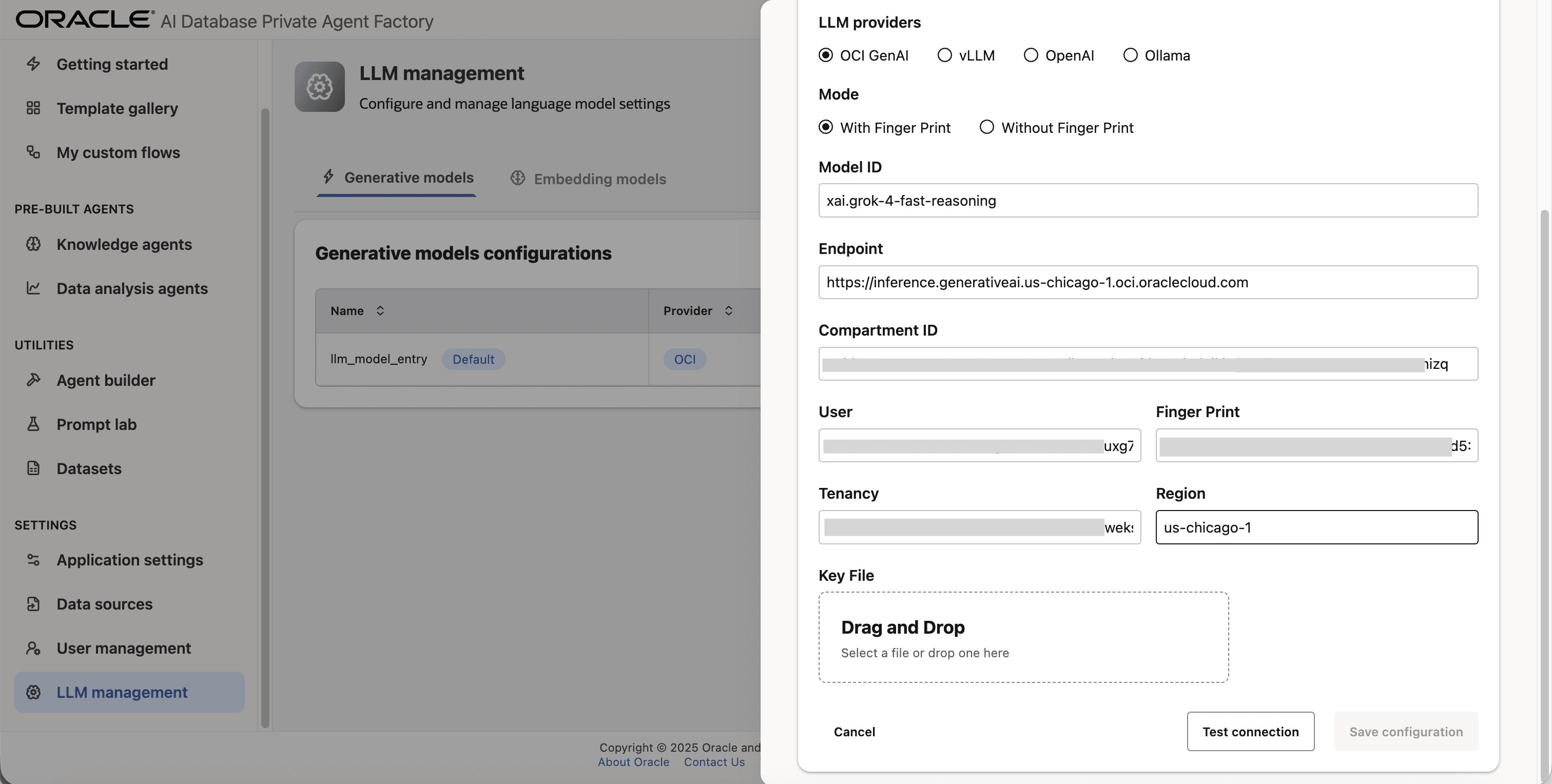
Step 9: Upload your private API key file under Key File. You can request it from your tenancy owner or by logging into your tenancy with your user. See Set Up API Authentication for OCI.
Step 10: Click on Test connection to validate the credentials are correct.
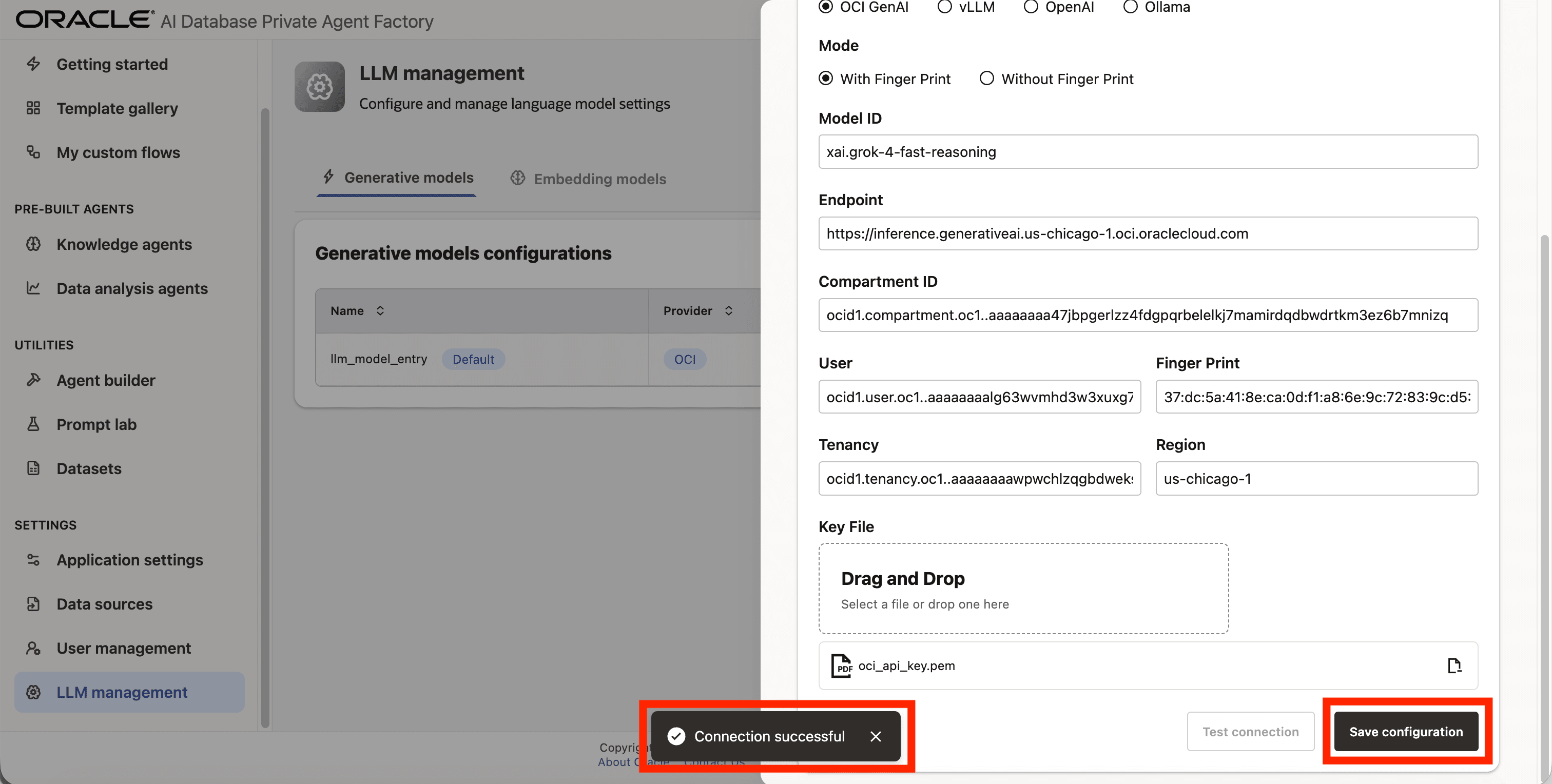
Step 11: A success message Connection successful will appear on screen and the Save Configuration button will be enabled, click on it to finalize the process.
Ollama
Agent Factory has support for Ollama so you can access the LLMs running locally on your machine.
Setup Ollama in Your Machine (Linux OCI VM)
Step 1: Open a terminal window in your system and start a new bash shell with root privileges.
sudo bashStep 2 (Optional): If you are working behind a proxy please set the appropriate proxies.
Step 3: Download and install ollama as instructed by the official site.
Step 4: Pull the llama3.2 model to your local machine.
ollama pull llama3.2Step 5: Edit the ollama service so Agent Factory’s container can access to it.
systemctl edit ollamaStep 6: Once the editor opens, paste the below two lines and close by using Ctrl + O, Enter, Ctrl + X
[Service]
Environment="OLLAMA_HOST=0.0.0.0:11434"Step 7: Refresh systemd and restart ollama so the changes are visible.
systemctl daemon-reexecsystemctl daemon-reloadsystemctl restart ollamaStep 8 (Optional): In a separate terminal verify ollama service is running by running the following command:
ollama run llama3.2Adding Ollama Model to Agent Factory
Below are the steps to configure the locally hosted Llama 3.2 model from Ollama that was set up in the previous section.
Step 1: Click LLM management on the left side navigation menu.

Step 2: Click Add configuration button placed on the top-right corner.

Step 3: A form will open, under Model type choose Generative model.

Step 4: Give your LLM configuration a preferred name under Configuration name, avoid whitespaces since they are not allowed.
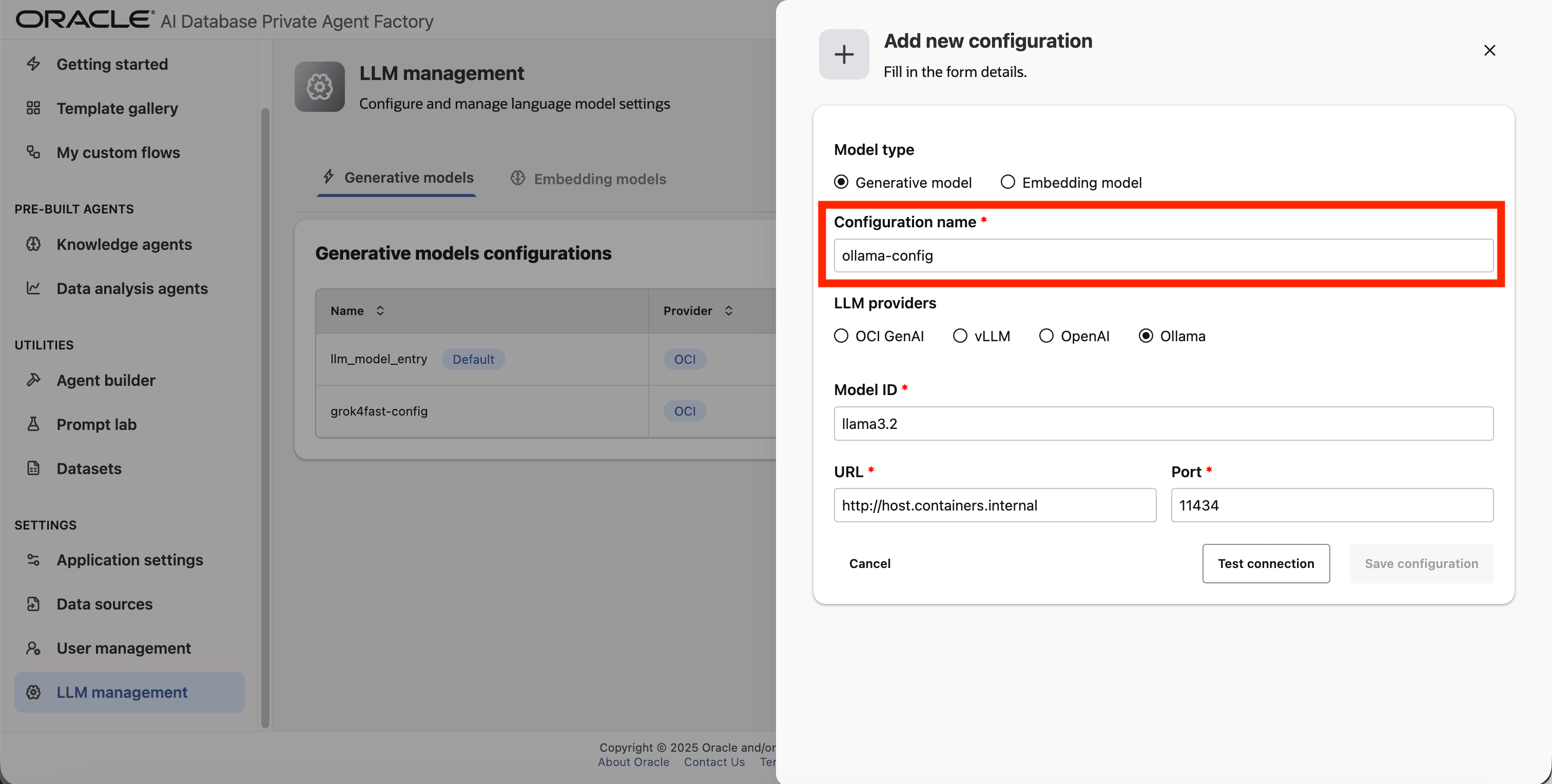
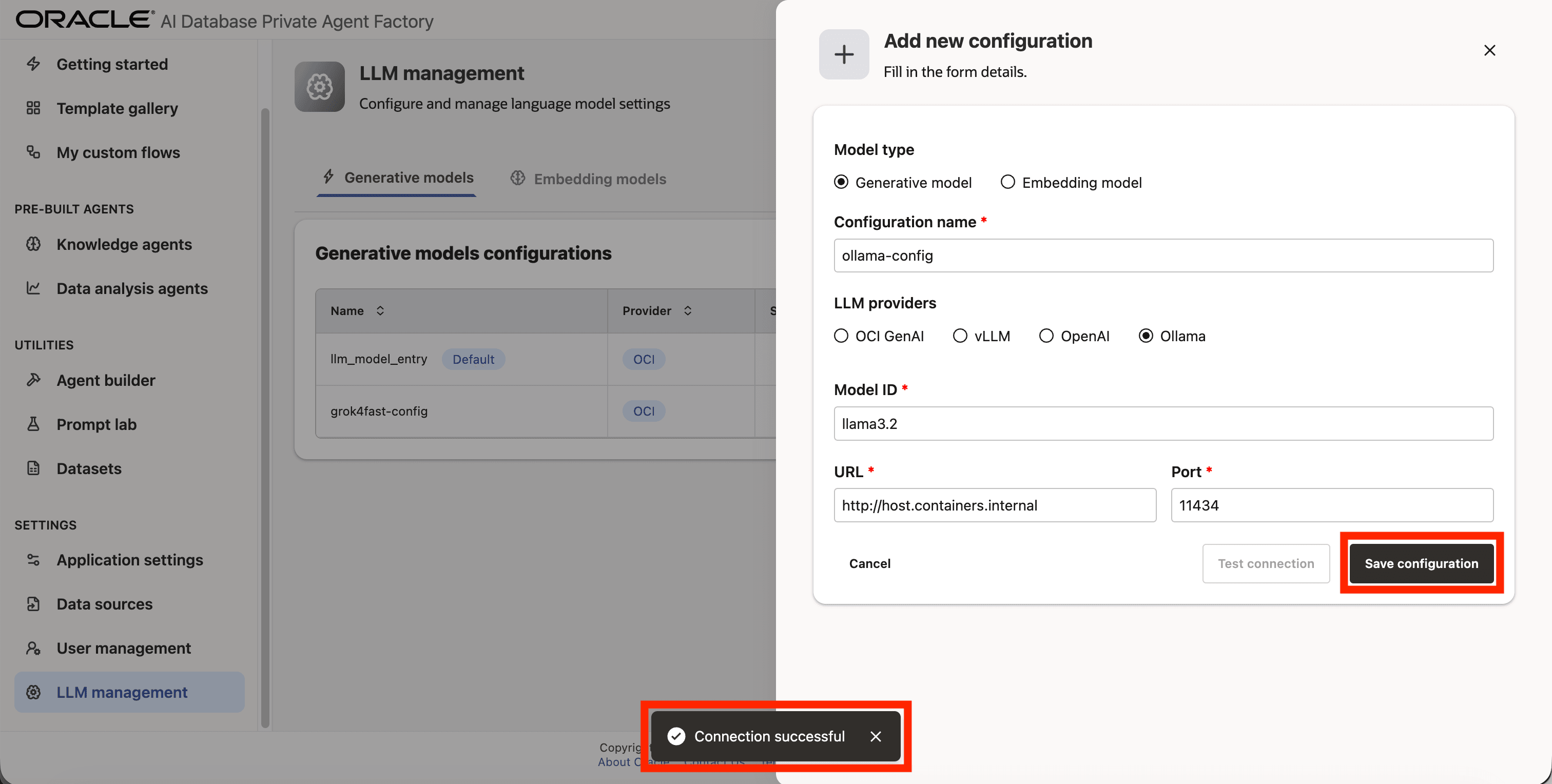
Step 5: From list of LLM providers pick Ollama.
