Introduction to Customer-Managed Encryption keys
Customer-Managed Encryption keys Overview
Oracle NoSQL Database Cloud Service (NDCS) protects data against security breaches by encrypting data-at-rest using data encryption keys. The data encyption keys are then encrypted using a master encryption key. By default, NDCS uses an Oracle-managed master encryption key.
NDCS also allows you to encrypt data encryption keys with your own master encryption key, termed as Customer-Managed Encryption Key (CMEK). CMEKs must be enabled in a dedicated environment prior to using this functionality. When you create a dedicated environment configured for CMEKs, Oracle NoSQL Database uses OCI block volumes to store and encrypt database data using a master encryption key that you control. Additionally, backups of your environment’s data reside in OCI object storage and are also encrypted using your master key. To raise a service ticket, see Requesting a Dedicated hosted environment.
You create and manage your own master encryption keys. NDCS uses the OCI Key Management Service (KMS) to store your master encryption key within vaults and manage their operational states.
Terminologies
- Customer Managed Encryption Key (CMEK): A master encryption key used to encrypt and decrypt Block Volume and Object Storage keys.
- Data-at-rest: Refers to data stored in Oracle NoSQL Database.
- Dedicated environment for CMEKs: An Oracle NoSQL environment that is dedicated to your tenancy and configured to use Customer Managed Encryption Keys.
- Key Management Service (KMS): An OCI service that stores and manages keys within vaults. KMS provides centralized management and control of encryption keys.
- Key rotation: The process of replacing an old encryption key with a new key to mitigate the risks if the key is ever compromised.
- Block Volume service: An OCI service, which lets you dynamically provision and manage block storage to meet the necessary application requirements.
- Object Storage service: An OCI service,which provides a fully programmable, scalable, and durable cloud storage for data.
- OCI Vault service: An OCI service that provides a secure, centralized location for managing encryption keys and secrets.
How does CMEK work?
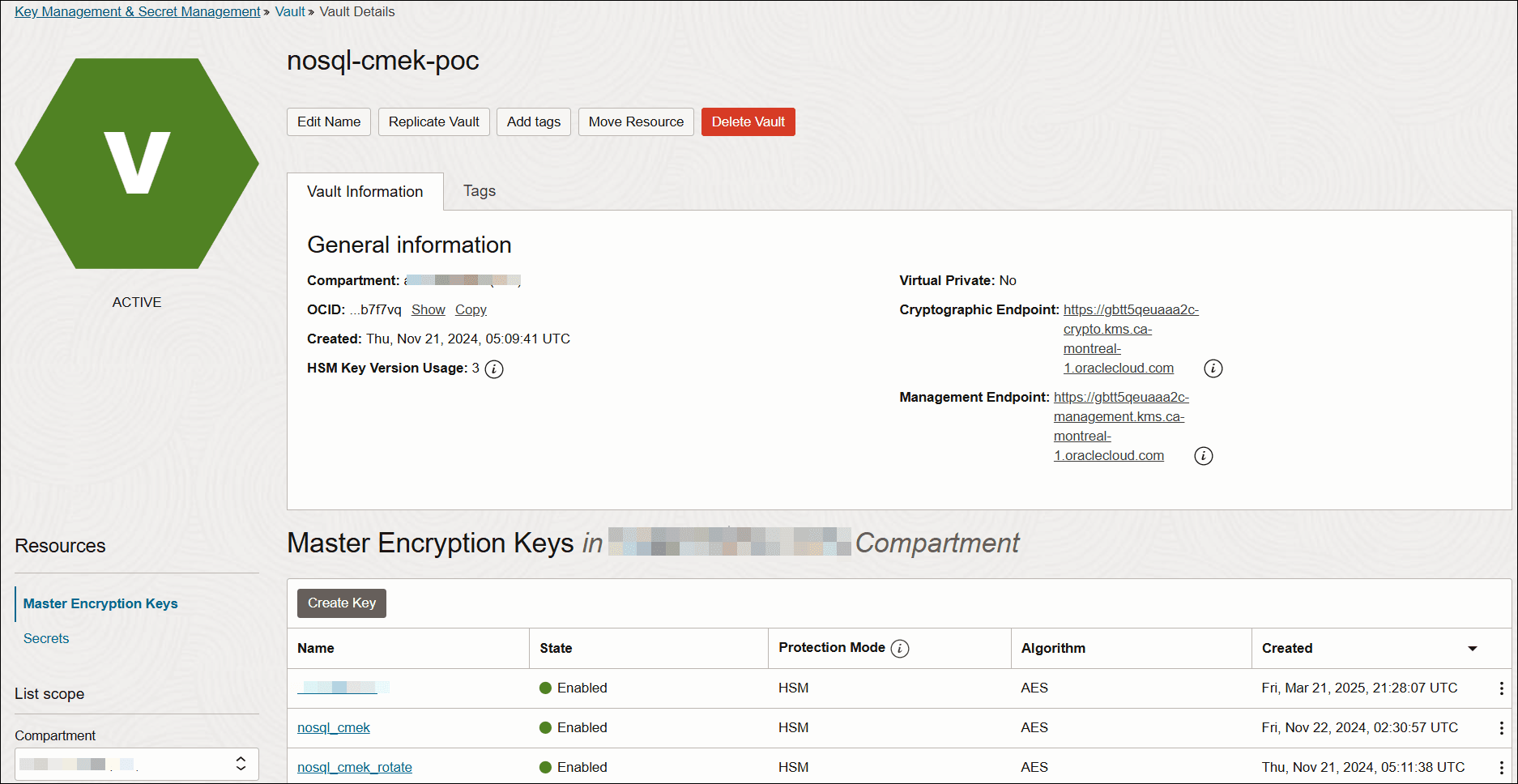
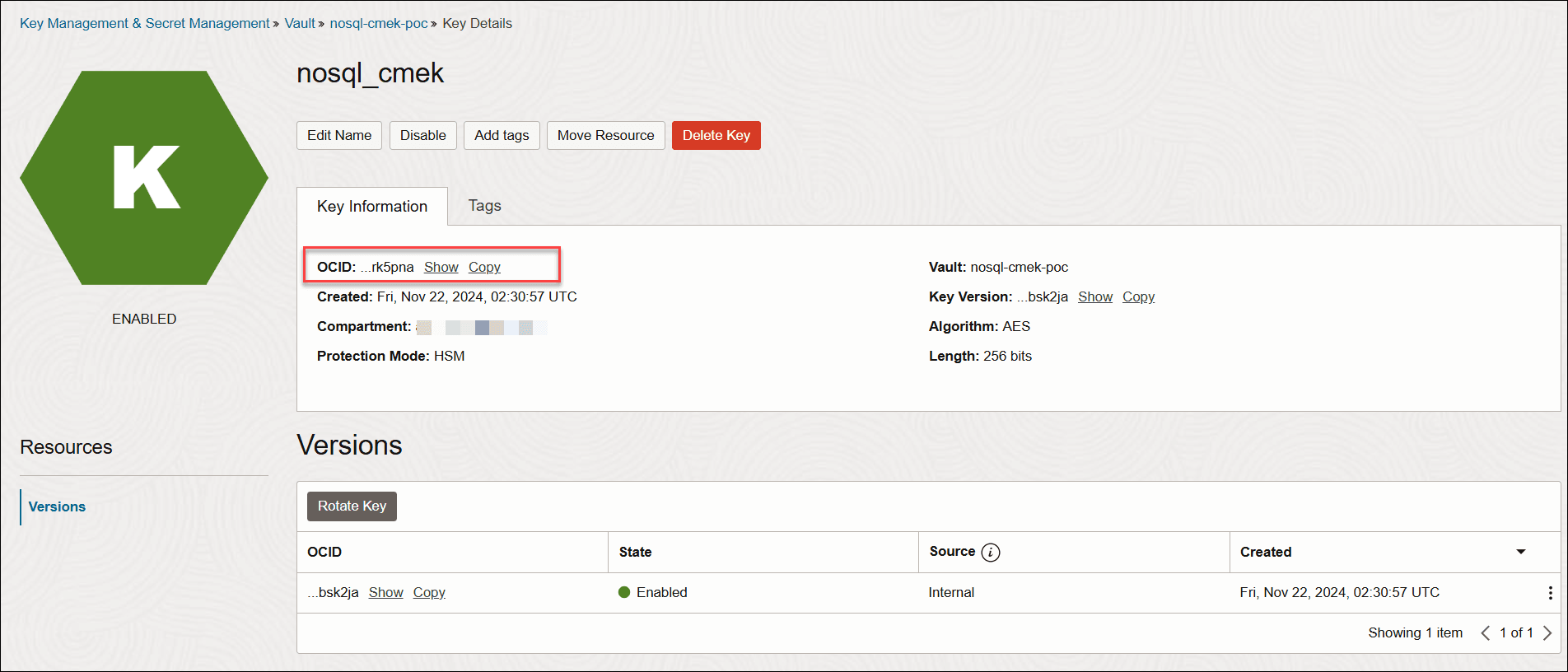
The OCI Vault service lets you create vaults in your tenancy as containers for encryption keys. When you create CMEK in a vault, a unique Oracle Cloud ID (OCID) is assigned to it.
You assign a CMEK to your dedicated environment through the OCI console. The Block Volume service and Object Storage service use CMEK to encrypt Block Volume and Object Storage keys.
NDCS supports key rotation by allowing you to assign a new CMEK. You must first create a new key in your vault. To trigger a rotation, you update the new key in your dedicated environment from the OCI console. Rotating to a new CMEK does not re-encrypt any data stored in Block Volumes or in Object Storage. It only re-encrypts the Block Volume and Object Storage keys.
