Work with Expressions
Use expressions to evaluate and perform calculations on data stored in data objects, process pre-defined variables, process input, process output, and task outcomes.
-
Human tasks: Use an expression to dynamically determine the task title, summary, due date, and assignees.
-
Conditional sequence flows: Use an expression to define its condition.
-
Conditions and markers: Use an expression to define activation conditions and markers.
To create an expression for a flow element, click ![]() from the flow element’s properties field. This enables the expression mode and you can use the inline expression builder which gives auto-complete options for you to create and build your expression.
from the flow element’s properties field. This enables the expression mode and you can use the inline expression builder which gives auto-complete options for you to create and build your expression.
To create an expression while configuring data associations, enter the expression directly in the input or output fields of the data association editor. You can use the inline expression builder which gives auto-complete options for you to create and build your expression.
The following is an example image of the inline expression builder being used while configuring data association.
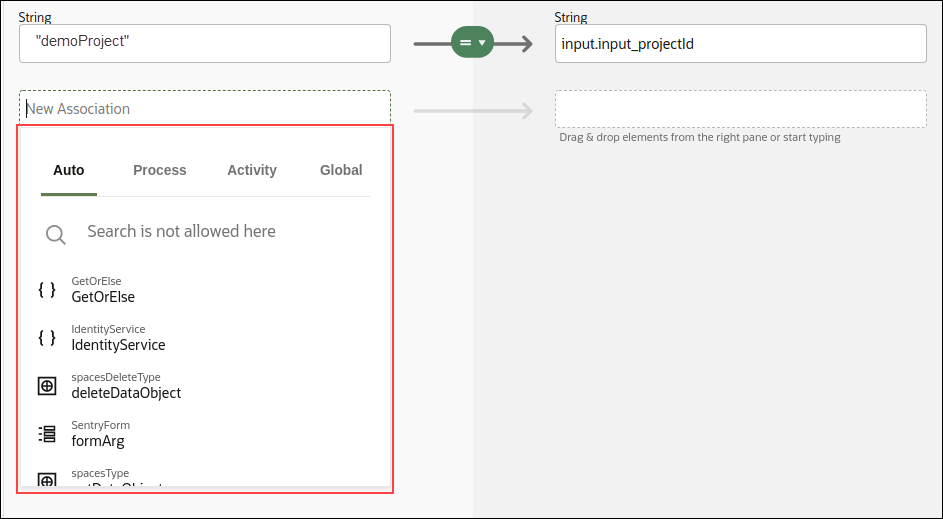
Description of the illustration exp-build.png
- Create expressions with data objects, operators, and functions. As soon as you put the cursor in the expression field, you get a list of suggested objects using which you can build the expression.
- As you choose the object, related suggestions for the next level are displayed below the field. The suggestions are context sensitive. For example, suggestions displayed for a Title field will be different from that of a Due Date field.
- Use Ctrl + Space to get more tabs and suggestions. A search field also displays that you can use to search data objects under the various tabs such as Process or Activity.
- The type that is expected to be entered into the expression field is auto-suggested at the top right of the field.
- If an expression is invalid, for example, if you type a number in a string field, an error message indicating the details of the error is displayed.
- If the configured expression is too long, you can expand the field by using Ctrl + Enter keys.
About Simple Expressions
Simple expressions are defined using a basic expression language and support. You can use these operators to write expressions and conditions to define your process flow. Generally these expressions perform their calculations based on the data objects in your business process. You can write expressions and conditions using the value of the data objects, but you can’t explicitly modify the value within the data object.
Here are some examples of expressions using operators:
-
totalAmount - discount
-
activationCount > 3
-
unitsSold <= 1200
Operator Precedence
Operator precedence defines the order in which the compiler evaluates operators. You can change operator precedence in an expression by using parentheses. In Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Process Automation, the operator precedence is:
-
Addition, Subtraction
-
Multiplication, Division, Remainder
-
Plus, Minus
-
Less than, Greater than, Less than or equal to, Greater than or equal to
-
Equals, Not equals
-
Not
-
Conditional And
-
Conditional Or
The following sections lists Operators and Functions per type.