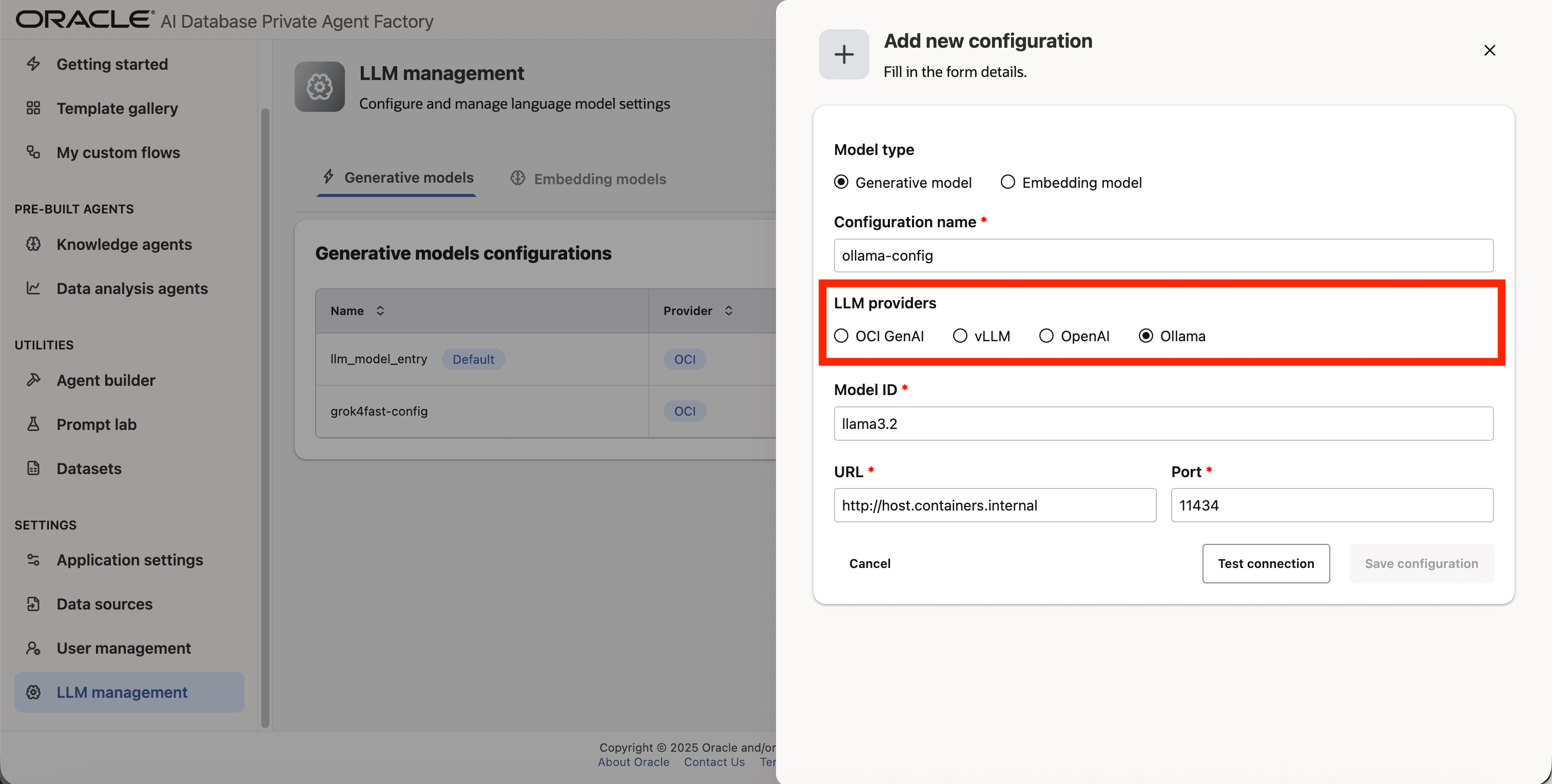
Step 6: Enter llama3.2 as Model ID.
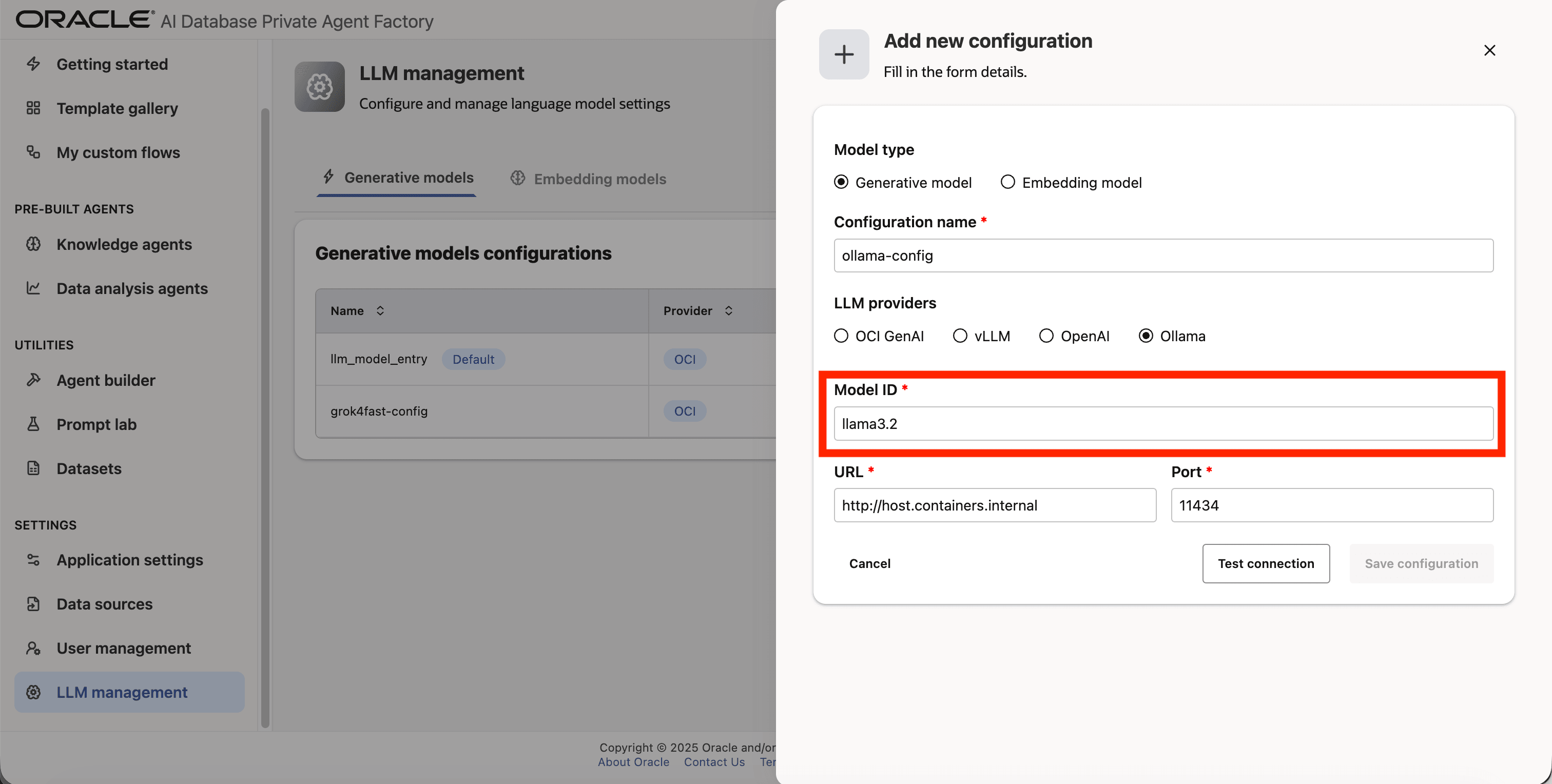
Step 7: Enter http://host.containers.internal as URL.
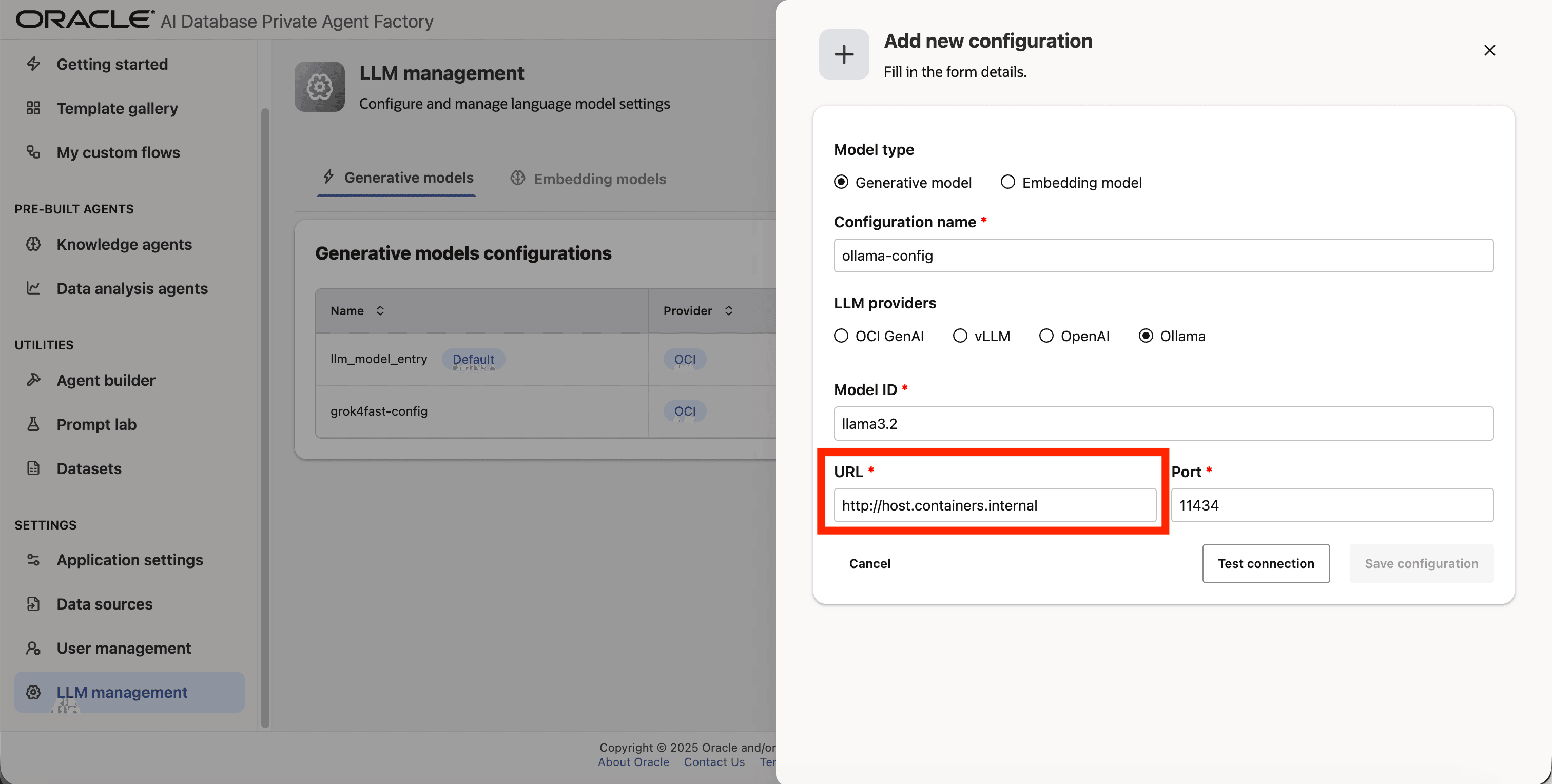
Step 8: Enter 11434 as Port.
