SRTP Configuration and Troubleshooting
The Secure Real-time Transport Protocol (SRTP) provides encryption and authentication for the call content and call signaling streams. Authentication provides assurance that packets are from the purported source, and that the packets have not been tampered with during transmission. Encryption provides assurance that the call content and associated signaling has remained private during transmission.
RTP and RTCP traffic are encrypted as described in RFC 3711: The Secure Real-time Transport Protocol (SRTP). The negotiation and establishment of keys and other cryptographic materials that support SRTP is described in RFC 4568: Session Description Protocol (SDP) Security Description for Media Streams. Cryptographic parameters are established with only a single message or in single round-trip exchange using the offer/answer model defined in RFC 3264: An Offer/Answer Model with the Session Description Protocol.
Session Description Protocol Security Descriptions for Media Streams (SDES), defined in RFC 4568, provides an alternative method for creating keys used to encrypt Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP) and Real-time Transport Control Protocol (RTCP) transactions.
This document should be used as a base reference only, outlining procedures to configure SRTP on the SBC node from its base configuration. An Oracle Systems Engineer should be consulted with regards to specific concerns as they apply to customer specific SBC configurations.
Configuration guides are available for download from https://docs.oracle.com/.
SRTP Topologies
End-to-end SRTP was supported in previous releases, and the SBC was transparent to the SRTP key negotiation and the SRTP flow. It was just adding its own IP to the media path and then relaying the SRTP packets as it does with RTP flows, so in terms of functionality, RTP and SRTP caused no difference in the SBC configuration and functionality.
However, release S-CX6.2.0 and higher includes support for termination of SRTP. This includes special configuration and treatment of RTP and SRTP flows.
SRTP topologies can be reduced to three basic topologies:
| Single Ended SRTP Termination |
SRTP enabled on inbound interface, disabled on outbound interface (or vice versa) If SRTP is enabled for the inbound realm/interface, the SBC will handle the request according to the capabilities defined in the SRTP configuration. If there is a crypto attribute in the offer, the SBC will attempt to parse the crypto attributes and parameters in the SDP. It accepts exactly one of the offered crypto attributes for a given media stream, if this is configured as a valid crypto-suite on the SD. If there is no crypto-suite configured on the SBC in the list of crypto-suites received, the SBC will reject the call with a “488 Not Acceptable Here” response. Before the request is forwarded to the callee, the SBC allocates resources, updates the SDP with proper media addresses and ports, and the original crypto attribute is removed from the SDP. Once the reply from the callee is received, SBC inserts the appropriate crypto attribute to form a new SDP, and forwards the response back to the caller. At this point, SRTP traffic is allowed between the caller and the SD. |
| Back-to-back SRTP Termination |
SRTP enabled on inbound interface, enabled on outbound interface. Separate crypto keys on either side. Similarly to the “Single End SRTP Termination” case above, before the request is forwarded to the callee, the SBC allocates resources and updates the SDP with proper media addresses and ports, however, at this point, the original crypto attribute is replaced with one generated by the SD. The construction of the crypto attribute in the SDP will be based on the configuration for the outbound realm/interface. Once the reply from the callee is received, the SBC could also accept or reject the “answer” from the callee according to the configuration and the list of crypto-suites supported. If accepted, the SBC will replace the original crypto attribute from the callee with its own to form a new SDP. The new SDP is forwarded back to the caller. At this point, SRTP media sessions are established on both sides. |
| Pass-through SRTP |
Crypto attribute is not intercepted, just forwarded, and the key negotiation is done end-to-end. If the configuration specifies “pass-through” mode, the SBC will not intercept the crypto attribute exchange between the caller and the callee. The crypto attribute will be forwarded as it is from the caller to the callee and vice versa. The SBC simply modifies media IP addresses and ports to enable media anchoring (if configured), hence SRTP flows pass transparently through the SD. |
Hardware Requirements
SRTP is supported on the Acme Packet 4600/6100/6300/6350 platforms and require IPSec network interfaces (NIU), which allows the use of the encryption needed for SRTP. Software Datapath also suppots SRTP for 1100/3900.
# show prom-info PHY
Contents of PHY
Assy, 4 Port SFP with QOS and IPSec
Part Number: 002-0603-58
Serial Number: 090850027933
FunctionalRev: 02.11
BoardRev: 02.00
PCB Family Type: Quad port GiGE SFP PHY
ID: 4 Port GiGE w/QoS & Encryption
Format Rev: 16
Options: 0
Manufacturer: Benchmark
Week/Year: 50/2008
Sequence Number: 027933
The SSM module is NOT a requirement for SRTP, although typically SRTP is deployed in conjunction with TLS for SIP. Therefore, TLS is used for encrypting signaling and SRTP is used for encrypting media. In this case, then the SSM module is also required to run TLS.
# show security ssm SSM (Security Service Module) V2 present.
If UDP/TCP is used for SIP, then SSM module is not a requirement.
Design Aspects - Configuration Elements
Here is a brief explanation on the elements needed for SRTP configuration. This is just a basic reference, the configuration of each element will depend on the desired design and will be described in the following sections.
Security, media-security, sdes-profileThis is the first element to configure, where the algorithm and the cryptos to be used are configured.
For sdes-profile, it is required to define the crypto-suites accepted, and also whether or not authentication and/or encryption are used for SRTP and if encryption is used for SRTCP. The “use-ingress-session-params” attribute is used to override previous parameters, specifying that the SBC will accept encryption/no-encryption, authentication/no-authentication in SRTP/SRTCP, using in the egress SDP the same session parameter that was received in the ingress SDP.
