clustering
Format
clustering(table, method, scale=True, key_column=None, columns=None, weights=None, weights_def=None,
save_weights_as=None, spatial_col=None, crs=None, to_crs=None, plot=None, **kwargs)Parameters
The parameters for this pre-defined function are described in the following table.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
method |
A string specifying the clustering algorithm to execute. The options are: DBSCAN, KMEANS ,and AGGLOMERATIVE. |
scale |
If specified, it calls the function
oml.create to store a pandas
DataFrame containing spatial lag in a table
with the specified name.
|
key_column |
If defined, the specified column is added to the
resulting pandas DataFrame. Otherwise, a column
with the index of the DataFrame is attached to the
result.
|
columns |
An array of strings indicating the features that form the training set. |
weights |
Required when trying to use spatial weights already
stored in the data store. Internally it calls the function
olm.ds.load. The supported parameters are
ds_name and obj_name,
indicating the data store name and object name,
respectively.
|
weights_def |
Required if the parameter weights
is not specified. Establishes the relationship between neighboring
locations.
This is passed as a json object specifying the type of the weights definition and its parameters. Each parameter is defined in detail in the API Reference documentation. The following lists the supported types and parameters:
|
save_weights_as |
Only used if weights_def is
defined. Specifies how the spatial weights are stored in the data
store. The value is a json file that determines the parameters of
oml.ds.save. The supported parameters are:
[ds_name, obj_name, overwrite_ds, append, overwrite_obj,
grantable, compression]. Some parameter names slightly
differ from those in the oml.ds.save function. The
parameter overwrite_obj is used to indicate whether
an already existing object should be replaced with the current
object.
|
spatial_col |
Specifies the column containing the geometries. The column can be specified in the table’s metadata. If not specified, the column name is retrieved from the table. |
crs |
Specifies the Coordinate Reference System. If not specified, it is inferred from the table. |
to_crs |
If specified, the Coordinate Reference System will change to the specified value. |
plot |
A dictionary specifying the properties of the Plot Clusters function. If defined, a plot showing the resulting clusters is included in the response. |
Example
This example shows how to run the agglomerative with regionalization algorithm over a given dataset, specifying the number of clusters and the type of spatial weights.
The clustering algorithm is set in the method parameter,
while the number of clusters and the spatial weights are defined in the
n_clusters and weights_def parameters
respectively. The features considered for clustering are specified in the
columns parameter.
select *
from table(
pyqEval(
'{
"oml_connect": true,
"table": "oml_user.la_block_groups",
"columns": ["median_income"],
"method": "AGGLOMERATIVE",
"n_clusters": 6,
"key_column": "geoid",
"weights_def": {"type": "Queen"}
}',
'{ "geoid": "VARCHAR2(50)", "label": "NUMBER" }',
'clustering'
)
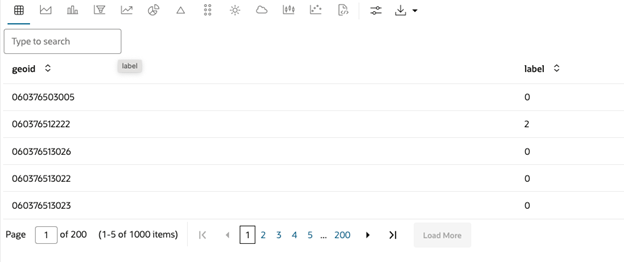
);The result contains the index column specified in the
key_column parameter and the labels of each row, indicating to
which cluster they belong.
You can visualize the clusters using the select IMAGE clause and the
oml_graphics_flag parameter set to true. In
the following code, the plot parameter indicates that it uses a
basemap as background. Also, note that the output format (out_fmt)
is set to PNG.
select IMAGE
from table(
pyqEval(
par_lst => '{
"oml_connect": true,
"oml_graphics_flag": true,
"table": "oml_user.la_block_groups",
"columns": ["median_income"],
"method": "AGGLOMERATIVE",
"n_clusters": 6,
"key_column": "geoid",
"weights_def": {"type": "Queen"},
"plot": {"with_basemap": true}
}',
out_fmt => 'PNG',
scr_name => 'clustering'
)
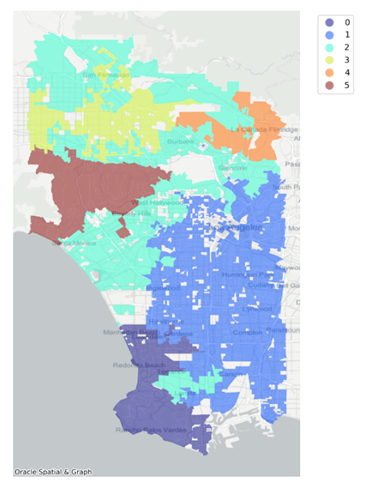
);The result is a map with the observations colored according to the cluster
they are assigned. Note that there are six clusters as specified in the
n_clusters parameter. By defining spatial weights, the
agglomerative clustering algorithm executes regionalization. This means that
observations assigned to the same cluster share common characteristics and are
geographically connected.