Unary
| Operator | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| + | Plus | Has no effect on the value of the numeric operand. Use it to explicitly indicate that a certain value is positive. |
| - | Minus | Negates an arithmetic expression. |
| ! | Not | Logical complement operator. Negates the value of a Boolean expression. |
Equality and Relational
| Operator | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| = or == | Equal to | Returns true if the first operand is equal to the second operand |
| != | Not equal to | Returns true if the first operand isn't equal to the second operand |
| > | Greater than | Returns true if the first operand is greater than the second operand |
| >= | Greater than or equal to | Returns true if the first operand is greater than or equal to the second operand |
| < | Less than | Returns true if the first operand is less than the second operand |
| <= | Less than or equal to | Returns true if the first operand is less than or equal to the second operand |
Conditional
| Operator | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| and | Conditional And | Returns true if both operands evaluate to true |
| or | Conditional Or | Returns true if either operand evaluates to true |
String
| Function/Operator | Description | Usage Expression | Usage Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| + | String concatenation | “pine” + “apple” | “pineapple” |
| == | Equals | “apples” == “apples” | true |
| != | Not equals | “apples” != “oranges” | true |
| > | Greater than | “word” > “work” | false |
| >= | Greater than or equals | “work” >= “work” | true |
| < | Less than | “word” < “work” | true |
| <= | Less than or equals | “work” <= “work” | true |
| contains | Returns true if the first argument string contains the second argument string; otherwise returns false | “caramel”.contains(“ram”) | true |
| endsWith | Returns true if the first argument string ends with the second argument string; otherwise returns false | “immutable”.endsWith(“table”) | true |
| length | Returns the number of characters in a string | “house”.length() | 5 |
| lowerCase | Returns a string with all the characters in the argument converted to lower-case representation | “Example”.lowerCase() | “example” |
| startsWith | Returns true if the first argument string starts with the second argument string, otherwise returns false | “caramel”.startsWith(“car”) | true |
| substring | Returns the substring of the first argument starting at the position specified in the second argument and continuing to the end of the string | “care”.substring(2) | “are” |
| substring | Returns the substring of the first argument starting at the position specified in the second argument with length specified in the third argument | “care”.substring(1,3) | “car” |
| upperCase | Returns a string with all the characters in the argument converted to upper-case representation | “Example”.upperCase() | "EXAMPLE" |
| replaceAll | Replaces each substring of this string that matches the given pattern with the given replacement. | "care".replaceAll("e", "t") | "cart" |
| indexOf | Returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified substring, or -1 if there is no such occurrence. | "care".indexOf("a") | 2 |
Numeric
The following table includes operators for both Integer and Number.
| Operator | Description | Usage Expression | Usage Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| + | Addition | 2 + 8 | 10 |
| - | Subtraction | 7 – 4 | 3 |
| * | Multiplication | 3 * 4 | 12 |
| / | Division | 3 / 2 | 1.5 |
| % | Remainder | 3 % 2 | 1 |
| == | Equals | 12 == 13 | false |
| != | Not equals | 12 != 13 | true |
| > | Greater than | 15 > 16 | false |
| >= | Greater than or equals | 15 >= 15 | true |
| < | Less than | 12 < 10 | false |
| <= | Less than or equals | 12 <= 12 | true |
| abs | Returns the absolute value of a number | abs(- 6) | 6 |
In addition to the above, the following specific operators are also available for Number.
| Operator | Description | Usage Expression | Usage Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| floor | Returns the largest (closest to positive infinity) number that isn't greater than the argument and is an integer | floor(5.60) | 5 |
| ceil | Returns the smallest (closest to negative infinity) number that isn't less than the argument and is an integer | ceil(5.60) | 6 |
| round | Returns the number that is closest to the argument and is an integer | round(5.60) | 6 |
Date and Time
Date and Time types include Date, Time, and DateTime. All of them have the following operators.
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| + | Addition (valid only when the second argument is a duration) |
| - | Subtraction (valid only when the second argument is a duration) |
| == | Equals |
| != | Not equals |
| > | Greater than |
| >= | Greater than or equals |
| < | Less than |
| <= | Less than or equals |
| format | Returns the formatted string of date-time using the provided format picture |
In addition, Date, Time, and DateTime have specific operators as listed under each of them.