# show running-config sdes-profile
sdes-profile
name sdes1
crypto-list AES_CM_128_HMAC_SHA1_80 AES_CM_128_HMAC_SHA1_32
srtp-auth enabled
srtp-encrypt enabled
srtcp-encrypt enabled
egress-offer-format same-as-ingress
use-ingress-session-params srtcp-encrypt
srtp-auth
srtp-encrypt
mki disabled
key
salt
Media-sec-policy instructs the SBC how to handle the SDP received/sent under a realm (RTP, SRTP or any of them) and, if SRTP needs to be used, the sdes-profile that needs to be used.
(media-sec-policy)# show
media-sec-policy
name msp1
pass-through disabled
inbound
profile sdes1
mode srtp
protocol sdes
outbound
profile sdes1
mode srtp
protocol sdes
The security-policy is the element that creates the security-association inside the SBC, needed to make the real SRTP encryption/unencryption. Each security-policy created must have a unique priority.
# verify-config
------------------------------------------------------------------
WARNING: security-policy [media] has invalid remote-ip-addr-match
------------------------------------------------------------------
Total:
1 warnings
security-policy
name media
network-interface M00:0
priority 2
local-ip-addr-match 11.0.0.11
remote-ip-addr-match 0.0.0.0
local-port-match 0
remote-port-match 0
trans-protocol-match UDP
direction both
local-ip-mask 255.255.255.255
remote-ip-mask 0.0.0.0
action srtp
ike-sainfo-name
outbound-sa-fine-grained-mask
local-ip-mask 0.0.0.0
remote-ip-mask 255.255.255.255
local-port-mask 0
remote-port-mask 65535
trans-protocol-mask 255
valid enabled
vlan-mask 0xFFF
Design Considerations
The intents of the design considerations explained here are to:
- Minimize interoperability issues by standardizing field configurations
- Provide guidelines for new users to the Session Border Controller
- Document when and why configuration elements should be changed from their default values
- Facilitate transition of customers from Systems Engineering to Technical Support by making configurations consistent (yielding predictable behavior)
Further, each design considers the following aspects:
- Flexibility: how resilient the configuration is, and how adaptable the configuration is (i.e. when turning up new connected networks)
- Scalability: minimizing redundant configuration objects and setting a templated foundation to allow overlay configuration with minimal disruption
- Compatibility: working with other popular devices in carriers’ VoIP networks
The main aspects treated here focused on which traffic is desired under a realm, so each design needs to consider the following, previous to any configuration:
- SIP Traffic: SIP over UDP/TCP (unsecured transport) or over TLS (secured transport protocol).
- Media Traffic: media over
RTP, media over SRTP or media over both RTP and SRTP allowed at the same time.
This would differentiate the IP design, since:
- For media over RTP only or SRTP only, just one IP address will be used for them
- For media over both RTP/SRTP allowed at the same time, then the recommendation is to use two different IPs on the same network-interface. One will send RTP traffic and the other IP will be used for SRTP traffic. This should be considered for correct IP plan under the network.
Secured/Unsecured Network - By default, the SBC considers that SIP traffic, when SRTP is configured, should run over secured transport protocol, TLS. If this is not the case, the SBC needs to be instructed to allow SIP traffic over non-secured transport protocol (UDP/TCP).
sip-interface
state enabled
realm-id access1
description
sip-port
address 11.0.0.11
port 5060
transport-protocol UDP
tls-profile
allow-anonymous all
ims-aka-profile
carriers
…
secured-network enabled
When secured-network is set to DISABLED under a sip-interface where SRTP is configured, the sip-interface will only allow SIP over TLS. If SIP is received over UDP/TCP, the SBC will reject the call with “488 Not Acceptable Here”.
When secured-network is set to ENABLED, the SBC understands the network is secured and it accepts SIP traffic on UDP/TCP.
Media traffic - Every realm under the configuration should be instructed to the type of media that should handle whether that be RTP only, SRTP only or both RTP and SRTP. For each realm, it can be differentiated between the inbound and outbound media type, giving the flexibility of having different protocols for inbound or for outbound.
The “mode” parameter under the media-sec-policy controls the media protocol defined for each inbound/outbound flow under a realm.
- RTP Only
The “mode” parameter under the inbound/outbound section of the media-sec-policy should be set to RTP. In this case, no profile should be defined, and the protocol should be set to “None”.
(media-sec-policy)# show
media-sec-policy
name removeCrypto
pass-through disabled
inbound
profile
mode rtp
protocol none
outbound
profile
mode rtp
protocol none
This is mostly used in single ended SRTP termination configurations, where this media-sec-policy removes the SRTP component part from the SDP to offer/accept only SRTP. This media-sec-policy should be applied under the realm where only RTP is desired.
realm-config
identifier backbone
description
addr-prefix 0.0.0.0
network-interfaces
M10:0
…
media-sec-policy removeCrypto
In the case of RTP only, no sdes-profile and no security-policy are needed.
- SRTP Only
The “mode” parameter under the media-sec-policy should be set to SRTP. The “profile” parameter should be set to the configured sdes-profile, and the protocol should be set to SDES.
In this case, only SRTP is accepted in the realm. An INVITE arriving to the realm without SRTP capabilities is rejected by the SBC with a “488 Not Acceptable Here”.
(media-sec-policy)# show
media-sec-policy
name SRTP1
pass-through disabled
inbound
profile sdes1
mode srtp
protocol SDES
outbound
profile sdes1
mode srtp
protocol SDES
# show running-config sdes-profile
sdes-profile
name sdes1
crypto-list AES_CM_128_HMAC_SHA1_80 AES_CM_128_HMAC_SHA1_32
srtp-auth enabled
srtp-encrypt enabled
srtcp-encrypt enabled
egress-offer-format same-as-ingress
use-ingress-session-params srtcp-encrypt
srtp-auth
srtp-encrypt
mki disabled
key
salt
realm-config
identifier access1
description
addr-prefix 0.0.0.0
network-interfaces
M00:0
…
media-sec-policy SRTP1
Finally, a security-policy should be applied to perform the RTP/SRTP or SRTP/SRTP conversion at the flow level. One security-policy is needed for the media traffic.