The Block Volume service and Object Storage service manage all the data operations.
CMEK Creation
Oracle NoSQL Database Cloud Service supports integration exclusively with OCI Vault service to create vaults and uses KMS to create, store, and manage CMEKs in vaults. For more details on vault, see OCI Vault topic in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Documentation.
You must first create a vault from the OCI console and then create CMEK in the vault.
For details, see Creating a Vault topic in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Documentation.
CMEK Creation:
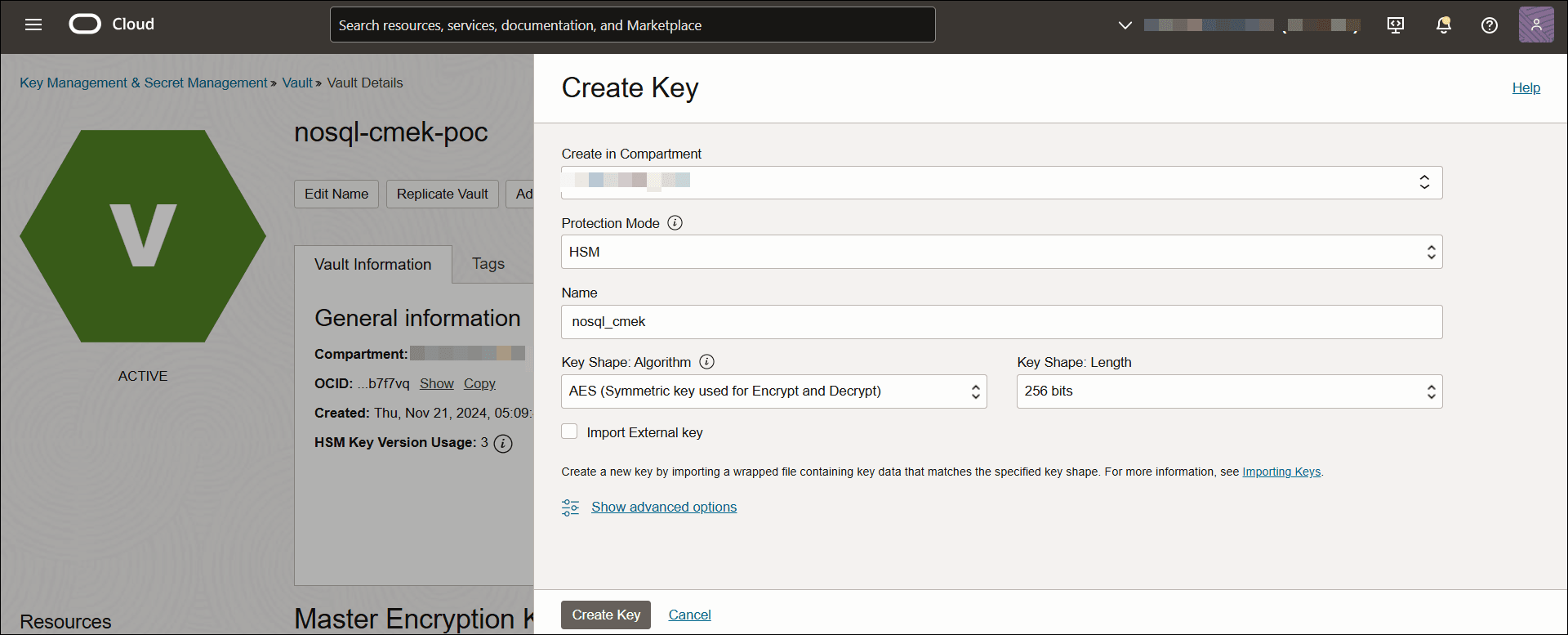
When creating a CMEK, you specify its protection mode, algorithm, and length.
Follow these steps to create a CMEK. For more details, see Creating a Master Encryption Key topic in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Documentation.
- Create a vault.
After creating a CMEK, you assign it to your dedicated environment. The Block Volume service and Object Storage service in the dedicated environment access the CMEK internally using the CMEK's OCID.
CMEK Lifecycle in Vault:
A vault supports the following operations:
- Creation: You create a CMEK in a vault.
- Disabling/Enabling: You can disable/enable a CMEK to control its usage.