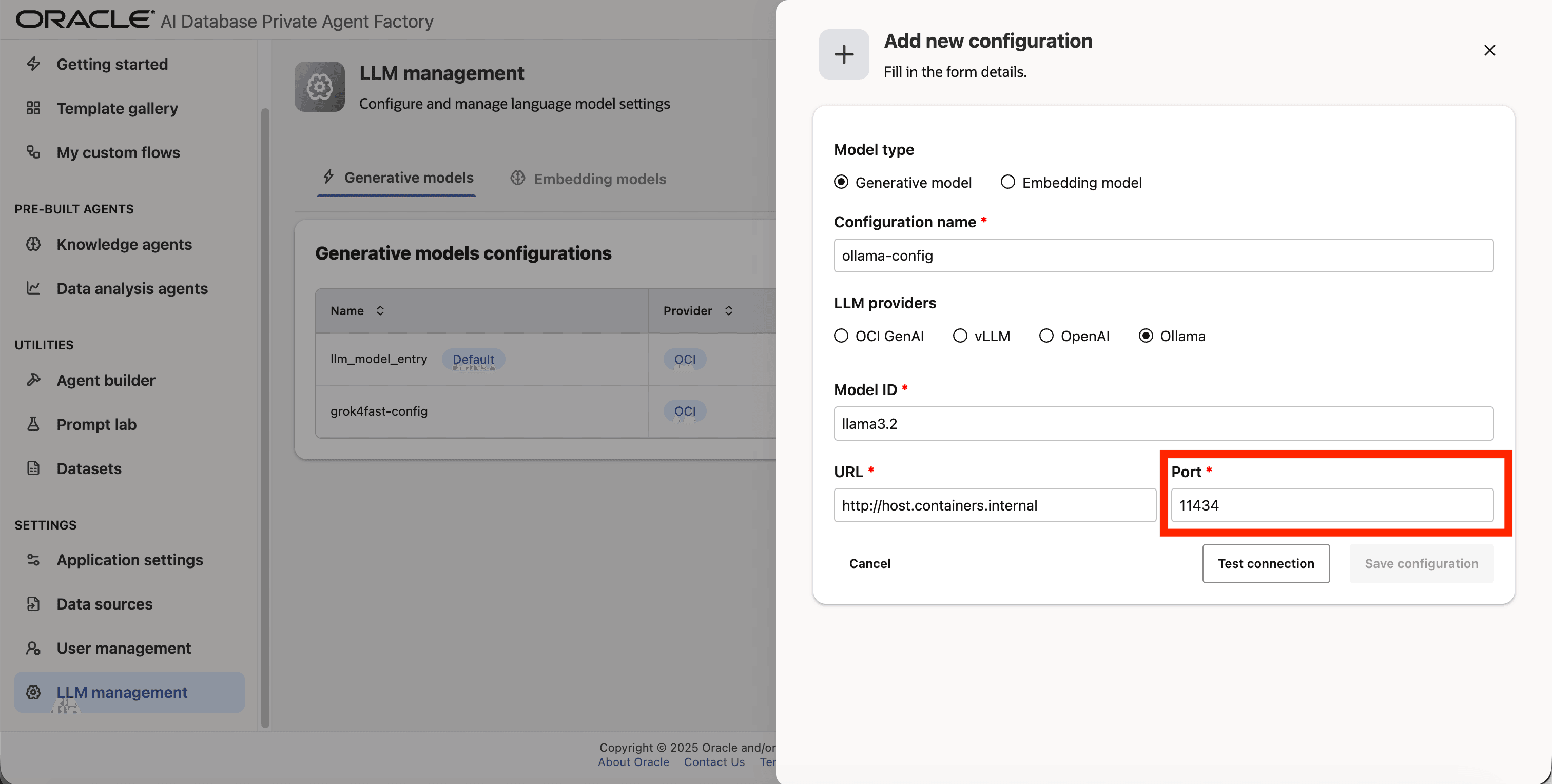
Step 9: Click on Test connection to validate the credentials are correct.
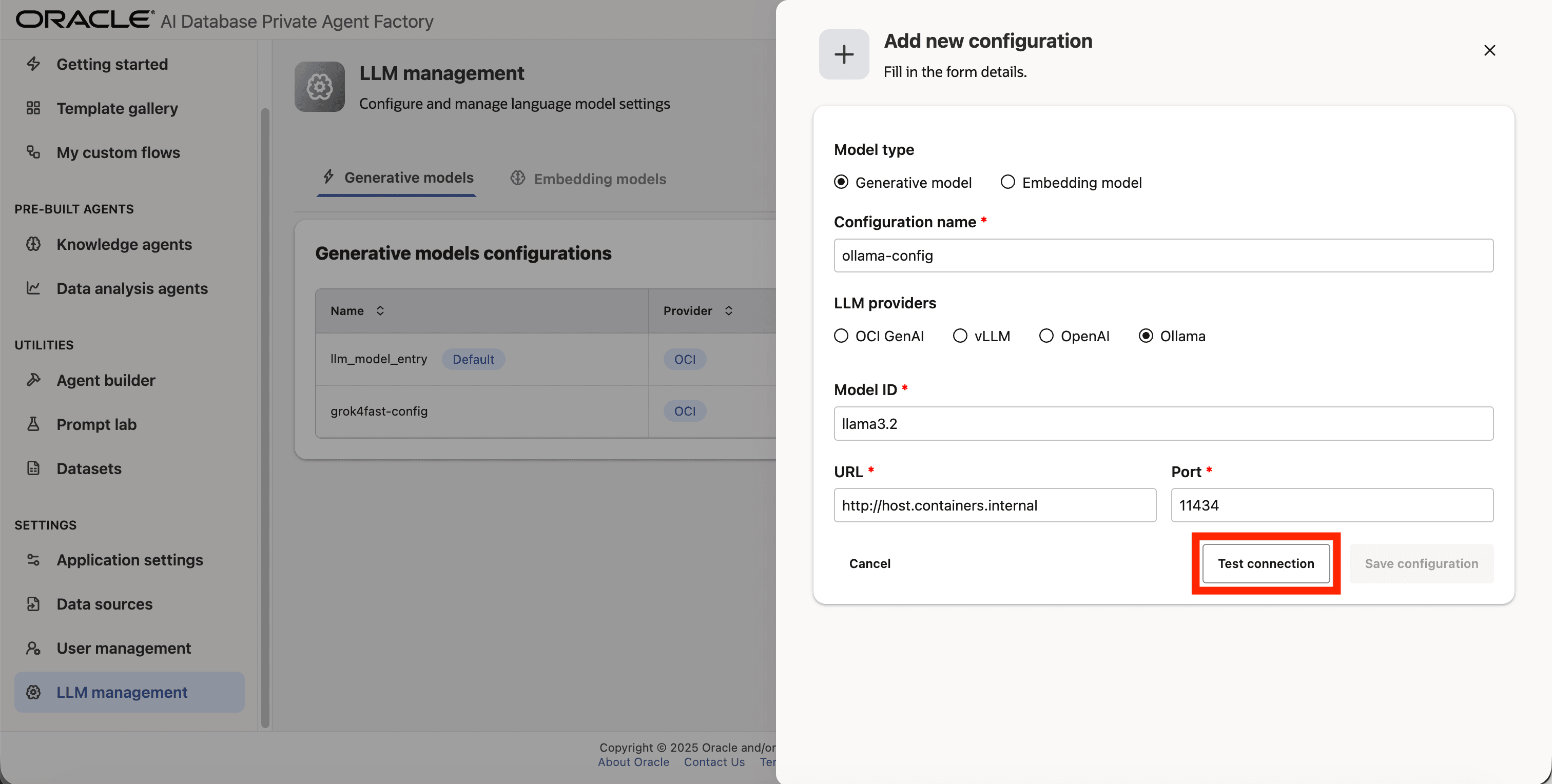
Step 10: A success message “Connection successful” will appear on screen and the Save Configuration button will be enabled, click on it to finalize the process.
OpenAI
The following models are currently supported:
gpt-4ogpt-4o-mini
Adding OpenAI Model to Agent Factory
Step 1: Click on LLM management on the left side navigation menu.

Step 2: Click on Add configuration button placed on the top-right corner.

Step 3: A form will open, under Model type pick Generative model.

Step 4: Give your LLM configuration a preferred name under Configuration name, avoid whitespaces since they are not allowed.
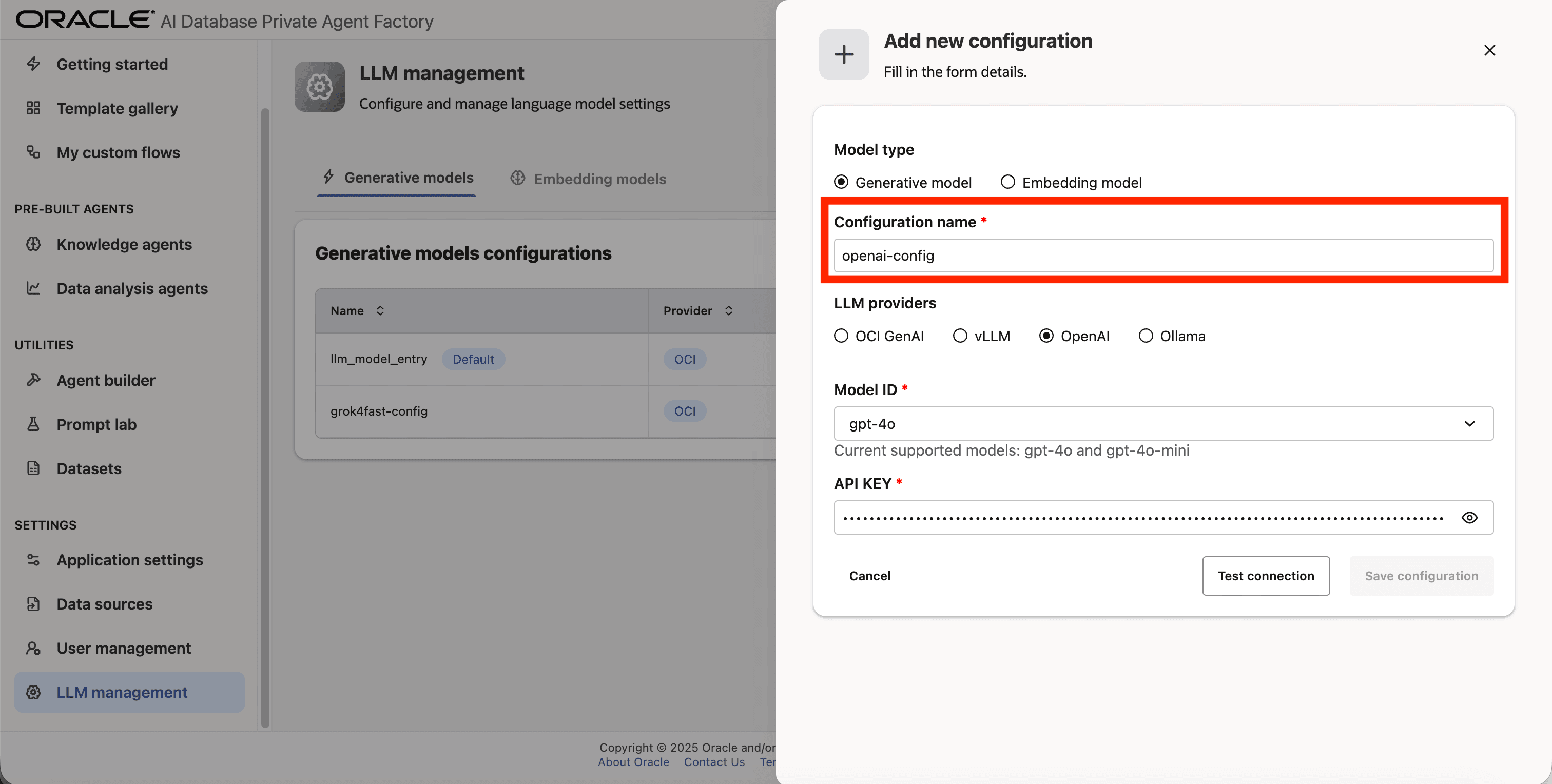
Step 5: From the list of LLM providers pick OpenAI.