The local-port-match is set to 0 for an SRTP security-policy, meaning all ports on the IP address configured in local-ip-match are subject to this security-policy. Hence, to avoid a clash with the SIP signaling port (typically 5060) when signaling and media are managed on the same IP address, a second security-policy with a higher priority is required to exempt the SIP signaling port from the media security-policy.
Note that in the case where the SIP traffic runs on a different IP/Subnet from media, then this second security-policy for SIP signaling is not required.
security-policy
name signaling
network-interface M00:0
priority 1
local-ip-addr-match 11.0.0.11
remote-ip-addr-match 0.0.0.0
local-port-match 5060
remote-port-match 0
trans-protocol-match ALL
direction both
local-ip-mask 255.255.255.255
remote-ip-mask 0.0.0.0
action allow
ike-sainfo-name
outbound-sa-fine-grained-mask
local-ip-mask 255.255.255.255
remote-ip-mask 255.255.255.255
local-port-mask 0
remote-port-mask 0
trans-protocol-mask 0
valid enabled
vlan-mask 0xFFF
security-policy
name media
network-interface M00:0
priority 2
local-ip-addr-match 11.0.0.11
remote-ip-addr-match 0.0.0.0
local-port-match 0
remote-port-match 0
trans-protocol-match UDP
direction both
local-ip-mask 255.255.255.255
remote-ip-mask 0.0.0.0
action srtp
ike-sainfo-name
outbound-sa-fine-grained-mask
local-ip-mask 0.0.0.0
remote-ip-mask 255.255.255.255
local-port-mask 0
remote-port-mask 65535
trans-protocol-mask 255
valid enabled
vlan-mask 0xFFF
- Both RTP/SRTP support
The “mode” under the media-sec-policy should be set to ANY. Also, the profile should be configured with the sdes-profile that would be used in case of SRTP and the protocol should be set to SDES, depending on which protocol is required.
When inbound mode=any, the SBC will accept SDP with only RTP description, SDP with only SRTP description and SDP with 2 m lines having both RTP and SRTP description.
(sdes-profile)# egress-offer-format
<enumeration> format of offer SDP in 'any' mode
{same-as-ingress | simultaneous-best-effort}
- Same-as-ingress: The SBC will use to build the egress SDP offer the mode received in the ingress realm. So if the SBC received only RTP in the ingress realm, it will insert only RTP in the egress SDP, and if it received only SRTP in the ingress SDP, it will set the egress SDP to only SRTP.
- Simultaneous-best-effort: The SBC will insert additional SRTP description in the SDP if the ingress SDP contained only RTP and vice-versa, so the resultant SDP should contain both RTP and SRTP media profiles contained in 2 different media lines in the SDP.
# show running-config sdes-profile
sdes-profile
name sdes1
crypto-list AES_CM_128_HMAC_SHA1_80 AES_CM_128_HMAC_SHA1_32
srtp-auth enabled
srtp-encrypt enabled
srtcp-encrypt enabled
egress-offer-format same-as-ingress
use-ingress-session-params srtcp-encrypt
srtp-auth
srtp-encrypt
mki disabled
key
salt
(media-sec-policy)# show
media-sec-policy
name SRTP1
pass-through disabled
inbound
profile sdes1
mode any
protocol SDES
outbound
profile sdes1
mode any
protocol SDES
(media-sec-policy)#
realm-config
identifier access1
description
addr-prefix 0.0.0.0
network-interfaces
M00:0
…
media-sec-policy SRTP1
Finally, we need to configure the security-policy for SRTP. Since in this case both RTP and SRTP can be present under the same realm, the recommendation is to use different IPs for RTP and for SRTP.
The SRTP IP must be in the same subnet (network-interface) as the IP used for RTP. For its definition, the IP used for RTP will continue being defined under the steering-pool, while the IP for SRTP needs to be defined under the security-policy. When RTP needs to be used, the SBC will use the IP configured in the steering-pool, whereas when SRTP needs to be inserted into the SDP, the SBC will choose the IP from the security-policy AND an available port from the steering-pool configured for RTP, so the dimensioning of the port range of the steering-pool should consider both RTP and SRTP estimated traffic.
If SIP traffic runs over the same subnet (network-interface), it is recommended not to use the IP used for SRTP traffic. That way, it is not necessary to configure a second security-policy for SIP traffic.
In the example below, 11.0.0.10 is used for RTP and 11.0.0.11 is used for SRTP. In the case that SIP traffic is desired under the same network, it would be recommended not to use 11.0.0.11, as this is reserved for SRTP use and the security-policy configured for it would apply.
steering-pool
ip-address 11.0.0.10
start-port 20000
end-port 49999
realm-id access
security-policy
name media
network-interface M00:0
priority 1
local-ip-addr-match 11.0.0.11
remote-ip-addr-match 0.0.0.0
local-port-match 0
remote-port-match 0
trans-protocol-match UDP
direction both
local-ip-mask 255.255.255.255
remote-ip-mask 0.0.0.0
action srtp
ike-sainfo-name
outbound-sa-fine-grained-mask
local-ip-mask 0.0.0.0
remote-ip-mask 255.255.255.255
local-port-mask 0
remote-port-mask 65535
trans-protocol-mask 255
valid enabled
vlan-mask 0xFFF
last-modified-by admin@10.0.3.99
last-modified-date 2010-07-20 04:59:53
High Availability
In order for SIP and SRTP to work properly in the HA environment, both sip-config and ipsec-global-config elements should be configured.