- Deletion: You can delete a CMEK from the vault. Deletion is a two-step process with a waiting period to prevent accidental deletion.
Note:
CMEK's status is disabled during this waiting period.
For details on enabling, disabling, and deleting CMEK, see CMEK Key Management Workflow.
CMEK Management Operations
Oracle NoSQL Database Cloud Service manages CMEK's operations in dedicated environments. This includes CMEK's assignment to a dedicated environment, CMEK rotation, removal, disabling in vault, re-enabling, and deletion.
The following table describes the tasks involved in CMEK management. For details on CMEK key management tasks, see CMEK Key Management Workflow.
Table - CMEK Management Tasks
| User tasks | NDCS tasks |
|---|---|
|
CMEK assignment: You assign a CMEK to your dedicated environment from the OCI console. |
|
| CMEK rotation: You update CMEK in your dedicated environment. |
|
| CMEK disable: You disable CMEK from the vault. |
|
| CMEK re-enable: You re-enable the disabled CMEK from the vault. |
|
| CMEK deletion: You delete CMEK from the vault. |
|
| CMEK removal: You unassign CMEK from your dedicated environment. |
|
CMEK Access Control
Oracle NoSQL Database Cloud Service uses Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Identity and Access Management (IAM) to provide secure access to Oracle cloud. OCI IAM enables you to implement access control to use KMS functionality.