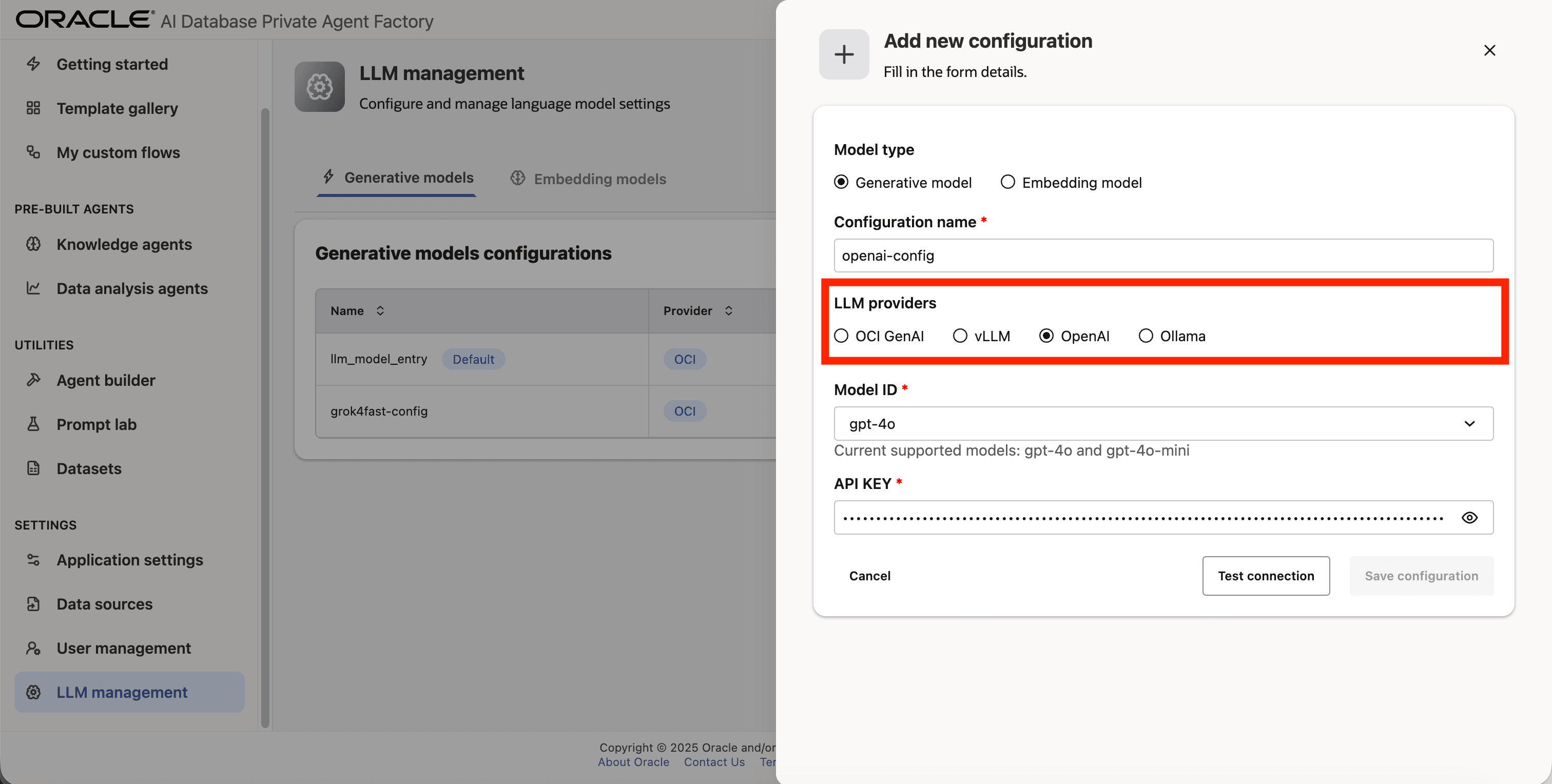
Step 6: Select gpt-4o as the Model ID
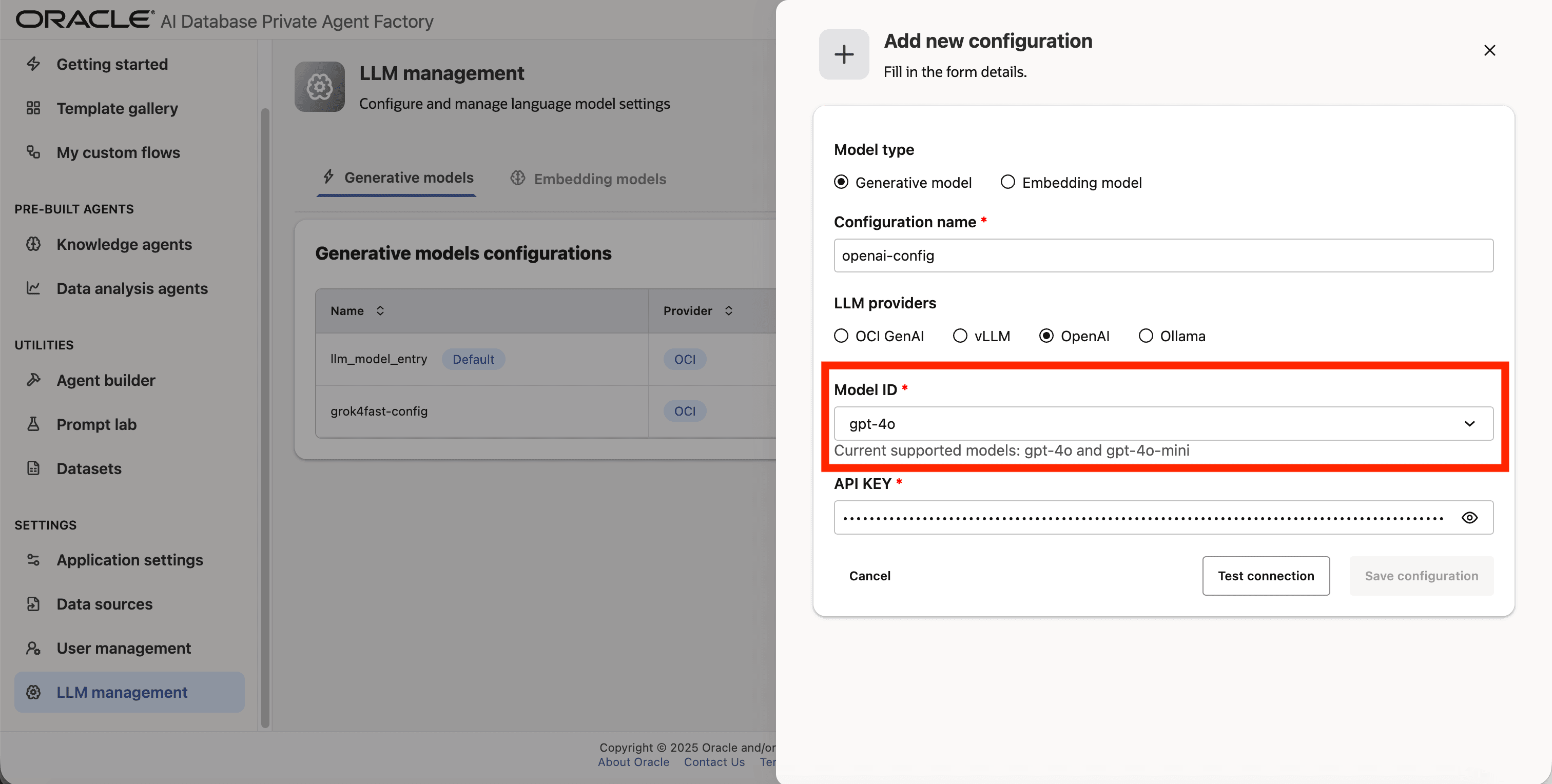
Step 7: Enter your API Key
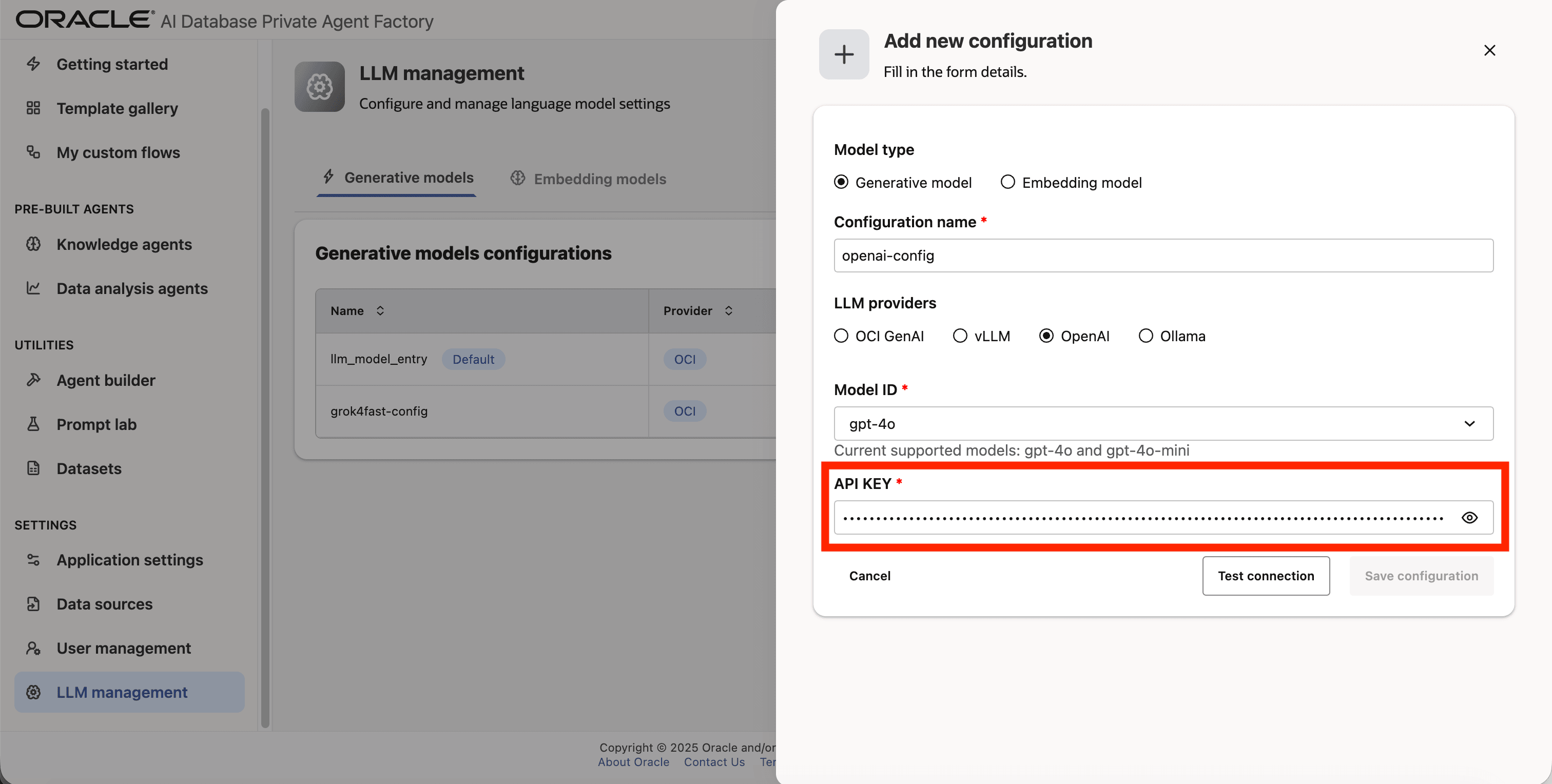
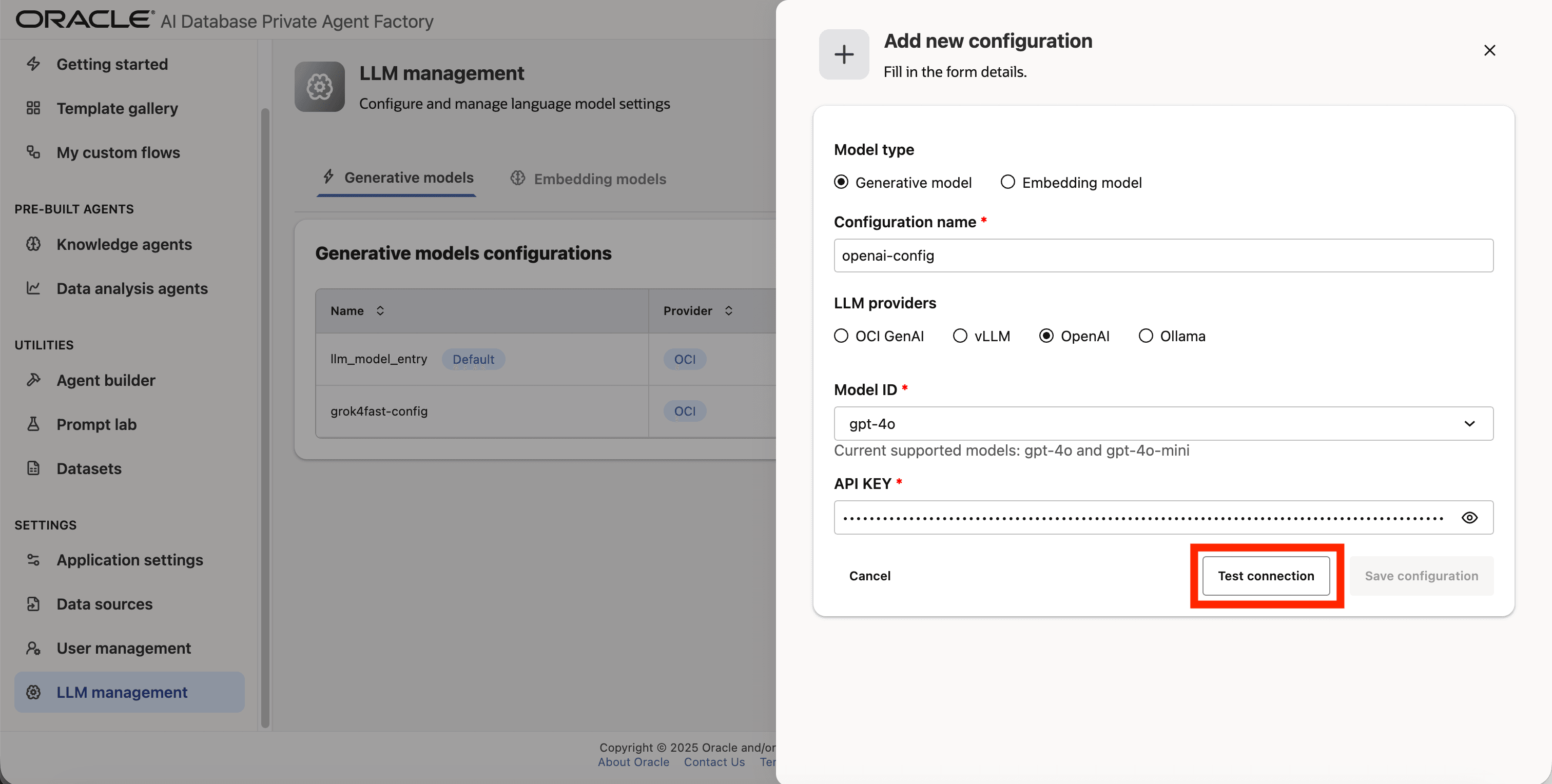
Step 8: Click on Test connection to validate the credentials are correct.
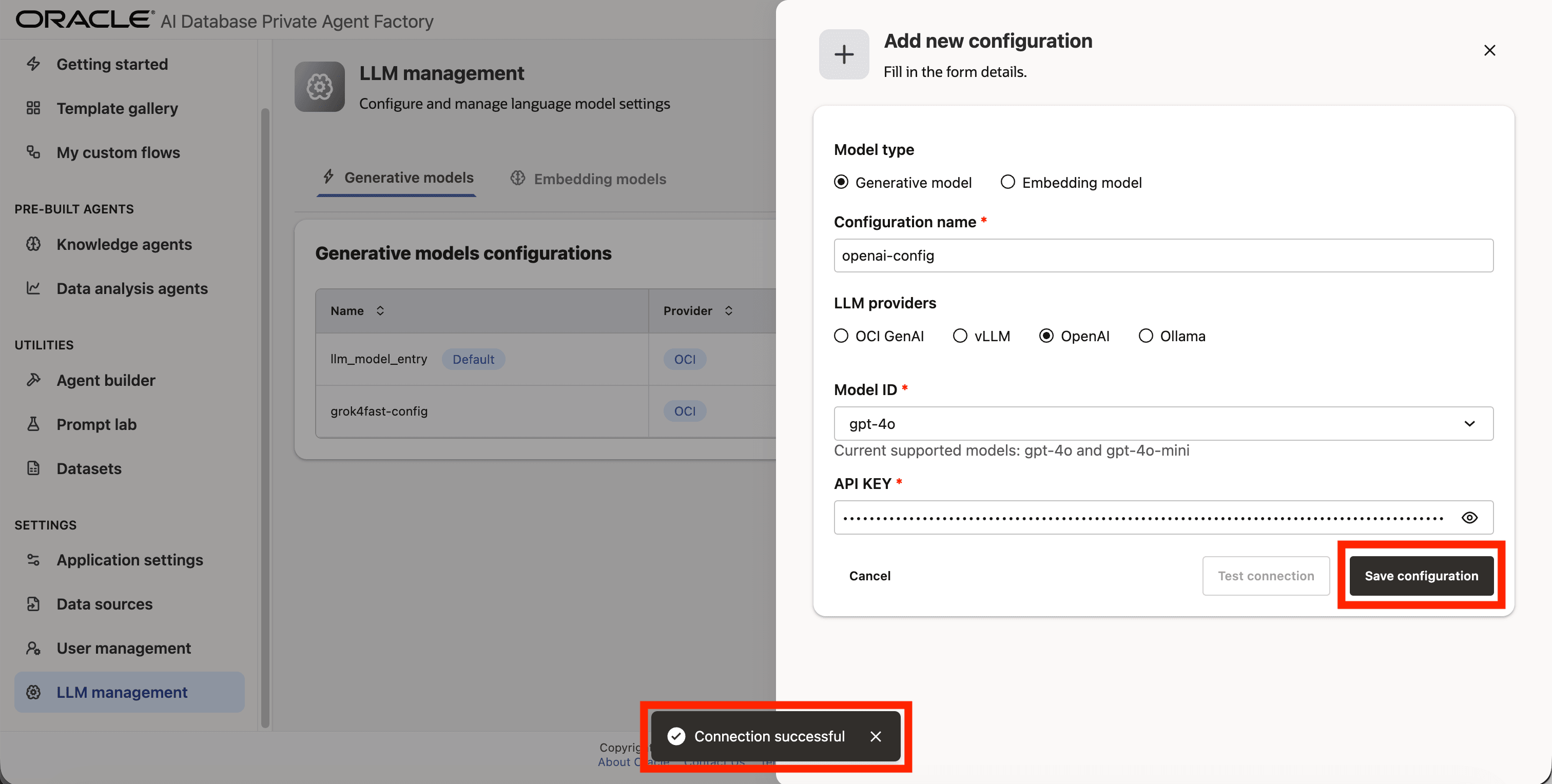
Step 9: A success message “Connection successful” will appear on screen and the Save Configuration button will be enabled, click on it to finalize the process.
vLLM
You can connect to any self-hosted model endpoint.