- red-ipsec-port: redundant IP security synchronization port
- red-max-trans: max redundant transactions to keep
- red-sync-start-time: redundant sync start timeout
- red-sync-comp-time: redundant sync complete timeout
ipsec-global-config
red-ipsec-port 1994
red-max-trans 10000
red-sync-start-time 5000
red-sync-comp-time 1000
sip-config
… …
red-sip-port 1988
red-max-trans 10000
red-sync-start-time 5000
red-sync-comp-time 1000
Notes on the Reference Configuration
The intention of this document is not to provide a full set of configurations, as the flexibility of the SRTP configuration makes valid a high number of different possible configurations. The objective is to present some common and valid configurations that have been tested and verified in Oracle labs.
In the cases considered here, there is a considered “access” or “peer1A” network, in the 172.18.1.0/24 network, and a considered “core” or “peer1B” in the 172.18.2.0/24 network. In all cases SIP and media traffic runs on the same subnets.
To simplify the use of this BCP, no other elements are configured in this case, so no redundancy or DDoS prevention are configured in the configurations exposed. The configurations follow the guides of BCP for access (using policy based realm bridging) and peering scenarios. For TLS, it is assumed single-side authentication in all cases.
The configurations presented use SDES mechanism for SRTP encryption. No SRTP pass-through cases are presented here, as there is nothing required for the SBC to be transparent to the SRTP negotiation end-to-end.
Single-Ended SRTP Termination on secured networks.
This is the typical access scenario where SRTP is deployed completely in the access network, allowing the users to use TLS for SIP and SRTP for media. In the core network, UDP is used for SIP and RTP is used for media.
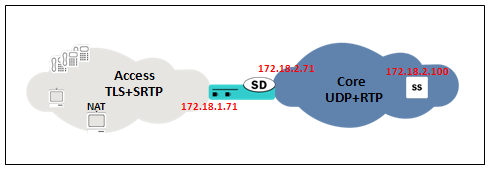
The IP used for SIP and SRTP in the SBC in the access network is 172.18.1.71, and the IP used for SIP and RTP in the core network is 172.18.2.71. The SIP Registrar/Proxy in the core network is in 172.18.2.100.
In this case, secured-network is set to DISABLED under the access sip-interface and ENABLED on the core sip-interface. Two security-policies are configured, one for SRTP and one that creates the exception for SIP signaling. Also, two media-sec-policies are created, one in the access network with mode=SRTP and one in the core with mode=RTP.
RTP and Single-Ended SRTP Termination on unsecured networks.
This is a very common architecture, where both RTP and SRTP endpoints reside in the access network, especially while in transition from RTP to SRTP. This means that both UDP/RTP and TLS/SRTP can be present in the access network. In the core network, UDP for SIP and RTP for media will be used.
In this case, in the access network we will use 172.18.1.71 for SIP traffic (UDP and TLS) and also for RTP traffic. 172.18.1.72 will be used for SRTP traffic. In the core network, 172.18.2.71 will be used for SIP and RTP. The SIP Proxy/Registrar uses 172.18.2.100.
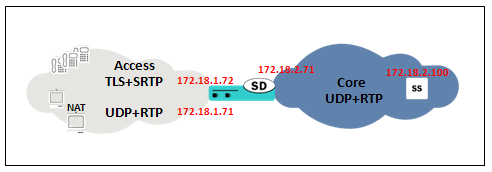
Secured-network parameter is set to ENABLED under the access sip-interface and ENABLED on the core sip-interface. Only one security-policy is configured for SRTP under 172.181.72. Two media-sec-policies are created, one in the access network with mode=any and one in the core with mode=RTP. As in the access network both RTP and SRTP endpoints could be present, the egress-offer-format is set to simultaneous-best-effort.
Back-to-back SRTP Termination
Normally deployed in peering scenarios where SRTP is needed in both networks that the SBC is interconnecting. In that case, the Session Border Controller is doing SRTP termination so the SRTP key exchange is different in the two connected networks.
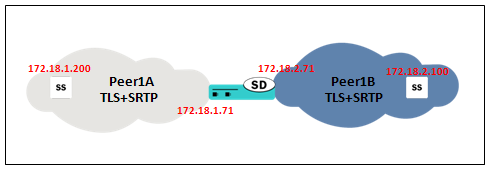
In the SBC, 172.18.1.71 will be used for SIP (TLS) and SRTP in the peer1A network, while 172.18.2.71 will be used in the 172.18.2.71.
The peer element sending traffic in the peer1A network will be in 172.18.1.200, while the peer element in the peer1B will be 172.18.2.100.
Secured-network is set to DISABLED under both sip-interfaces. Two security-policies are configured per peer1 realm, one for SRTP and one that creates the exception for SIP signaling, so four security-policies are configured in total. Also, two media-sec-policies are created, one in the peer1A network with mode=SRTP and one in the peer1B with mode=SRTP, where each one is linked with a different SDES profile, to allow different cryptos between networks. Note that this is not required, and the same SDES profile could be used for both networks, the key exchange would keep different as the SBC would terminate the SRTP anyway, so configuring different SDES profiles would be only needed in the case where the crypto-suites supported in each network are different or have different characteristics.
Troubleshooting
A network capture taken on both access and core network should show RTP packets with the same sequence number, however, if SRTP termination is done in the SBC, the payload contained in RTP packets with the same sequence number will be different because of the encryption/unencryption done by the SD.
To troubleshoot SRTP on the Session Border Controller, following commands can be used:
# show sa stats srtp
03:07:17-186
SA Statistics ---- Lifetime ----
Recent Total PerMax
SRTP Statistics
ADD-SA Req Sent 2 2 2
ADD-SA Req Rcvd 2 2 2
…
DEL-SA Req Sent 2 2 2
DEL-SA Req Rcvd 2 2 2
…
MOD-SA Req Sent 0 0 0
MOD-SA Req Rcvd 0 0 0
..