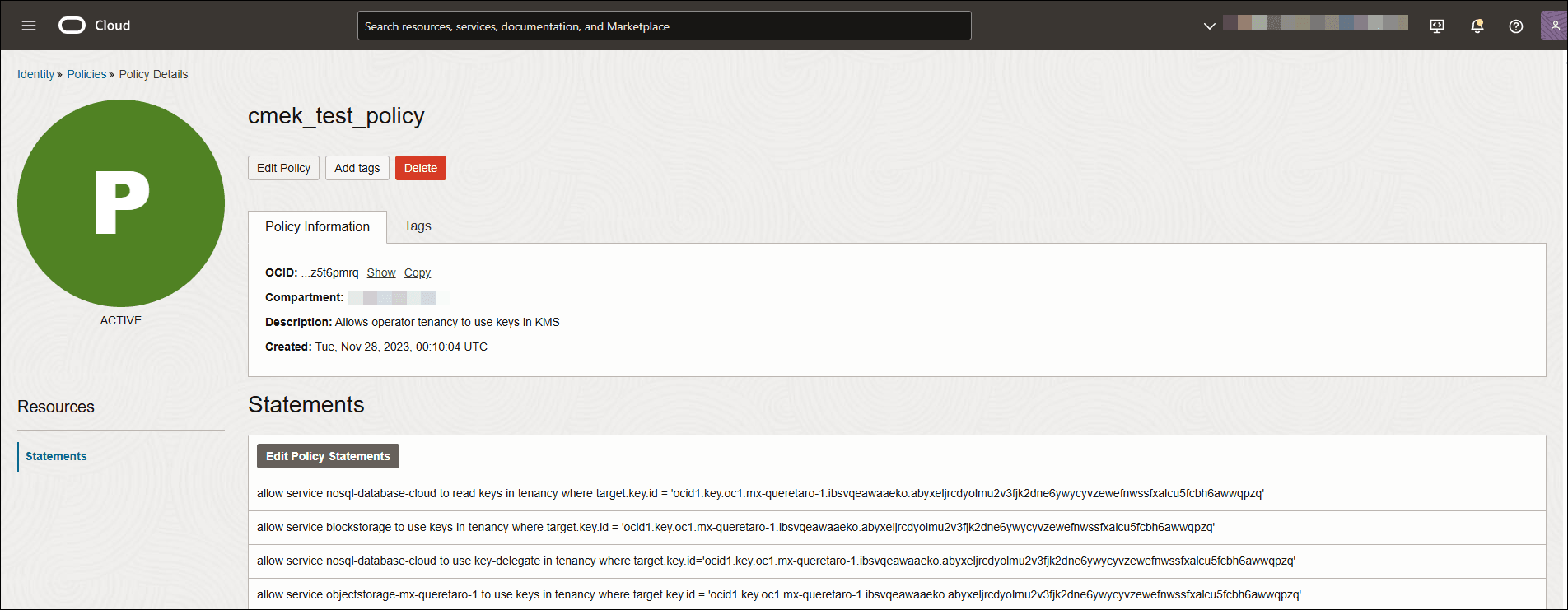
You must create policies to access CMEK in the vault, Block Volumes, and Object Storage for all the required operations. For more details on policies, see How Policies Work in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Documentation.
The following are the basic IAM policy requirements in your tenancy for CMEK usage:
-
To grant Block Volumes access to use CMEK in the required compartment:
allow service blockstorage to use keys in compartment <name_of_compartment> where target.key.id = <key-ocid>where,
name_of_compartment:Compartment name in your dedicated environment.key-ocid:OCID of your CMEK. -
To grant Object Storage in a region and compartment access to use CMEK:
allow service objectstorage-<region> to use keys in compartment <name_of_compartment> where target.key.id = <key-ocid>where,
region:Region where your Object Storage resides.name_of_compartment:Compartment name in your dedicated environment.key-ocid:OCID of your CMEK. -
To grant Oracle NoSQL Database Cloud Service access to key-delegate CMEK:
You add a key-delegate permission when you want to allow an integrated service such as NDCS to use a key in a specific compartment.allow service nosql-database-cloud to use key-delegate in compartment <name_of_compartment> where target.key.id = <key-ocid>where,
name_of_compartment:Compartment name in your dedicated environment.key-ocid:OCID of your CMEK. -
To grant Oracle NoSQL Database Cloud Service access to read CMEK:
allow service nosql-database-cloud to read keys in compartment <name_of_compartment> where target.key.id = <keyocid>where,
name_of_compartment:Compartment name in your dedicated environment.key-ocid:OCID of your CMEK.
