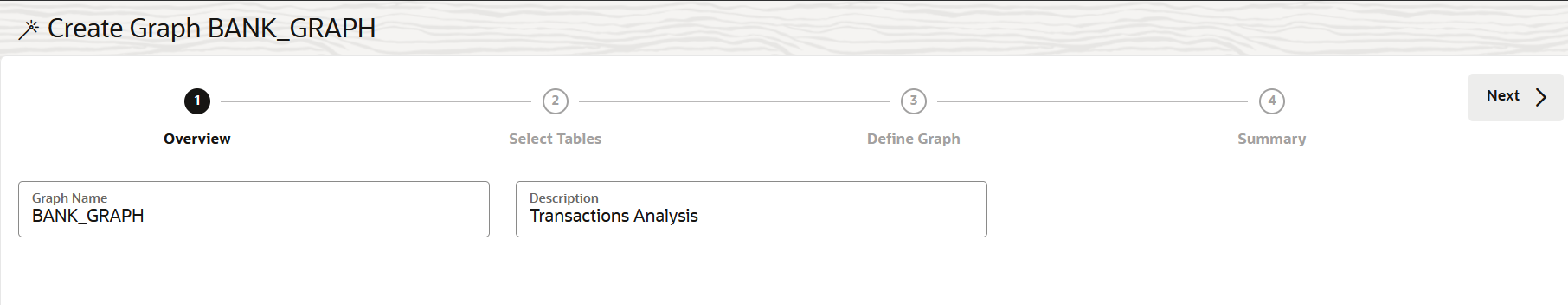
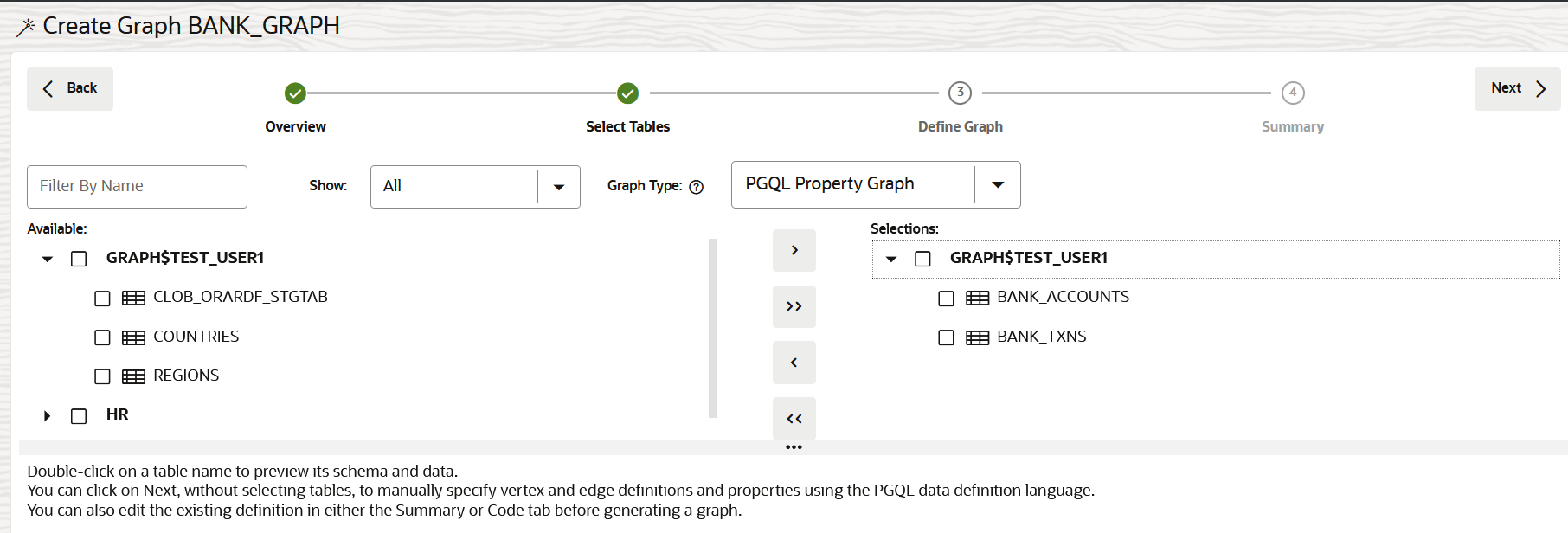
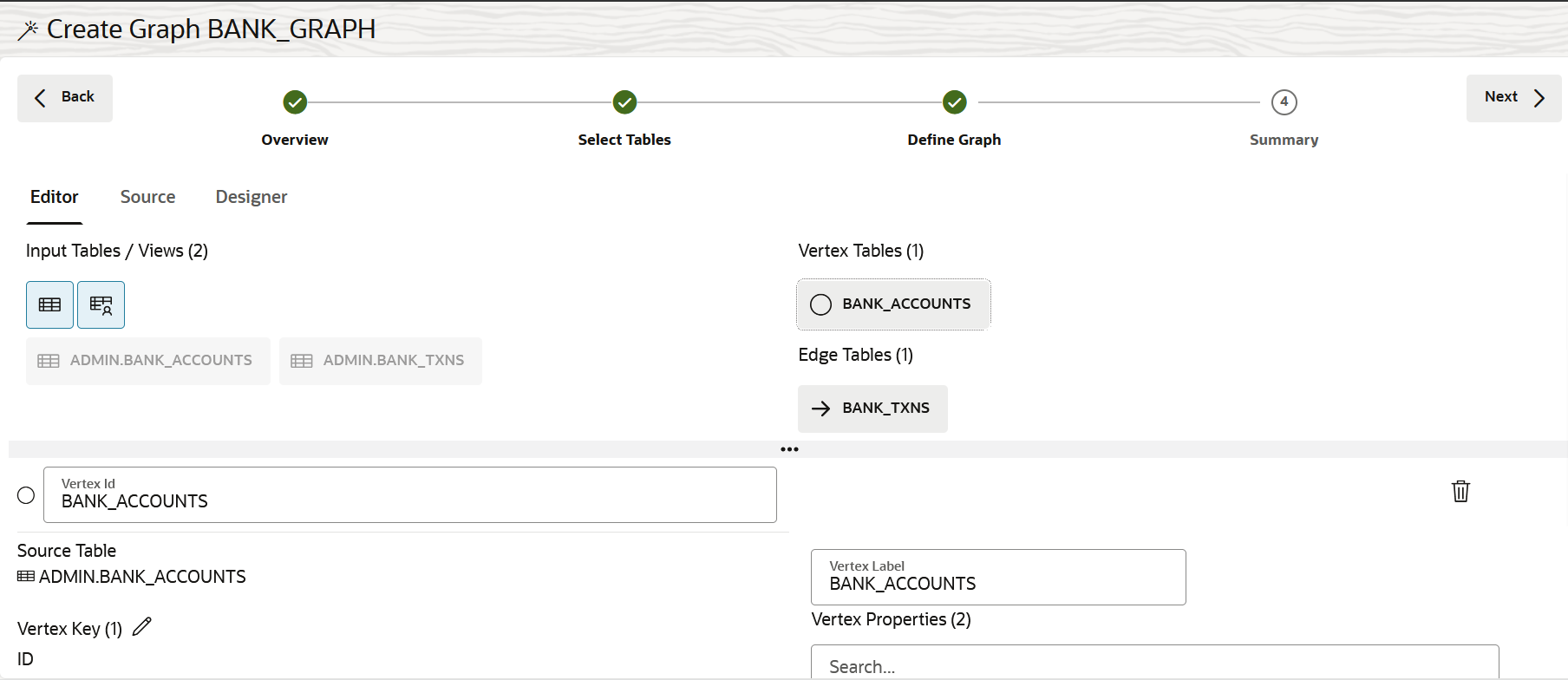
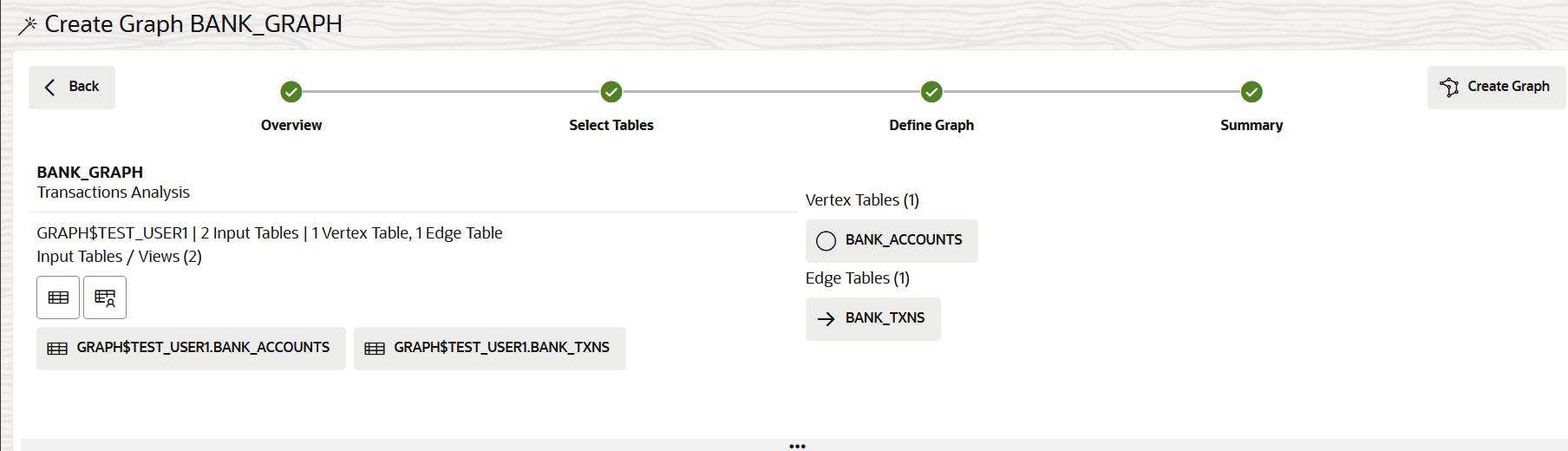
Create a Property Graph from Existing Relational Tables
You can create a property graph from existing relational tables.
Note:
-
The PG Objects graph type is desupported. It is recommended that you create a PGQL Property Graph or SQL Property Graph.
-
SQL property graphs are supported only in Oracle AI Database 26ai. Therefore, if you are using an Autonomous AI Database instance with Oracle AI Database 26ai, then you have the option to create SQL property graphs.
It is also important to note that when creating a graph, the property graph wizard will throw a warning if the source tables used to create a PGQL or SQL property graph include any Datetime data types in the primary key. Additionally, a warning will be issued if the tables contain composite vertex keys in the case of PGQL property graphs.
However, you can still create a property graph by ignoring the warning. But you cannot load the property graph into memory.