SA Added 4 4 4
SA Add Failed 0 0 0
SA Deleted 4 4 4
Show
security srtp commands show the security association created for
SRTP encryption and its detailed information.
show security
srtp <network_interface> debug/brief/detail/raw
Note:
there is a warning when these commands want to be run, as it should be done carefully in production systems:WARNING: This action might affect system performance and take a long time to finish. Are you sure [y/n]?:
- Show security srtp status <network_interface>
- Show security spd <network_interface>
# show security srtp sad M00 debug
WARNING: This action might affect system performance and take a long time to finish.
Are you sure [y/n]?: y
SRTP security-association-database for interface 'M00':
Displaying SA's that match the following criteria -
direction : both
src-addr-prefix : any
src-port : any
dst-addr-prefix : any
dst-port : any
trans-proto : ALL
Inbound:
destination-address : 62.2.139.213
destination-port : 10012
vlan-id : 0
sal-index : 2
sad-index : 10
ssrc : 1514612894
encr-algo : aes-128-ctr
auth-algo : hmac-sha1
auth-tag-length : 80
flags -
ms: 5489040, ls: 8
mtu : 1500
mki : 0
mki length : 0
lifetime byte count -
ms: 0x 0, ls: 0x 0
packet count -
ms: 0x 0, ls: 0x 12F
roll over count : 0
anti replay highest seq num : 11814
highest seq num : 0
auth error count : 0
anti replay count : 0
mki mismatch count : 0
ssrc mismatch count : 1
# show security srtp sad M00 raw
WARNING: This action might affect system performance and take a long time to finish.
Are you sure [y/n]?: y
SRTP security-association-database for interface 'M00':
Displaying SA's that match the following criteria -
direction : both
src-addr-prefix : any
src-port : any
dst-addr-prefix : any
dst-port : any
trans-proto : ALL
Inbound:
Index I VLN P <-- Masks --> SAD Next
TP Dest. IP Address SPI Pr ID TS P V Pr VLN TS P V Index Link
0000a 0 01 00000000 00000000 00000000 11 000 00 0 0 ff 000 00 0 0 0000a 00000
00000000 d58b023e
Index Flags MS Flags LS EX Flg MTU SSRC MKI MKI Len ROC
0000a 05489040 00000008 00202a 05dc 5a47289e 00000000 00000000 00000000
Master key: f6 8e c5 af 6c af 96 72 64 78 04 97 14 44 c1 a9
Master salt: 59 da 31 4d c2 3d 15 ca b6 3b 39 e1 27 2d
E-IV: 59 da 31 4d 98 7a 3d 54 b6 3b 39 e1 27 2d 00 00
HMAC ipad: 7a cc 93 f9 72 44 2d df ee df cc 89 3d a2 35 74 18 32 bb 25
HMAC opad: 2b 6d cc 43 49 fa 65 8e 4a d2 03 50 90 00 9f 10 16 6d 1a 90
Sequence Number Anti-replay window (128 bits wide)
00002f68 ffffffff ffffffff ffffffff ffffffff
Life Byte Count Packet Count Auth Err Anti-replay Err
0000000000000000 0000000000000271 00000000 00000000
ICV Len HSN MKI Mismatch SSRC Mismatch
04 00000000 00000000 00000001
Log.secured provides logs of the security-association activities related to SRTP.
Enhanced Traffic Controller (ETC) NIU support
The ETC NIU supports only the SDES protocol for SRTP. The configuration element “security-policy” is no longer required for SRTP using the ETC NIU. AES_CM_128 encryption and HMAC_SHA1_80 or HMAC_SHA1_32 authentication suites are supported on the ETC NIU. ARIA Cipher suite are also supported.
The ETC NIU contains one Cavium hardware chip that provides encryption/decryption. In order to support 10,000 concurrent sessions and overcome the 1 GB bandwidth limitation per port, a major design goal is to split the traffic between any 2 ports on ingress and remaining 2 ports on egress. Upon reaching 10,000 concurrent sessions limit, subsequent calls will be rejected.
Following is the list of commands to be used in order to get SRTP and ETC specific information.
show nat flow-info srtp statistics will show the global statistics for all SRTP flows.
SBASNQ06# show nat flow-info srtp statistics
PPM_ID_SRTP_E:
PPX Global Statistics
---------------------
alloc_count : 50
dealloc_count : 16
input-packets : 0
output-packets : 0
sessions-count : 2
init-requests : 4
init-success : 4
init-fail : 0
modify-requests : 0
modify-success : 0
modify-fail : 0
delete-requests : 2
delete-success : 2
delete-fail : 0
query-requests : 0
query-success : 0
query-fail : 0
resources-error : 0
protect-fail : 0
unprotect-fail : 0
status-err : 0
bad-param : 0
alloc-fail : 0
dealloc-fail : 0
terminus : 0
auth-fail : 0
cipher-fail : 0
replay-fail : 0
replay-old : 0
algo-fail : 0
no-such-op : 0
no-ctx : 0
cant-check : 0
key-expired : 0
nonce-bad : 0
read-failed : 0
write-failed : 0
parse-err : 0
encode-err : 0
pfkey-err : 0
mki-changed : 0
srtp-pkt-too-small : 0
srtcp-pkt-too-small : 0
PPM_ID_SRTP_D:
PPX Global Statistics
---------------------
alloc_count : 50
dealloc_count : 16
input-packets : 0
output-packets : 0
sessions-count : 3
init-requests : 2
init-success : 2
init-fail : 0
modify-requests : 1
modify-success : 1
modify-fail : 0
delete-requests : 0
delete-success : 0
delete-fail : 0
query-requests : 0
query-success : 0
query-fail : 0
resources-error : 0
protect-fail : 0
unprotect-fail : 0
status-err : 0
bad-param : 0
alloc-fail : 0
dealloc-fail : 0
terminus : 0
auth-fail : 0
cipher-fail : 0
replay-fail : 0
replay-old : 0
algo-fail : 0
no-such-op : 0
no-ctx : 0
cant-check : 0
key-expired : 0
nonce-bad : 0
read-failed : 0
write-failed : 0
parse-err : 0
encode-err : 0
pfkey-err : 0
mki-changed : 0
srtp-pkt-too-small : 0
srtcp-pkt-too-small : 0
show nat flow-info srtp by-addr 3.0.0.2 all
This command will show the crypto information details for a flow with the given source address. If “all” is used, the details for all the SRTP flows will be displayed. However, “all” does not to display the statistics from the octeon srtp code.