CMEK Monitoring and Logging
Oracle NoSQL Database Cloud Service supports logging all CMEK-related events in your dedicated environment and alerts with appropriate notifications.
OCI Audit Logs
Oracle NoSQL Database Cloud Service uses OCI Audit services to log all key state changes. The audit log information includes:
- Timestamp of when the state change was detected.
- Previous and new states of CMEK. For details on CMEK lifecycle management, see CMEK Key Management Workflow.
- Impacted endpoint.
- Special actions taken.
OCI Alarms
Oracle NoSQL Database Cloud Service uses OCI Monitoring service to actively and passively monitor your cloud resources using the metrics and alarms features. You can set up OCI alarms based on these metrics:
Table - CMEK Metrics and Alarms
| Metric | Display name | Unit | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| EncryptionKeyStatus | Encryption Key Status | integer |
The status of the encryption key as seen by Oracle NoSQL Database Cloud Service. If the value is 0, the encryption key is disabled. If the value is 1, the encryption key is enabled and able to perform encryption/decryption. Oracle-managed keys always return 1. |
| EncryptionKeyType | Encryption Key Type | integer |
The current type of encryption key assigned to Oracle NoSQL Database Cloud Service. If the value is 0, an Oracle-managed key is being used. If the value is 1, a CMEK is being used instead. |
OCI Console
Oracle NoSQL Database Cloud Service uses the OCI Notification service to display critical alerts on the OCI Console for the affected dedicated environment.
You will be notified for the following CMEK-related events:
- New CMEK is assigned to a dedicated environment.
- CMEK is changed in a dedicated environment.
- CMEK is removed from a dedicated environment.
- CMEK is being deleted from the vault and is in a waiting period.
- CMEK is deleted from the vault.
- CMEK is re-enabled in the vault.
- Encryption process is started in a dedicated environment.
- Encryption process is completed in a dedicated environment.
The alerts include the following:
- Current status of CMEK.
- If a dedicated environment is unavailable, reason for unavailability.
CMEK Service Availability
Oracle NoSQL Database Cloud Service monitors the CMEK service availability in the vault and enforces appropriate actions when CMEK is disabled or deleted. NDCS provides clear error messages and logs when your dedicated environment becomes unavailable or irrecoverable due to CMEK issues.
If a CMEK is disabled, Oracle NoSQL Database Cloud Service triggers the following actions:
- Immediately disables all access to the dedicated environment.
- Shuts down instances on the dedicated environment.
- Disables all monitoring on the dedicated environment.
- Ensures that data in Block Volumes and Object Storage of the dedicated environment can't be accessed.
For details on disabling CMEK, see CMEK Disable.
If a CMEK is deleted, Oracle NoSQL Database Cloud Service triggers the following actions:
- Immediately marks the dedicated environment as irrecoverable.
- Shuts down instances on the dedicated environment.
- Disables all monitoring on the dedicated environment.
- Schedules the dedicated environment for permanent termination.
For details on deleting CMEK, see CMEK Delete.
If a CMEK is re-enabled, Oracle NoSQL Database Cloud Service suggests the following actions:
- You must raise a CAM ticket for bringing the environment back online after its CMEK has been re-enabled in the vault.
For details on re-enabling CMEK, see CMEK Restore.