Call REST
The call REST action is used to make a REST call in conjunction with the service definitions.
Internally, this action uses the REST Helper, which is a public utility. Its parameters are as follows.
| Parameter Name | Description |
|---|---|
| endpoint | The endpoint ID as defined in the service configuration. |
| uriParams | A key/value pair map that will be used to override path and query parameters as defined in the service endpoint. |
| body | A structured object that will be sent as the body. |
| requestType | The content-type of the request, either 'json', 'form', or 'url'.
Note: Note that this is deprecated. Instead, use 'contentType' and 'fileContentType'. |
| headers | An object; each property name is a header name and value that will be sent with the request. |
| contentType | An optional string value with an actual MIME type, which will be used for the "content-type" header. When used with "fileContentType", this is also used as the type for the File blob. |
| responseType | If set, the specified type is used to do two things at run-time:
See the definition for "responseType" in Service Data Provider Properties for details on how the assigned type is used in that context. |
| filePath | An optional path to a file to send with the request. If "contentType" is set, that is used as the type for the File contents. If “contentType” is not set, a lookup of common file extensions will be used. |
| filePartName | Optional, used with filePath to allow override of the default name ("file") for the FormData part. |
| fileContentType | An optional string, used in combination with "contentType", "multipart/form-data", and "filePath". |
| hookHandler | Used primarily by vb/ServiceDataProvider when externalizing data fetches. See Service Data Provider for details. |
| requestTransformOptions | A map of values to pass to the corresponding transform, as the "options" parameter. |
| requestTransformFunctions | A map of named transform functions, called before making the request, where the function is: fn(configuration, options) |
| responseTransformFunctions | A map of named transform functions, called before making the response, where the function is: fn(configuration, options) |
| responseBodyFormat | A string that allows an override of the standard Rest behavior, which normally looks for a “content-type” header to determine how to read and parse the response. Possible values are "text", "json", "blob", "arrayBuffer", "base64", "base64Url", and "formData". |
| responseFields | This is an "advanced" field, for use specifically with JET Dynamic Forms. The value would typically be a variable that is bound to the <oj-dynamic-form> "rendered-fields" attribute. This is how a calculated layout can tell the Rest Action call which fields to fetch.
Note: The vb/BusinessObjectsTransform transform is necessary to create a query from this value. Note: When "responseFields" is provided, "responseType" is ignored. |
Using multipart/form Data
If you have set "contentType" to "multipart/form-data", the Call REST action interprets your request "body" object as the form parts. Each property of the body object is a form part, which is a key-value pair with its own content type and disposition.
If "filePath" is also set, it is added as an additional part using the lookup of common file extension types.
If "filePath" is also set, it is added as an additional part using the sample simple file extension type association. The name of this part is "file", or can be specified using "filePartName".
You may optionally override the file type by using "fileContentType" for the file part.
For more about working with the multipart/form-data format, refer to this Oracle blog, Consuming REST APIs in VB - multipart/form-data.
Parameters Typically Required per Endpoint Type
These are the typically required parameters for each endpoint type:
- POST:
bodyparameter is set to the variable containing the new record's data.uriParamsparameter is used to provide any required input parameters.
Here's an example POST endpoint call:
const callRestCreateIncident = await Actions.callRest(context, { endpoint: 'fixitfast/putIncident', body: $variables.incidentPayload , uriParams: { id: $constants.incidentId, }, }); - GET:
uriParamsparameter is used to provide any required input parameters, such as an ID input parameter to get a single record.Here's an example of a GET endpoint call to get a single record. The
empIDToGet_ipvariable is an input parameter that passes the record's ID to the action chain that contains this Call REST call:const getEmployeeResult = await Actions.callRest(context, { endpoint: 'businessObjects/get_Employee', uriParams: { 'Employee_Id': empIDToGet_ip, }, });
- DELETE:
uriParamsparameter is used to provide the ID of the record to delete.Here's an example of a DELETE endpoint call to delete a record. The
empIDToDelete_ipvariable is an input parameter that passes the record's ID to the action chain that contains this Call REST call:const callRestBusinessObjectsDeleteEmployeeResult = await Actions.callRest(context, { endpoint: 'businessObjects/delete_Employee', uriParams: { 'Employee_Id': empIDToDelete_ip, }, });
- PATCH:
bodyparameter is set to the variable containing the record with the updated data.uriParamsparameter is used to provide the ID of the record to update.
Here's an example PATCH endpoint call:
const updateEmployeeResult = await Actions.callRest(context, { endpoint: 'businessObjects/update_Employee', uriParams: { 'Employee_Id': $variables.empID_pv, }, body: $variables.EmpUpdatedData_pv, });
Service Definitions
If your service connection details are static, the details, such as the server, path, and schema of the request and response, are stored in the openapi3.json file for the service connection.
