Specify a Custom URL for Your App
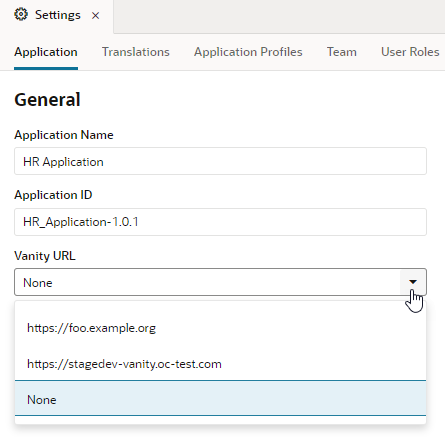
If you want your customers to see a different URL than the default one generated by Visual Builder for your application, you can specify a custom domain, also called a vanity URL, to shield customers from the details of your server’s hostname and domain.
To use a custom domain for your application, your service administrator must configure your instance to support the custom domain. For the steps to do this, see Create and Configure a Custom Endpoint for Your Visual Builder Instance in Administering Oracle Visual Builder in Oracle Integration 3.
Note that custom domains are subject to some limitations:
- If the custom endpoint is selected as the Vanity URL in the application's Settings editor, it can only be accessed from the custom domain root (for example,
https://mycustom.example.com) after the app is published. - If you publish a different web app in the same visual application, it immediately becomes the default app for the custom domain, and the previous web app will no longer be available at the custom domain.
- A custom domain can only be used to access one live app (in the visual application configured for the root URL). You can access other live apps in the same instance only by using the full Oracle Cloud URL, or by creating a different visual application and mapping it to a different custom domain.
- If a visual application contains more than one web app, only one of them can be accessed using the custom domain. It's not possible to specify which app in a visual application will be available at the custom domain because the domain is configured in the Settings for the visual application, not for individual web apps. If you are going to use a custom domain, it is recommended that the visual application only contain one web app to ensure that the correct app is loaded.
To map a custom domain to a visual application:
After configuring the custom domain, proceed to stage and publish the visual application, after which your user can enter the custom domain (for example, https://foo.example.org) in the browser to access the web app and the business object APIs. You can also access web apps deployed as PWAs. Note that the URL will not contain any additional path or query parameters because the app is loaded from the custom root domain ("/").