SBASNQ06# show nat flow-info srtp by-addr 3.0.0.2 all
Crypto Parameters 3.0.0.2:7001 -> 7.0.0.2:6058
=================
Collapsed : false
SRTCP Only : false
Crypto In
------------------
destination-address : 208.54.47.80
destination-port : 40000
vlan-id : 632
encr-algo : aes-128-ctr
auth-algo : hmac-sha1
auth-tag-length : 32
key index : 0
mki : none
roll-over-count : 0
---No Crypto Out---
PPM_ID_SRTP_D
PPX Statistics
--------------
Stream #1
ssrc : 3879260980
rtp-cipher-id : AES-128-ICM
rtp-auth-id : HMAC-SHA1
rtp-security-level : Crypto + Auth
rtp-total-packets : 5423
rtp-total-bytes : 954448
rtp-cipher-bytes : 867680
rtp-auth-bytes : 932756
rtcp-cipher-id : AES-128-ICM
rtcp-auth-id : HMAC-SHA1
rtcp-security-level : Crypto + Auth
rtcp-total-packets : 0
rtcp-total-bytes : 0
rtcp-cipher-bytes : 0
rtcp-auth-bytes : 0
key-lifetime : 42949672954294961871
direction : Receiver
Crypto Parameters 3.0.0.2:7001 -> 7.0.0.2:6058
=================
Collapsed : false
SRTCP Only : true
Crypto In
------------------
destination-address : 208.54.47.80
destination-port : 40000
vlan-id : 632
encr-algo : aes-128-ctr
auth-algo : hmac-sha1
auth-tag-length : 32
key index : 0
mki : none
roll-over-count : 0
---No Crypto Out---
PPM_ID_SRTP_D
PPX Statistics
--------------
Stream #1
ssrc : 0
rtp-cipher-id : NULL
rtp-auth-id : NULL
rtp-security-level : None
rtp-total-packets : 0
rtp-total-bytes : 0
rtp-cipher-bytes : 0
rtp-auth-bytes : 0
rtcp-cipher-id : NULL
rtcp-auth-id : NULL
rtcp-security-level : None
rtcp-total-packets : 0
rtcp-total-bytes : 0
rtcp-cipher-bytes : 0
rtcp-auth-bytes : 0
key-lifetime : 0
direction : Unknown
show mbcd errors
This command will show counters for SRTP errors, including SRTP Flow Add Failed, SRTP Flow Delete Failed, and SRTP Flow Update Failed.
SBASNQ06# show mbcd errors
22:29:33-160
MBC Errors/Events ---- Lifetime ----
Recent Total PerMax
Client Errors 0 0 0
Client IPC Errors 0 0 0
Open Streams Failed 0 0 0
Drop Streams Failed 0 0 0
Exp Flow Events 1 1 1
Exp Flow Not Found 0 0 0
Transaction Timeouts 0 0 0
Server Errors 0 0 0
Server IPC Errors 0 0 0
Flow Add Failed 0 2 2
Flow Delete Failed 0 0 0
Flow Update Failed 0 0 0
Flow Latch Failed 0 0 0
Pending Flow Expired 0 0 0
ARP Wait Errors 0 0 0
Exp CAM Not Found 0 0 0
Drop Unknown Exp Flow 0 0 0
Drop/Exp Flow Missing 0 0 0
Exp Notify Failed 0 0 0
Unacknowledged Notify 0 0 0
Invalid Realm 0 0 0
No Ports Available 0 0 0
Insufficient Bandwidth 0 0 0
Stale Ports Reclaimed 0 0 0
Stale Flows Replaced 0 0 0
Telephone Events Gen 0 0 0
Pipe Alloc Errors 0 0 0
Pipe Write Errors 0 0 0
Not Found In Flows 0 0 0
SRTP Flow Add Failed 0 0 0
SRTP Flow Delete Faile 0 0 0
SRTP Flow Update Faile 0 0 0
SRTP Capacity Exceeded 0 0 0
show mbcd statistics
This command will show counters for number of active SRTP/SRTCP flows, as well as the number of SRTP Sessions maintained.
SBASNQ06# show mbcd statistics
22:29:40-168
MBCD Status -- Period -- -------- Lifetime --------
Active High Total Total PerMax High
Client Sessions 1 1 1 1 1 1
Client Trans 0 1 3 3 3 1
Contexts 3 3 2 3 2 3
Flows 14 14 3 14 11 14
Flow-Port 2 2 2 2 2 2
Flow-NAT 13 13 5 16 11 13
Flow-RTCP 2 2 4 4 4 2
Flow-Hairpin 0 0 0 0 0 0
Flow-Released 0 0 0 0 0 0
MSM-Release 0 0 0 0 0 0
Rel-Port 0 0 0 0 0 0
Rel-Hairpin 0 0 0 0 0 0
NAT Entries 15 15 9 20 11 15
Free Ports 80000 80004 0 80004 80004 80004
Used Ports 4 4 4 4 4 4
Port Sorts - - 0 0 0
Queued Notify 0 0 0 0 0 0
MBC Trans 0 3 3 3 3 3
MBC Ignored - - 0 0 0
ARP Trans 0 0 0 0 0 0
Relatch NAT 0 0 0 0 0 0
Relatch RTCP 0 0 0 0 0 0
SRTP Only Flows 1 1 3 3 3 1
SRTCP Only Flow 3 3 3 3 3 3
SRTP Collapsed 0 0 0 0 0 0
SRTP Sessions 1 1 3 3 3 1
Flow Rate = 0.0
Load Rate = 0.0
show mbcd all
This command will show counters for number of active SRTP/SRTCP flows, as well as the number of SRTP Sessions maintained.