These are the required fields you need to configure a vLLM:
- Model ID: The model identifier/path that the vLLM server is serving (often a filesystem path or a registry-style name).
- URL: Host/DNS clients use to reach the server.
- Port: The port where the HTTP service is exposed.
Embedding Models
Agent Factory supports the following embedding models. Use these models for transforming text into numerical vectors, enabling semantic search, and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG). Agent Factory include out-of-the-box support for several high-performing embedding models, while also allowing you to bring your preferred models hosted on the OCI Generative AI service, or served via Ollama or vLLM endpoints.
Local Models
The following pre-trained sentence transformer model is bundled with the application and run locally.
multilingual-e5-base(768 dimensions)
Configure a Local Embedding Model
Below are the steps to configure a local embedding model multilingual-e5-base, which is available in Agent Factory out of the box.
Note: If you plan to use local embedding models, ensure the machine running the application has access to GPUs. Otherwise, embedding-related processes—such as Knowledge Agent ingestion—may take a significant amount of time.
Step 1: Click on LLM management on the left side navigation menu.

Step 2: Click on Add configuration button placed on the top-right corner.

Step 3: A form will open, under Model type choose Embedding model.
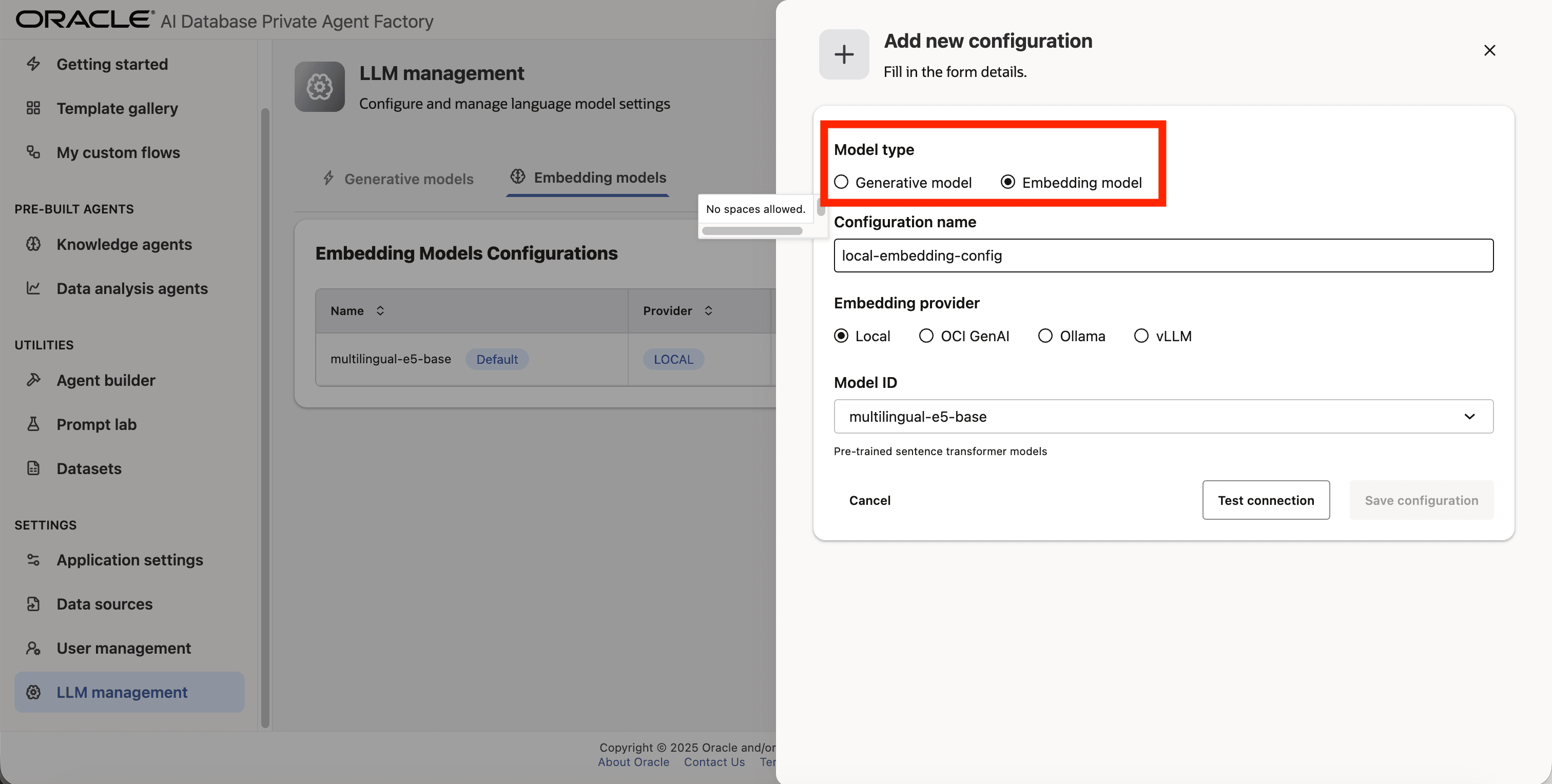
Step 4: Give your configuration a name, avoid using whitespaces since they are not allowed.
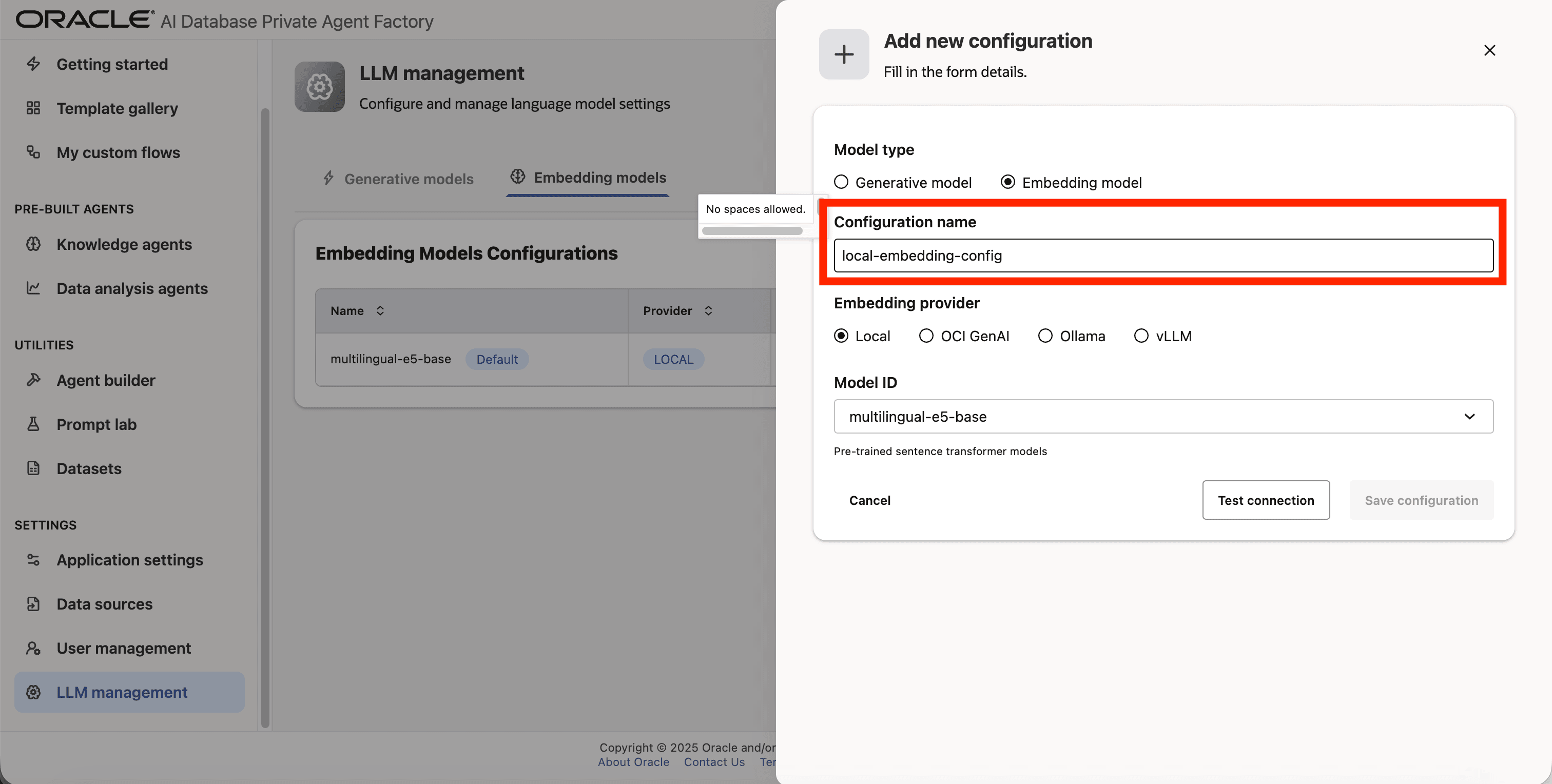
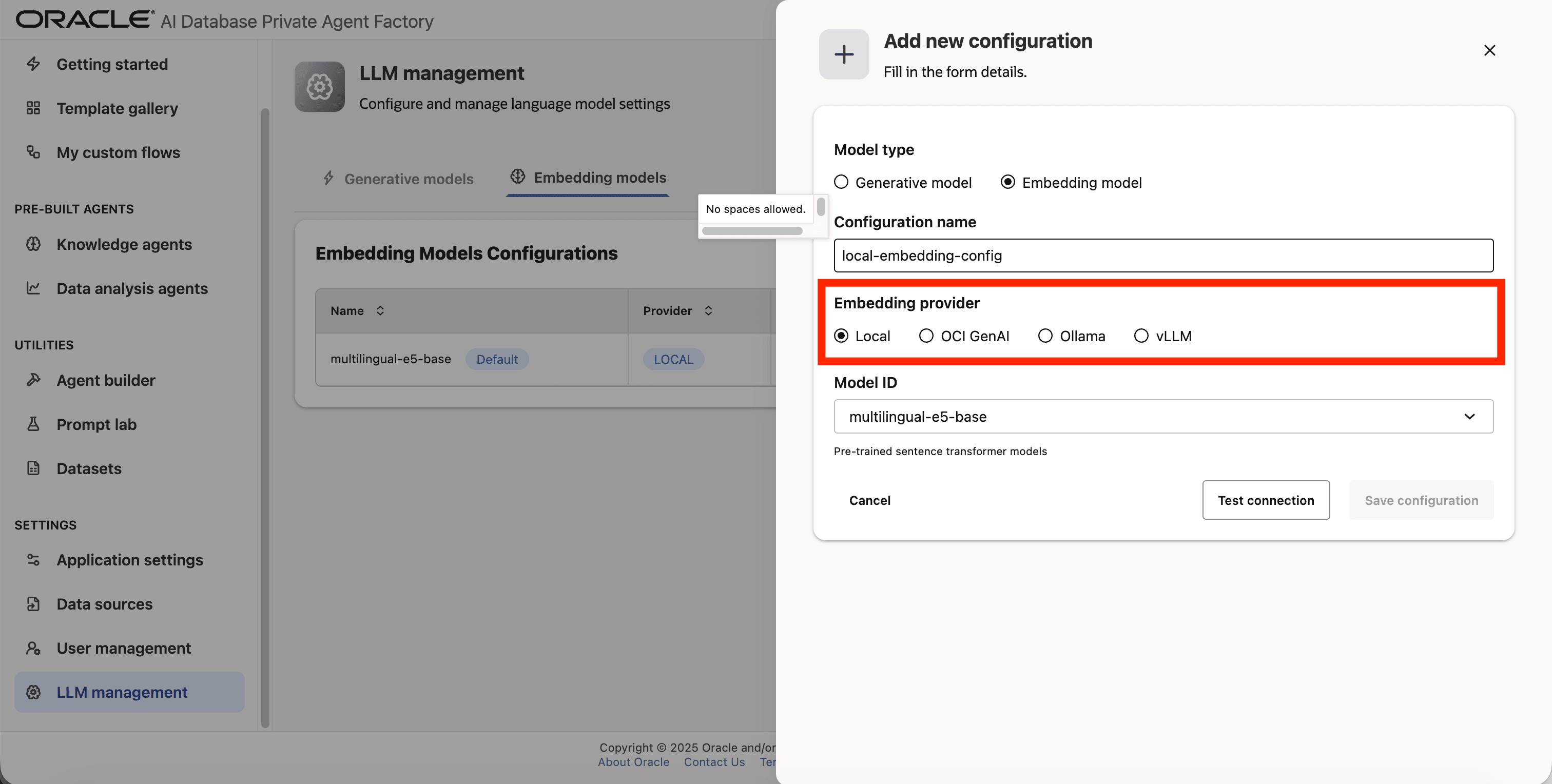
Step 5: For Embedding provider pick Local.