Date
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| year | Returns a number representing the year component of the date-time argument. |
| month | Returns a number representing the month component of the date-time argument. |
| day | Returns a number representing the day component of the date-time argument. |
Time
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| hours | Returns a number between 0 and 23, both inclusive, representing the hours component of the date-time argument |
| minutes | Returns a number between 0 and 59, both inclusive, representing the minutes component of the date-time argument. |
| seconds | Returns a number between 0 and 59, both inclusive, representing the seconds component of the date-time argument. |
DateTime
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| year | Returns a number representing the year component of the date-time argument. |
| month | Returns a number representing the month component of the date-time argument. |
| day | Returns a number representing the day component of the date-time argument. |
| hours | Returns a number between 0 and 23, both inclusive, representing the hours component of the date-time argument. |
| minutes | Returns a number between 0 and 59, both inclusive, representing the minutes component of the date-time argument. |
| seconds | Returns a number between 0 and 59, both inclusive, representing the seconds component of the date-time argument. |
| timezone | Returns an interval value, representing the time offset from UTC. |
| toTimezone |
Returns the date-time expressed in the time offset corresponding to the timezone ID provided. You have the following options for specifying a timezone ID:
Note: You must include double quotation marks around the timezone ID value.For more information about timezone IDs, see Class ZoneId in the Java Platform documentation. |
Boolean
| Operator | Description | Usage Expression | Usage Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| == | Equals | true == true | true |
| != | Not Equals | true != false | true |
| and | Conditional — And | true and false | false |
| or | Conditional — Or | true or false | true |
| not | Logical complement operator, inverts the value of a Boolean expression. | not true | false |
Duration
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| == | Equals |
| != | Not equals |
| > | Greater than |
| >= | Greater than or equals |
| < | Less than |
| <= | Less than or equals |
Array
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| [ ] | Access a particular element into the array |
| == | Equals |
| != | Not equals |
| length | Returns the number of elements contained within the array |
Other
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| == | Equals |
| != | Not equals |
Special Constants
| Constants | Description |
|---|---|
| null | Null value |
| true | Logical true |
| false | Logical false |
| ‘now’ | Current dateTime |
Casting
In some cases, it could be desirable to bypass the type validation in order to assign types that aren't necessarily compatible. For example, you may want to assign an 'int' value to a 'string' one and in order to do that you can use the conversion operation like this:
<conversionTypeName> ( <valueToConvert> )
where the 'conversionTypeName' is the type you want to see as the value.
Here are some conversion examples:
-
string(myIntDO)
-
int(myStringDO)
-
duration(mystringDO)
Note:
You can only cast to primitive types, so the 'conversionTypeName' will only accept those that have a valid value.
Assigning two values that are incompatible will result in a runtime error.
Additional Functions
Identity Service
| Function | Description | Available | Usage Function Prototype | Usage Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| getUserId | Returns a string containing the id for a specific user name. | Process wide | IdentityService.getUserId(<userName:string>): string | IdentityService.getUserId("wfaulkner") |
| getUserIds | Returns a string containing the ids (separated by commas) for a list of user names (also separated by commas). | Process wide | IdentityService.getUserIds(<userNames:string>): string | IdentityService.getUserIds("wfaulkner, jstein") |
Get or Else
| Function | Description | Available | Usage Function Prototype | Usage Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| boolean | Request an object property along with a backup value. The backup value is used if the first argument corresponds to a missing node or an uninitialized value. This function set is useful while dealing with an untrustworthy data source, where initialization isn’t guaranteed. | Process wide | GetOrElse.boolean(<expression:boolean>,<fallbackValue:boolean>): boolean | GetOrElse.boolean(myDO.boolAtt, true) |
| string | Process wide | GetOrElse.string(<expression:string>,<fallbackValue:string>): string | GetOrElse.string(myDO.stringAtt, "User") | |
| number | Process wide | GetOrElse.number(<expression:number>,<fallbackValue:number>): number | GetOrElse.number(myDO.numberAtt, 25.3d) | |
| integer | Process wide | GetOrElse.integer(<expression:integer>,<fallbackValue:integer>): integer | GetOrElse.integer(myDO.integerAtt, 12) |