SBASNQ06# show mbcd all
22:29:44-172
MBCD Status -- Period -- -------- Lifetime --------
Active High Total Total PerMax High
Client Sessions 1 1 1 1 1 1
Client Trans 0 1 3 3 3 1
Contexts 3 3 2 3 2 3
Flows 14 14 3 14 11 14
Flow-Port 2 2 2 2 2 2
Flow-NAT 13 13 5 16 11 13
Flow-RTCP 2 2 4 4 4 2
Flow-Hairpin 0 0 0 0 0 0
Flow-Released 0 0 0 0 0 0
MSM-Release 0 0 0 0 0 0
Rel-Port 0 0 0 0 0 0
Rel-Hairpin 0 0 0 0 0 0
NAT Entries 15 15 9 20 11 15
Free Ports 80000 80004 0 80004 80004 80004
Used Ports 4 4 4 4 4 4
Port Sorts - - 0 0 0
Queued Notify 0 0 0 0 0 0
MBC Trans 0 3 3 3 3 3
MBC Ignored - - 0 0 0
ARP Trans 0 0 0 0 0 0
Relatch NAT 0 0 0 0 0 0
Relatch RTCP 0 0 0 0 0 0
SRTP Only Flows 1 1 3 3 3 1
SRTCP Only Flow 3 3 3 3 3 3
SRTP Collapsed 0 0 0 0 0 0
SRTP Sessions 1 1 3 3 3 1
Flow Rate = 0.0
Load Rate = 0.0
22:29:44-172
NAT Entries ---- Lifetime ----
Recent Total PerMax
Adds 9 20 11
Deletes 4 5 4
Updates 2 2 2
Non-Starts 0 0 0
Stops 0 0 0
Timeouts 0 0 0
22:29:44-172
ACL Entries -- Period -- -------- Lifetime --------
Active High Total Total PerMax High
Static Trusted 4 4 0 4 4 4
Static Blocked 4 4 0 4 4 4
Dynamic Trusted 1 1 1 1 1 1
Dynamic Blocked 0 0 0 0 0 0
ACL Operations ---- Lifetime ----
Recent Total PerMax
App Requests 1 2 1
Added 1 9 8
Removed 0 1 1
Dropped 0 0 0
22:29:44-172
MBC Errors/Events ---- Lifetime ----
Recent Total PerMax
Client Errors 0 0 0
Client IPC Errors 0 0 0
Open Streams Failed 0 0 0
Drop Streams Failed 0 0 0
Exp Flow Events 1 1 1
Exp Flow Not Found 0 0 0
Transaction Timeouts 0 0 0
Server Errors 0 0 0
Server IPC Errors 0 0 0
Flow Add Failed 0 2 2
Flow Delete Failed 0 0 0
Flow Update Failed 0 0 0
Flow Latch Failed 0 0 0
Pending Flow Expired 0 0 0
ARP Wait Errors 0 0 0
Exp CAM Not Found 0 0 0
Drop Unknown Exp Flow 0 0 0
Drop/Exp Flow Missing 0 0 0
Exp Notify Failed 0 0 0
Unacknowledged Notify 0 0 0
Invalid Realm 0 0 0
No Ports Available 0 0 0
Insufficient Bandwidth 0 0 0
Stale Ports Reclaimed 0 0 0
Stale Flows Replaced 0 0 0
Telephone Events Gen 0 0 0
Pipe Alloc Errors 0 0 0
Pipe Write Errors 0 0 0
Not Found In Flows 0 0 0
SRTP Flow Add Failed 0 0 0
SRTP Flow Delete Faile 0 0 0
SRTP Flow Update Faile 0 0 0
SRTP Capacity Exceeded 0 0 0
22:29:44-172
---- Lifetime ----
Recent Total PerMax
Add incoming:
Request received 1 1 1
Duplicates received 0 0 0
Replies sent 1 1 1
Errors sent 0 0 0
Add outgoing:
Requests sent 1 1 1
Req retransmissions 0 0 0
Replies received 1 1 1
Errors received 0 0 0
Avg Latency=0.000 for 1
Max Latency=0.000
22:29:44-172
SRTP Flows ---- Lifetime ----
Recent Total PerMax
Adds 3 3 3
Deletes 2 2 2
Updates 0 0 0
---< NO DATA AVAILABLE >----(Subtract)
22:29:45-172
---- Lifetime ----
Recent Total PerMax
Notify incoming:
Request received 1 1 1
Duplicates received 0 0 0
Replies sent 1 1 1
Errors sent 0 0 0
Notify outgoing:
Requests sent 1 1 1
Req retransmissions 0 0 0
Replies received 1 1 1
Errors received 0 0 0
Avg Latency=0.000 for 1
Max Latency=0.000
---< NO DATA AVAILABLE >----(Other)
---< NO DATA AVAILABLE >----(Unknown)
show sipd errors
This command will show the counter for number of SIP sessions that failed to setup due to problems related to SRTP signaling.