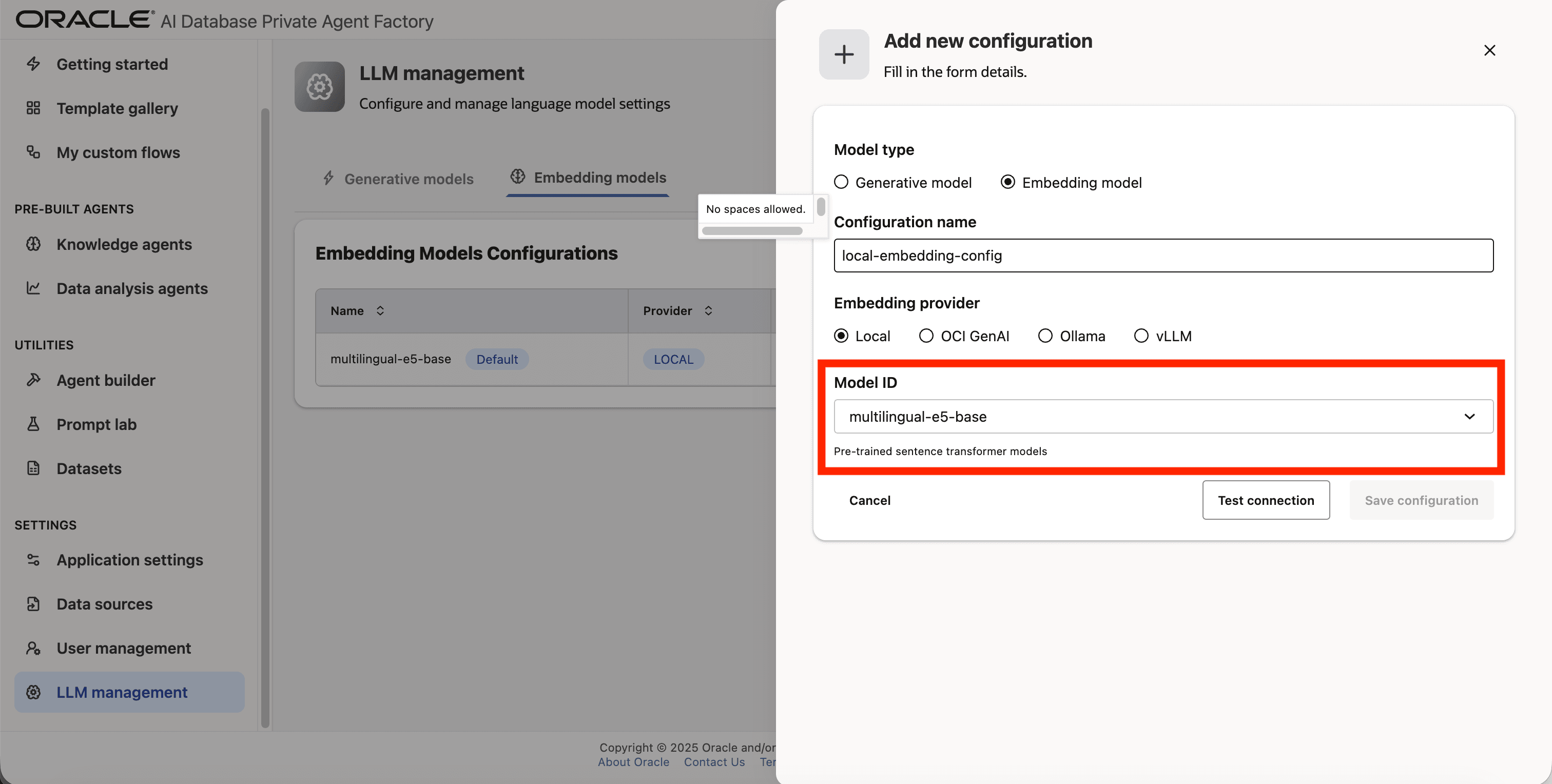
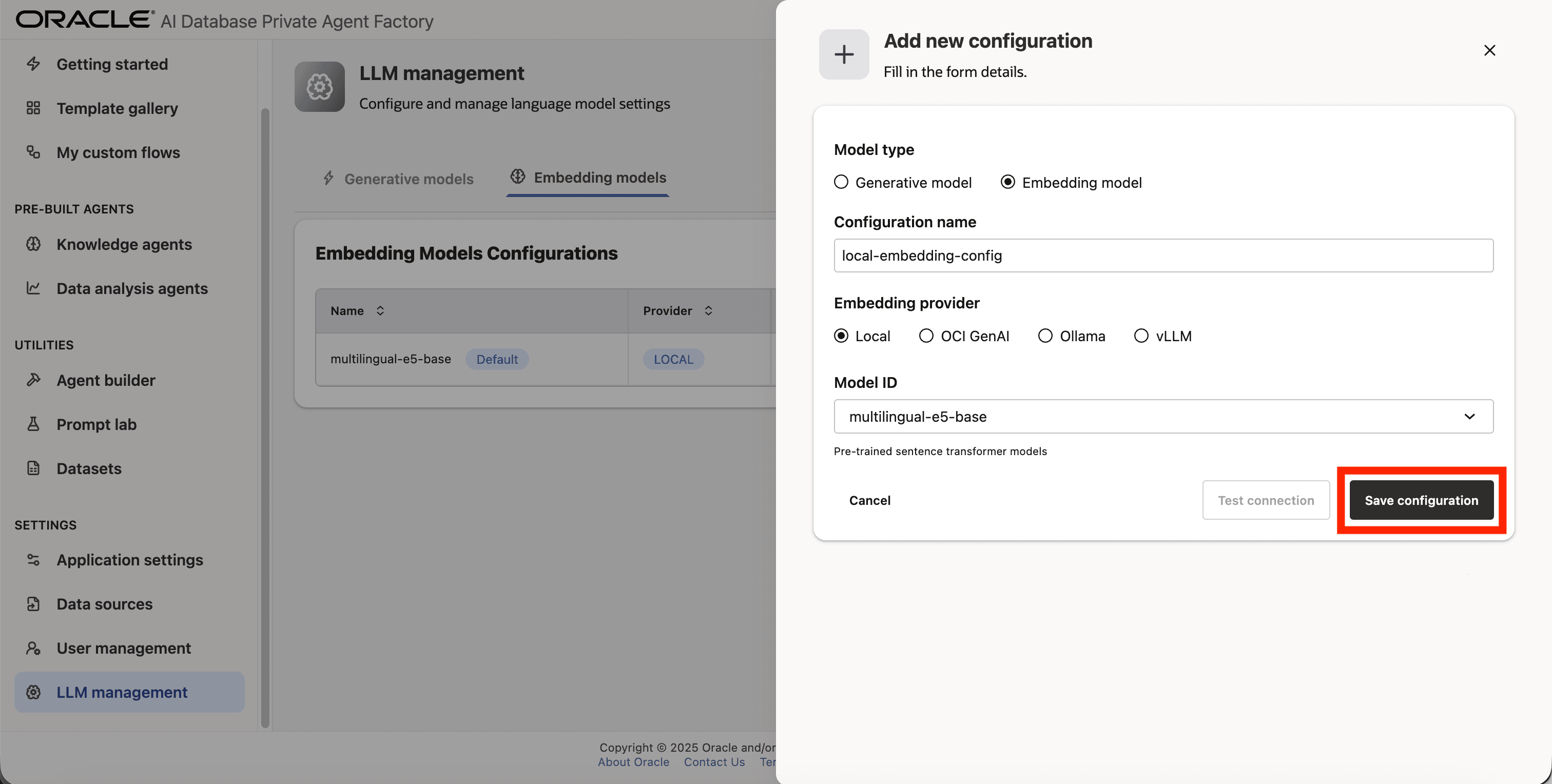
Step 6: Click on Model ID and pick multilingual-e5-base from the list.
Step 7: Verify the connection by clicking on Test connection.
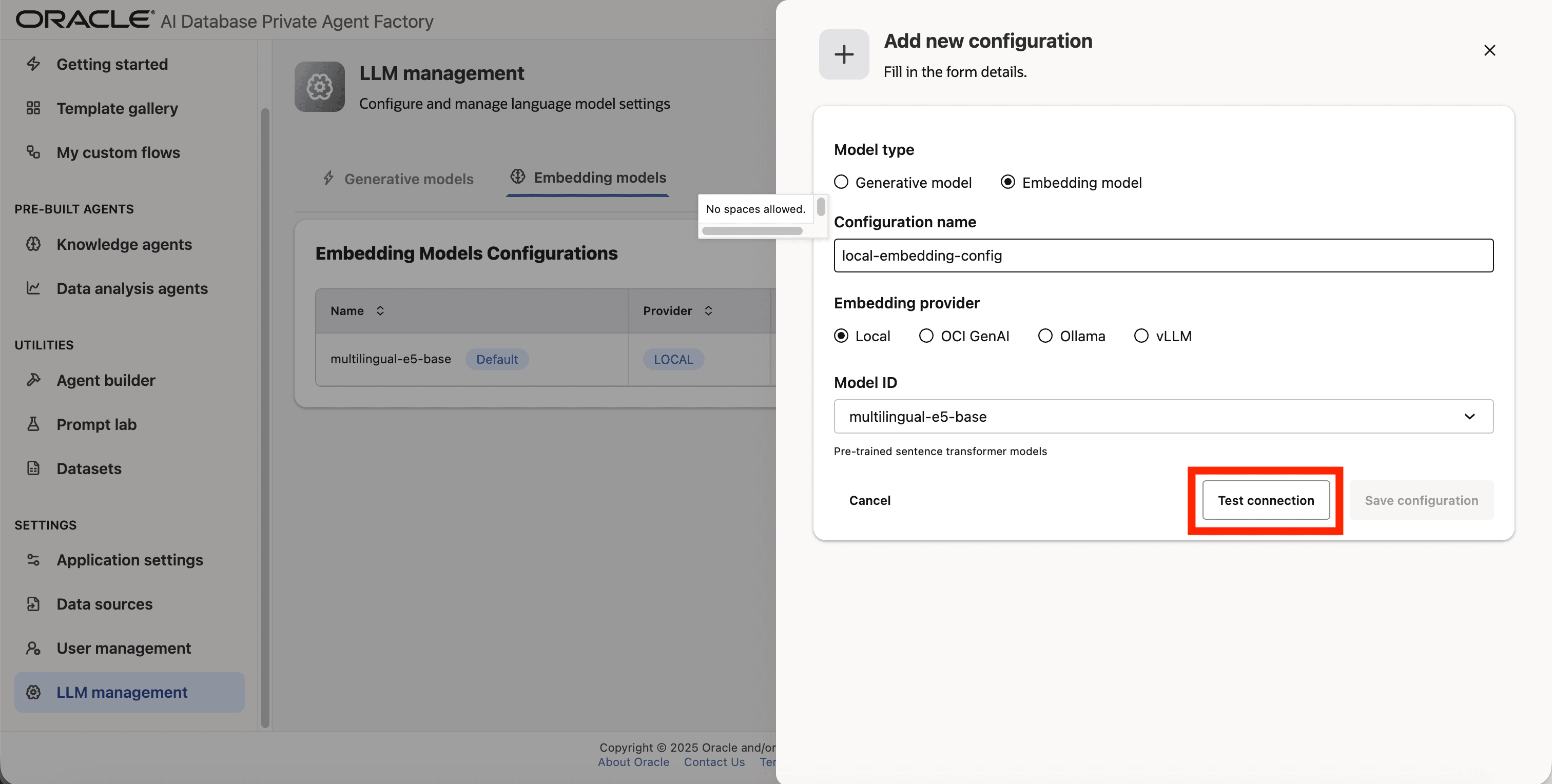
Step 8: Save the new configuration.
OCI Generative AI
The following Cohere embedding models from OCI Gen AI are supported:
cohere.embed-v4.0cohere.embed-multilingual-v3.0cohere.embed-multilingual-light-v3.0cohere.embed-english-v3.0
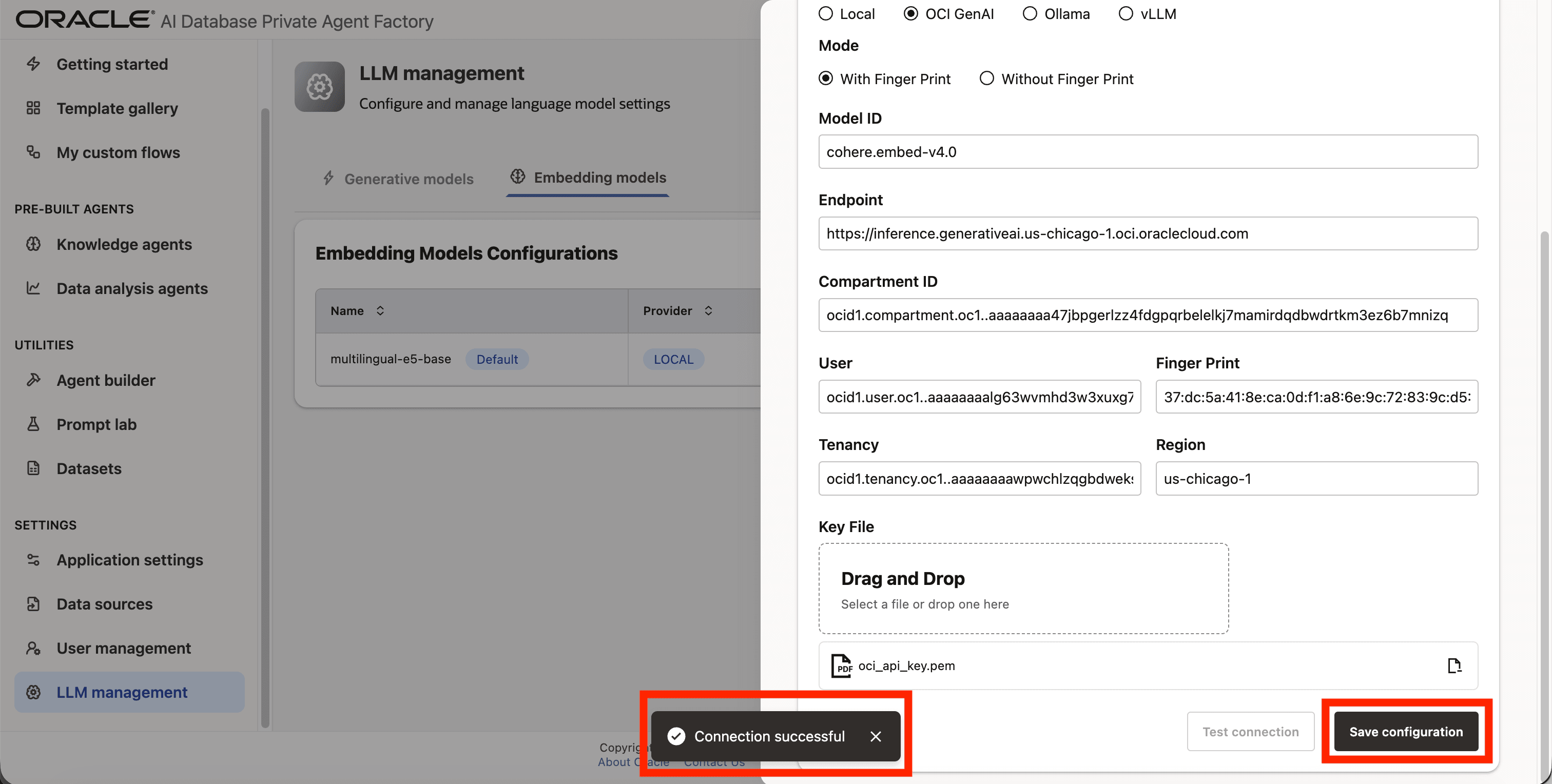
Configure an OCI Generative AI embedding model
Below are the steps to configure a local embedding model cohere.embed-v4.0 which is available through OCI Generative AI service using a Fingerprint based authentication.