To view or edit a service's definition, select the service connection in the Services pane, then open the Source tab. The editor uses the OpenAPI3 specification and JSON format.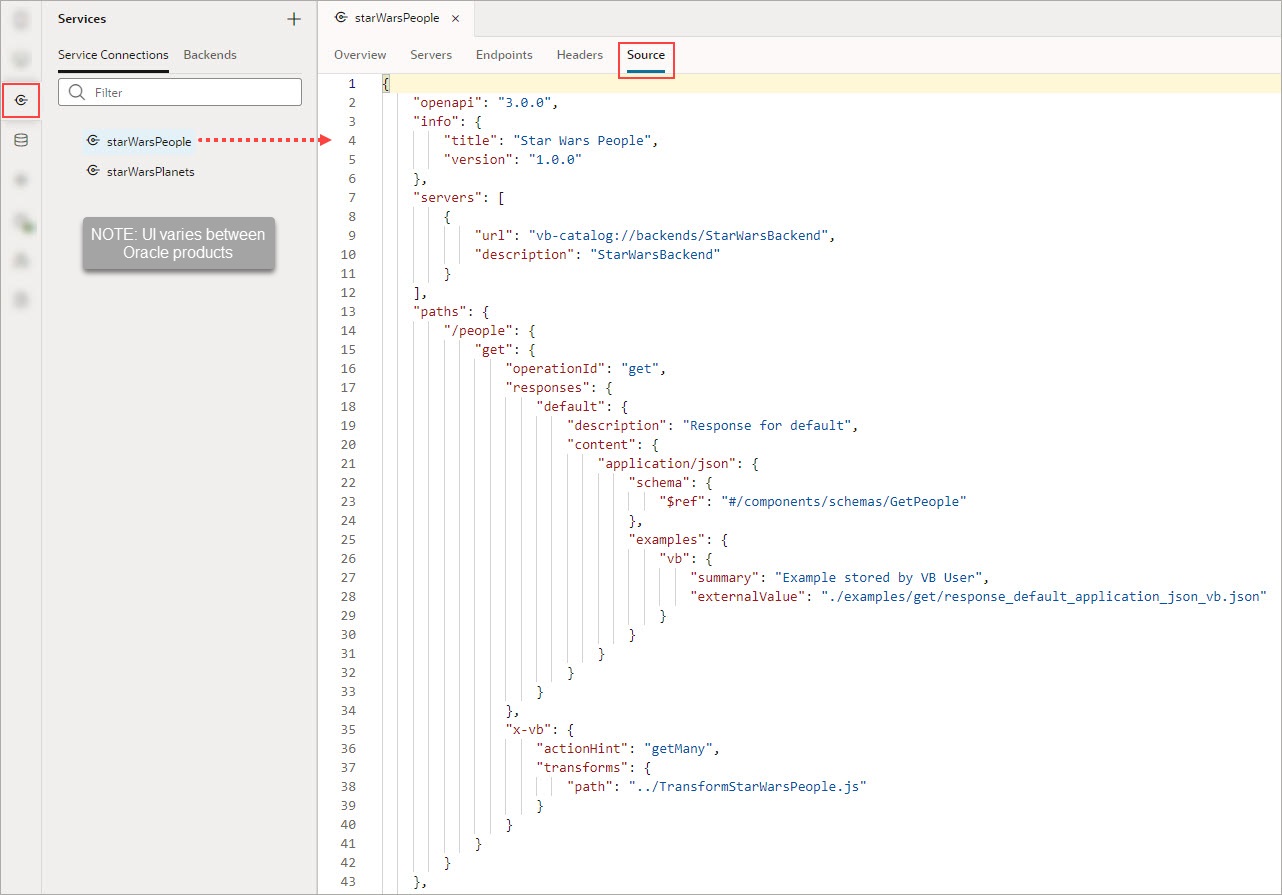
Description of the illustration jsac-service-connection-source-tab.jpg
Transforms
The requestTransformOptions, requestTransformFunctions, and responseTransformFunctions can be used to modify the request and response. Some built-in service endpoints have built-in transform functions for 'sort', 'filter', 'paginate', and 'select', so options for these transform functions can be defined using the same name via the requestTransformOptions property. For third party services, the options set are based on the type of transform functions supported.
When using the Rest Action, the transform names have no semantic meaning and all request and response transforms are called.
Request and response transform functions have the following signatures.
| Transform Type | Parameters | Return Value |
|---|---|---|
| Request | |
Configuration object; see "Parameters". Typically, returns the same object passed in, or a modified one. |
| Response | |
The return value is application-defined. The value is returned as the 'transformResults' of the REST call result: |
Example 1-28 A Simple Transform Function
You would assign request and response transform functions to a Call REST action when interacting with a third-party service or when you need to override a business object’s auto-generated transforms (vb/BusinessObjectTransforms). Otherwise, you should assign transform functions to a backend, service connection, or endpoint.
In this example, the transform functions are defined in the page module and assigned to a Call REST action. The arguments are automatically passed to the module functions.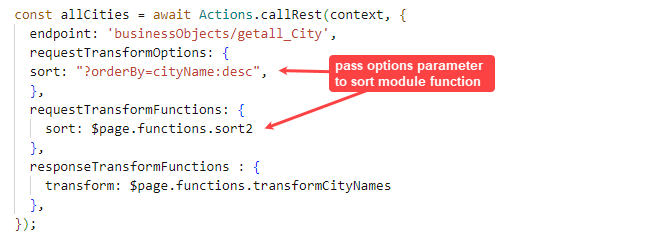
Description of the illustration jsac-callrest-transforms.png
class PageModule {
transformCityNames(result) {
let tr = {};
if (result.body) {
tr = result.body.items;
for (let i = 0; i < tr.length; i++) {
tr[i].cityName = tr[i].cityName + " (city)";
}
}
}
sort2(configuration, options) {
configuration.url = configuration.url + options;
return configuration;
}
}
Error Handling and Return Values
If the underlying REST API request returns a status code, the error object is returned for you to handle the error yourself, otherwise an auto-generated error notification is shown.
The object returned by the Call REST action returns these results:
| Result | Relevant Properties of Returned Object | Returned Object |
|---|---|---|
| Success |
If the returned object’s
|
*If a single record is returned, it is contained in the |
| Error |
If the returned object’s
|
|
For details about working with business objects, refer to Accessing Business Objects Using REST APIs.