Step 1: Click on LLM management on the left side navigation menu.

Step 2: Click on Add configuration button placed on the top-right corner.

Step 3: A form will open, under Model type pick Embedding model.
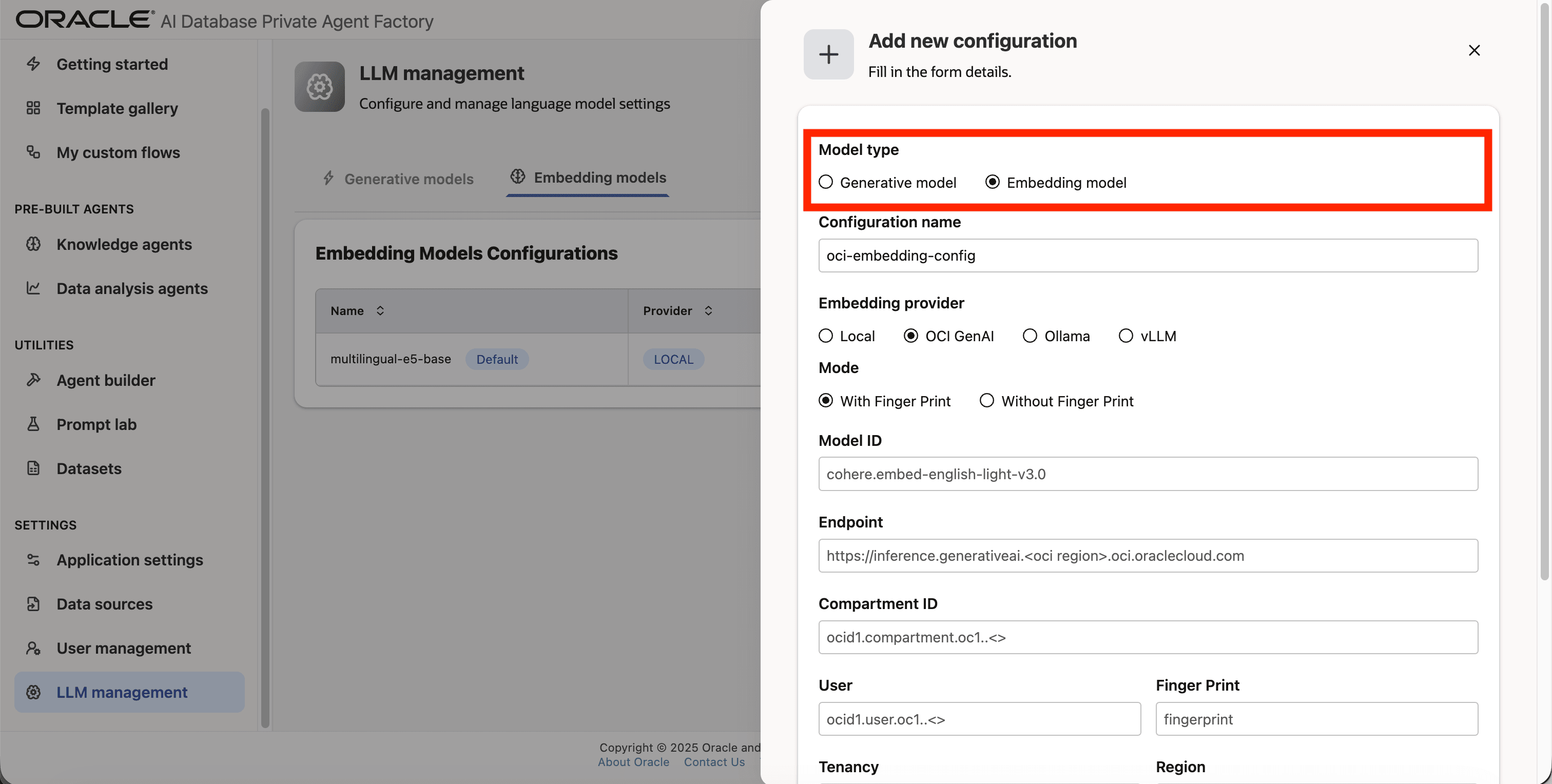
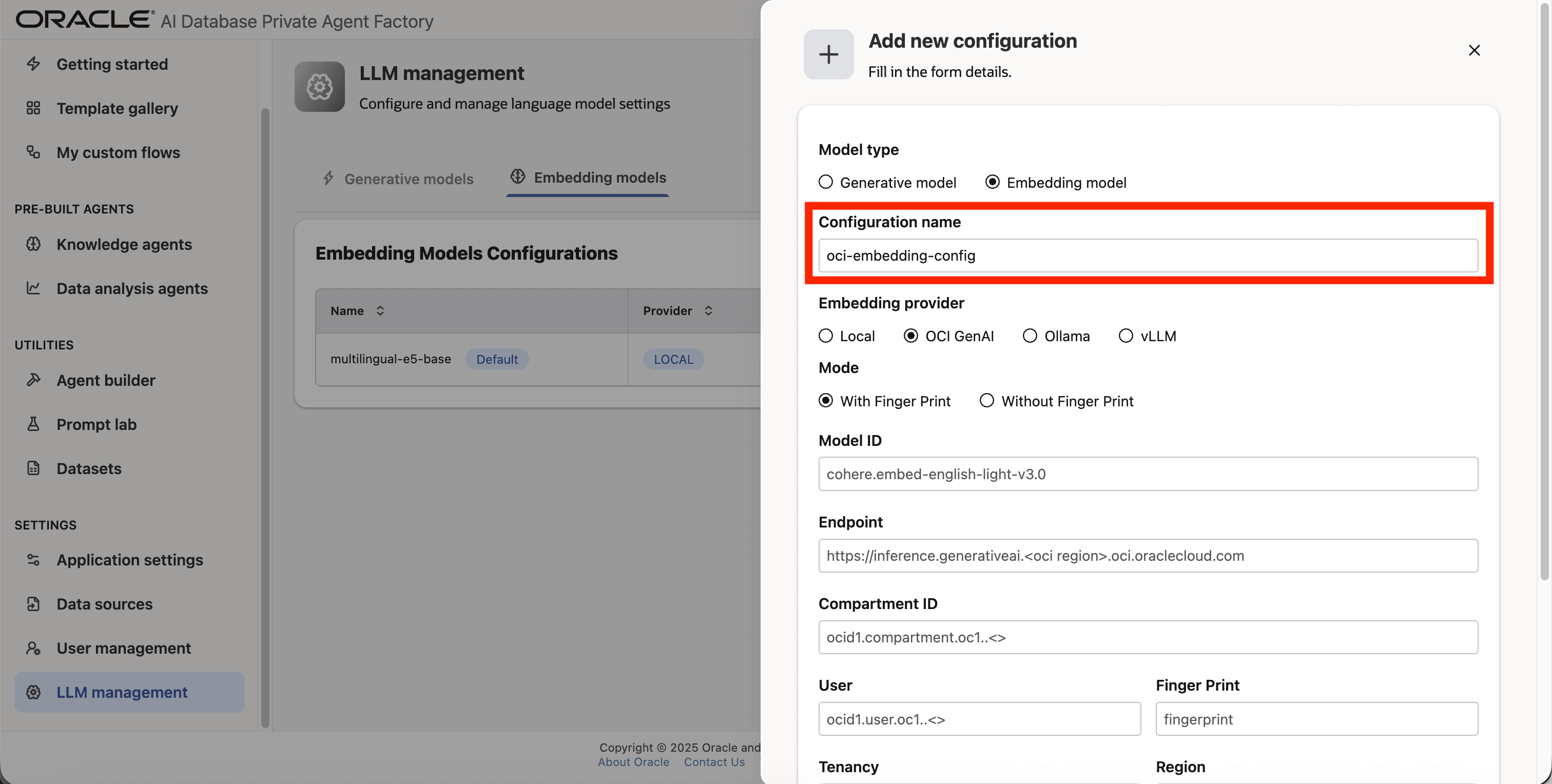
Step 4: Give your configuration a name, avoid using whitespaces since they are not allowed.
Step 5: Pick OCI GenAI as Embedding provider.
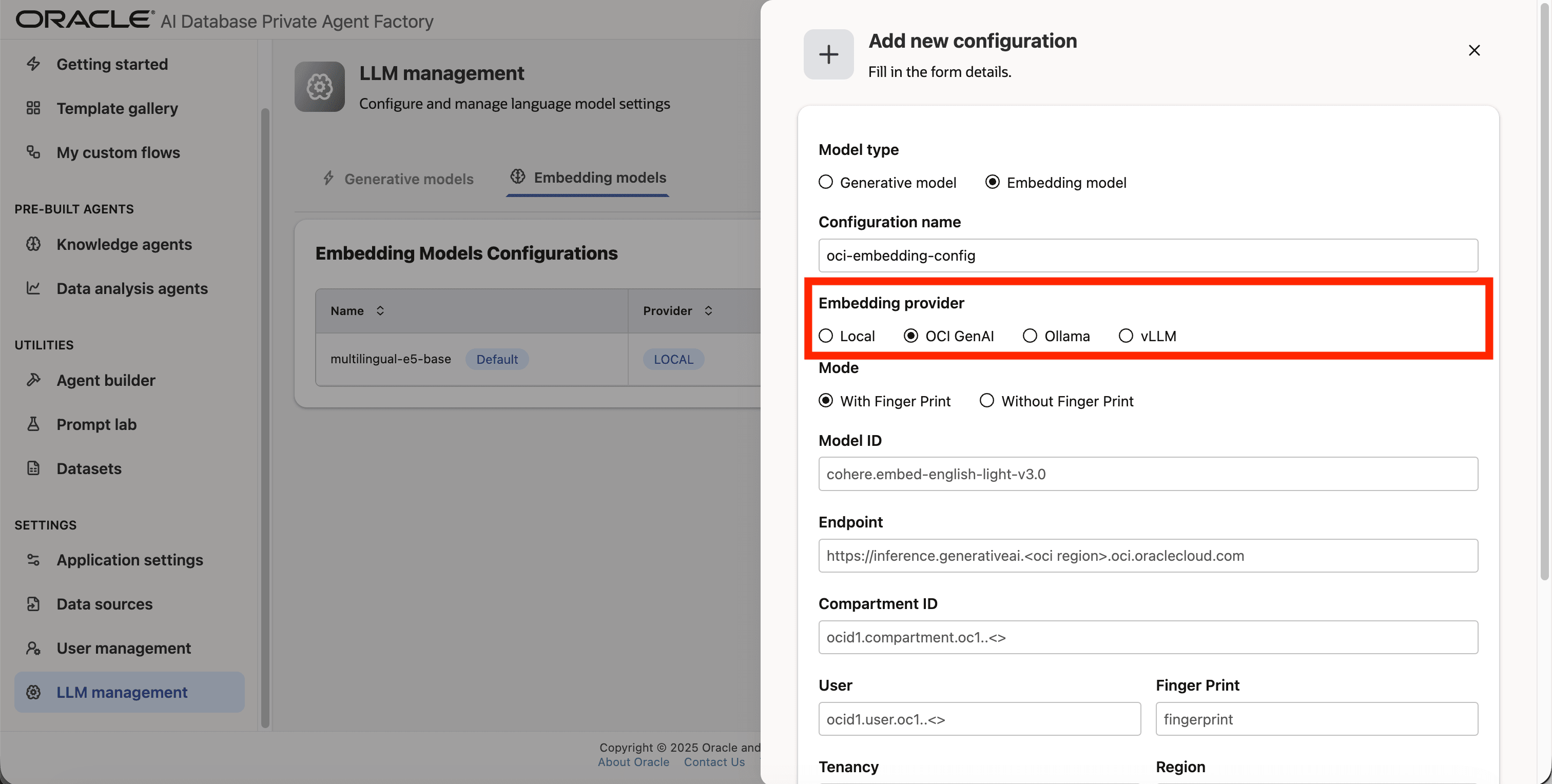
Step 6: For Mode choose With Finger Print
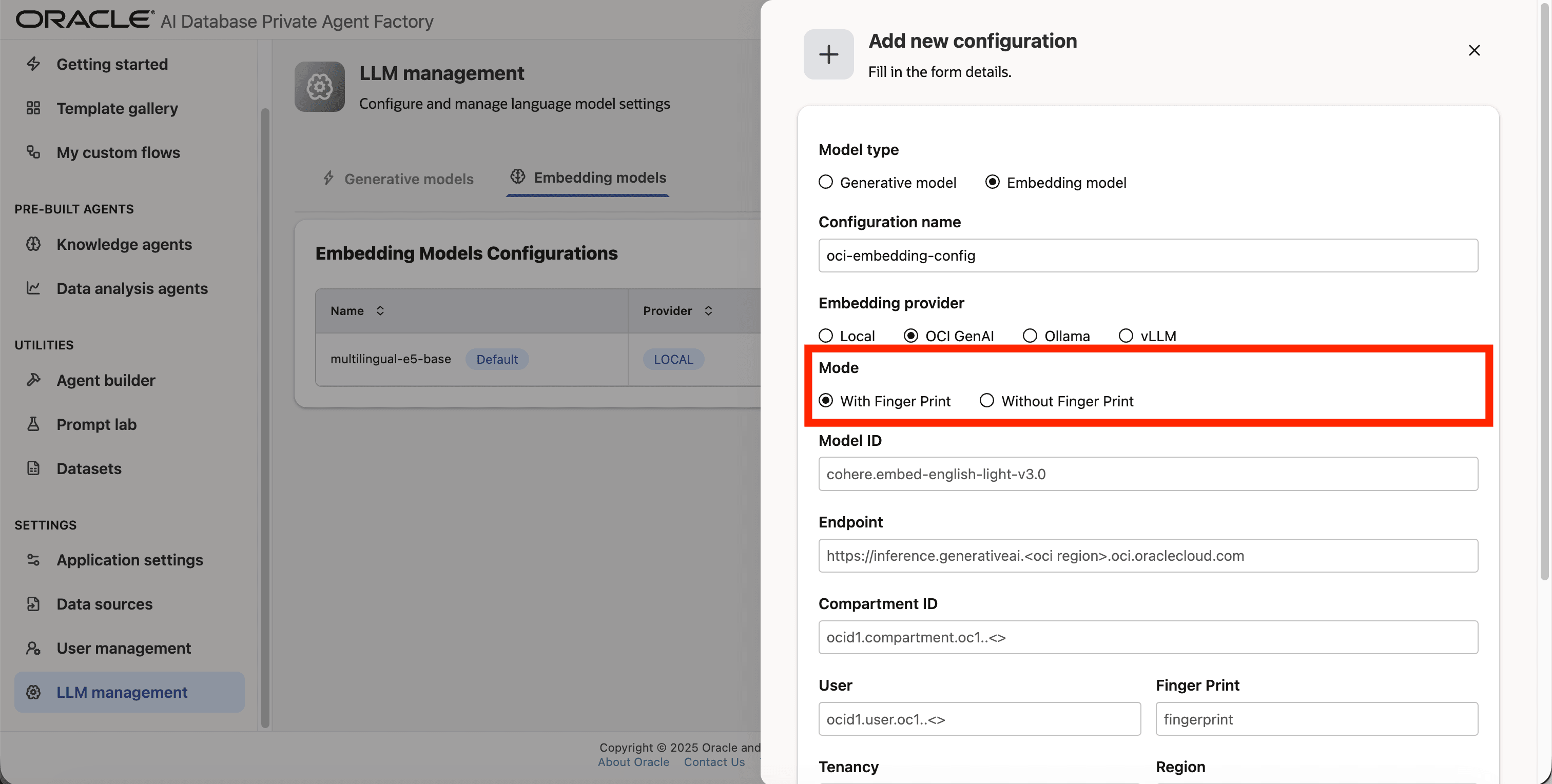
Step 7: Enter cohere.embed-v4.0 as Model ID.
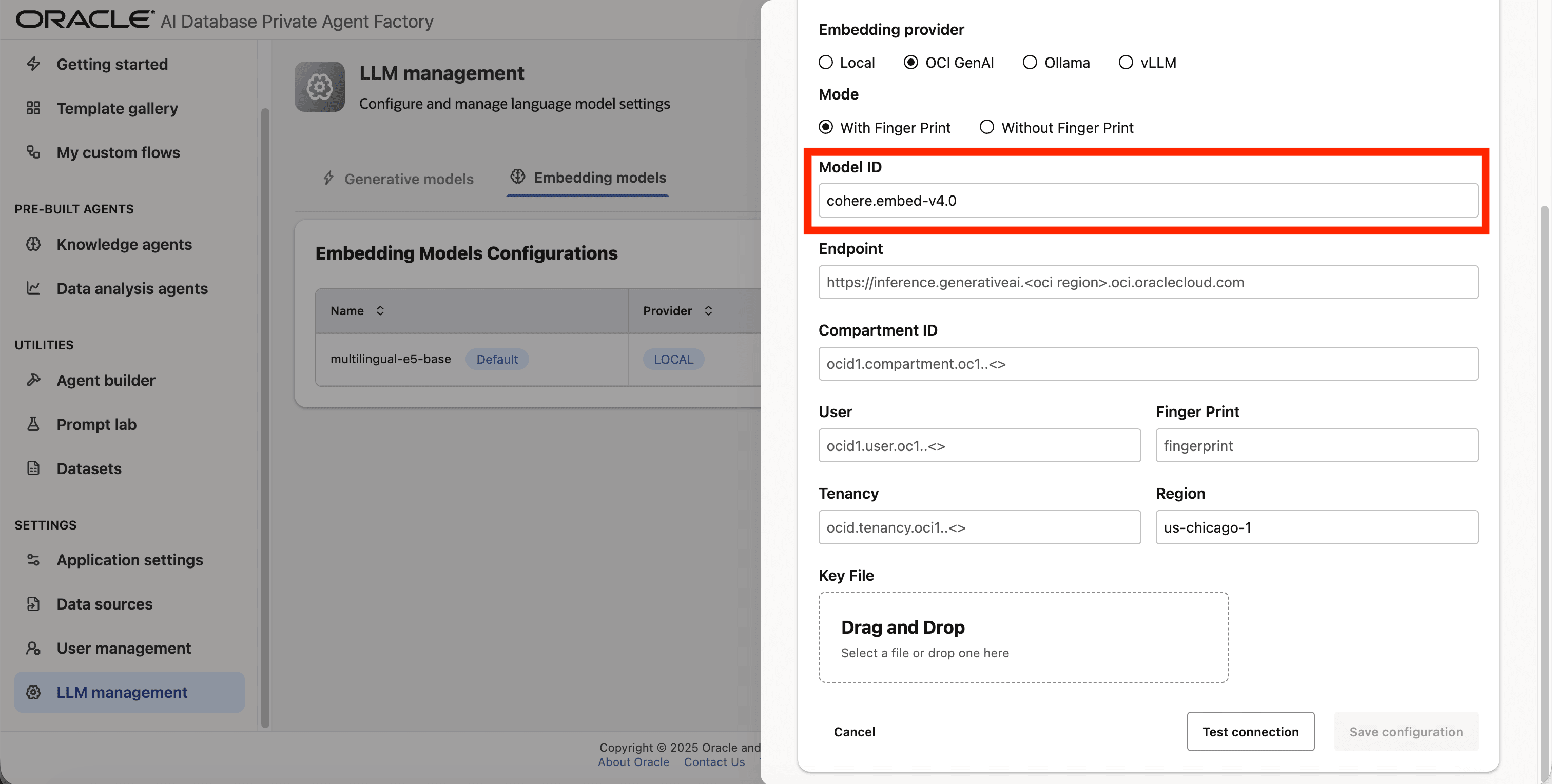
Step 8: Fill in Endpoint, Compartment ID, User, Tenancy, Finger print, and Region fields with your credentials from OCI.
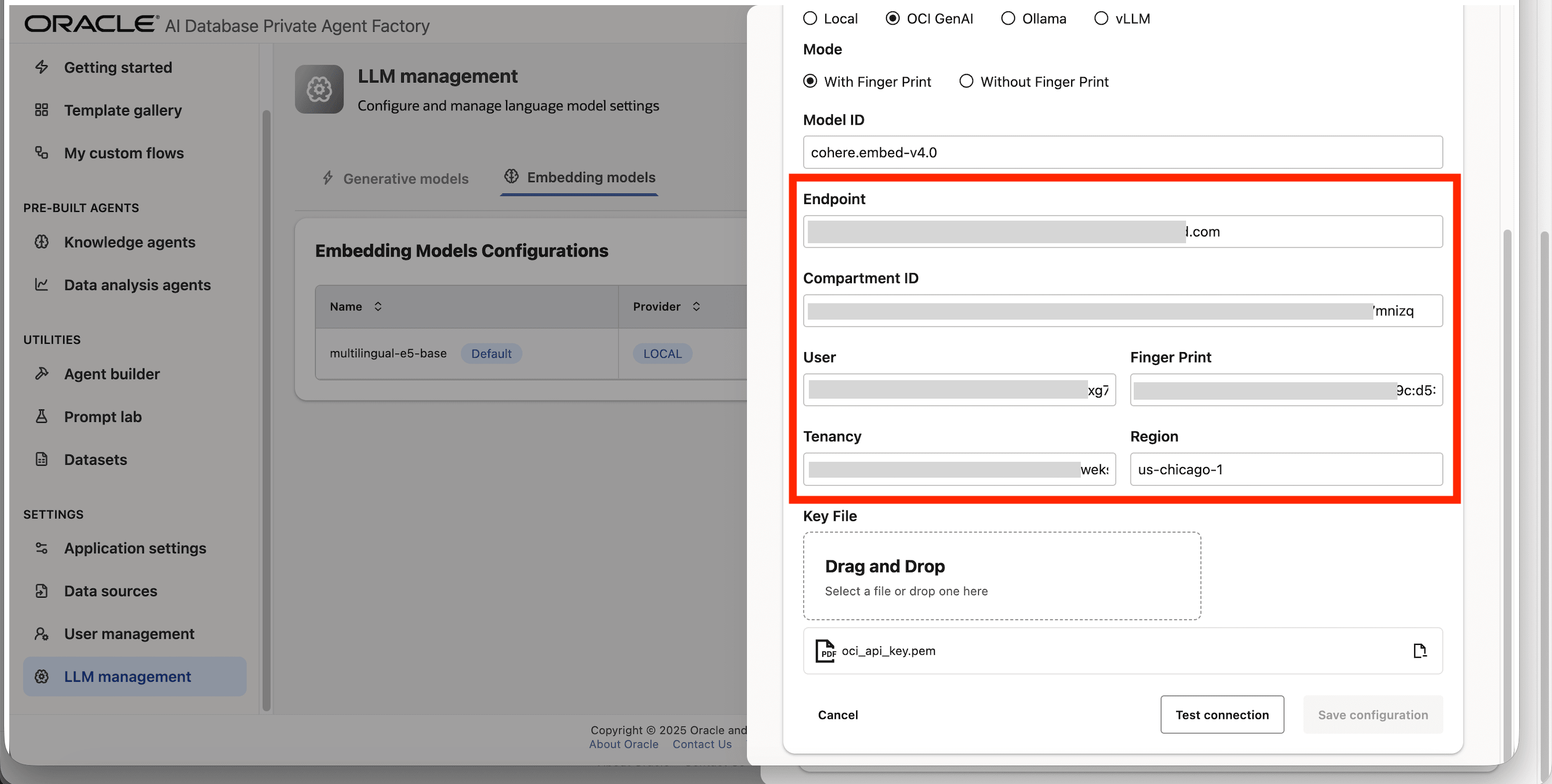
Step 9: Upload your private API key file under Key File.
Step 10: Click on Test connection to validate the credentials are correct.
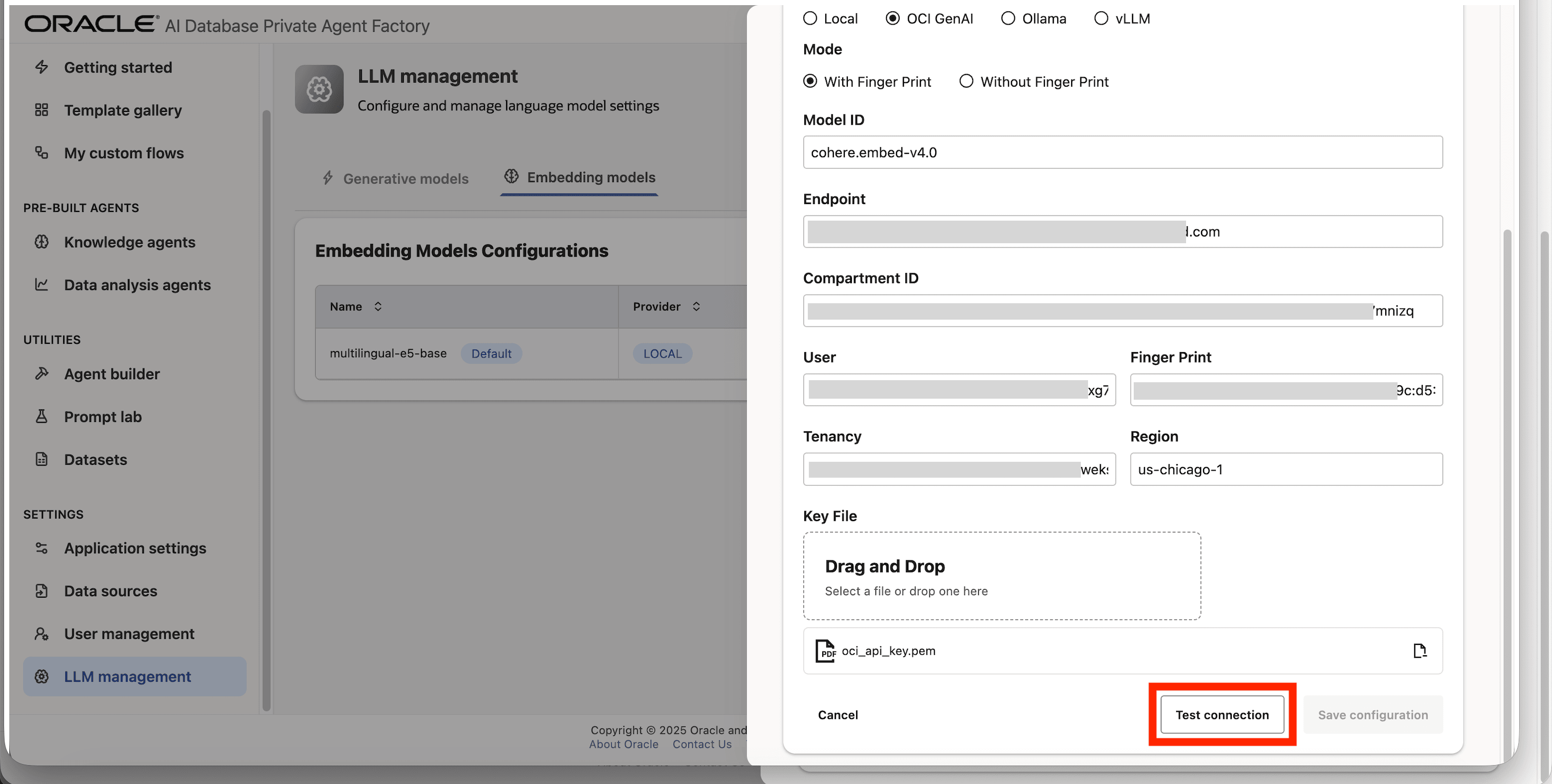
Step 11: A success message “Connection successful” will appear on screen and the Save Configuration button will be enabled, click on it to finalize the process.
vLLM/Ollama
You can connect to any self-hosted model endpoint.
These are the required fields you need to configure a vLLM:
- Model ID: The model identifier/path that the vLLM server is serving (often a filesystem path or a registry-style name).
- URL: Host/DNS clients use to reach the server.
- Port: The port where the HTTP service is exposed.