SBASNQ06# show sipd errors
22:29:50-178
SIP Errors/Events ---- Lifetime ----
Recent Total PerMax
SDP Offer Errors 0 0 0
SDP Answer Errors 0 0 0
Drop Media Errors 0 0 0
Transaction Errors 0 0 0
Application Errors 0 0 0
Media Exp Events 0 0 0
Early Media Exps 0 0 0
Exp Media Drops 0 0 0
Expired Sessions 0 0 0
Multiple OK Drops 0 0 0
Multiple OK Terms 0 0 0
Media Failure Drops 0 0 0
Non-ACK 2xx Drops 0 0 0
Invalid Requests 0 0 0
Invalid Responses 0 0 0
Invalid Messages 0 0 0
CAC Session Drop 0 0 0
Nsep User Exceeded 0 0 0
Nsep SA Exceeded 0 0 0
CAC BW Drop 0 0 0
SRTP Errors 0 0 0
show security srtp sessions
This command will be used to show the active srtp/srtcp sessions and the total allowed capacity of 10,000 sessions.
SBASNQ06# show security srtp sessions
Capacity=10000
SRTP Sessions -- Period -- ---- Lifetime ----
Active High Total Recent Total PerMax
1 1 3 3 3 1
show nat flow-info all
This command will also show the crypto information for the SRTP flows. This should not be executed in a production environment, since it dumps information about all the flows.
SBASNQ06# show nat flow-info all
Output curtailed due to size.
. . . . . continued
----------------------------------------------
SA_flow_key : 7.0.0.2 SA_prefix : 32
DA_flow_key : 10.176.28.218 DA_prefix : 32
SP_flow_key : 6058 SP_prefix : 16
DP_flow_key : 40000 DP_prefix : 16
VLAN_flow_key : 980
Protocol_flow_key : 17
Ingress_flow_key : 1
Ingress Slot : 1
Ingress Port : 0
NAT IP Flow Type : IPv4 to IPv4
XSA_data_entry : 208.54.47.80
XDA_data_entry : 3.0.0.2
XSP_data_entry : 40000
XDP_data_entry : 7001
Egress_data_entry : 0
Egress Slot : 0
Egress Port : 0
flow_action : 0X1
optional_data : 0
FPGA_handle : 0x000000c1
assoc_FPGA_handle : 0x00000000
VLAN_data_entry : 632
host_table_index : 6
Switch ID : 0x00000005
average-rate : 0
weight : 0x0
init_flow_guard : 300
inact_flow_guard : 300
max_flow_guard : 86400
payload_type_2833 : 0
index_2833 : 0
pt_2833_egress : 0
qos_vq_enabled : 0
codec_type : 0
HMU_handle : 0
SRTP Crypto In : NONE
SRTP Crypto Out : AES_CM_128_HMAC_SHA1_32
----------------------------------------------
Input Link Parameters - IFD Index: 0x5
----------------------------------------------
IFD Byte Enable: false
EPD Mode Enable: true
Retain: false
ABJ Mode: true
Disable Empty: false
Ignore On Empty: false
TGID: 0x6
WRGID: 0x0
TG Enable: true
WRG Enable: false
Output Link Parameters - OFD Index: 0x5
----------------------------------------------
shaped_flow: false
latency_sensitive: false
pkt_mode: Packet Mode
zero_min_credit_flow: false
parent_pipe_num: 0x1
delta: 0x1
flow_credit_min_exp: 0x0
flow_credit_min_man: 0x0
IFD 0x00000005: dropCount = 0x00000000
IFD 0x00000005: acceptCount = 0x00001f35
----------------------------------------------
dump-np-stats
octeon statistics
This command displays all of the octeon statistics
SBASNQ06# dump-etc-stats
ACME Net-Net 4500 Firmware SCX6.3.0 F-1 GA (Build 156)
Build Date=07/13/11
----------------- HyperChicken Stats and FPGA Register DUMP -------------------------
Revision : 1.05
Date stamp : WED MAR 23 02:00:00 2011
----------------- Port 0 -------------------------
Hyperchicken FPGA Internal MacPhy Stats Reg dump:
MAC Stats on ch0:
Tx Bytes : addr(0xd8010000): 0x00345ec2
Rx Bytes : addr(0xd8010004): 0x003fe0ec
Rx Undersz Fr : addr(0xd8010008): 0x00000000
Rx Frag Fr : addr(0xd801000c): 0x00000000
Rx 64B Fr Ok : addr(0xd8010010): 0x000000b5
Rx 65-127B Fr Ok : addr(0xd8010014): 0x000000fe
Rx 128-255B Fr Ok : addr(0xd8010018): 0x00003a49
Rx 256-511B Fr Ok : addr(0xd801001c): 0x00000005
Rx 512-1023B Fr Ok : addr(0xd8010020): 0x00000007
Rx 1024-Max Fr Ok : addr(0xd8010024): 0x00000299
Rx Oversz Fr : addr(0xd8010028): 0x00000000
Tx 64B Fr Ok : addr(0xd801002c): 0x00000367
Tx 65-127B Fr Ok : addr(0xd8010030): 0x0000002f
Tx 128-255B Fr Ok : addr(0xd8010034): 0x00003a48
Tx 256-511B Fr Ok : addr(0xd8010038): 0x00000001
Tx 512-1023B Fr Ok : addr(0xd801003c): 0x00000002
Tx 1024-Max Fr Ok : addr(0xd8010040): 0x00000000
Tx Oversz Fr : addr(0xd8010044): 0x00000000
Rx Fr Ok : addr(0xd8010048): 0x00003ea4
Rx Fr ChkSeq Err : addr(0xd801004c): 0x00000000
Rx Broadcast Fr Ok : addr(0xd8010050): 0x00000031
Rx Multic Fr Ok : addr(0xd8010054): 0x00003b2d
Rx Cntl Fr Ok : addr(0xd8010058): 0x00000000
Rx FrLen/Typ ooRng : addr(0xd801005c): 0x00000000
Rx Vlan Tag Fr Ok : addr(0xd8010060): 0x0000002c
Rx Pause Fr Ok : addr(0xd8010064): 0x00000000
Rx CtlFr+uns opcode: addr(0xd8010068): 0x00000000
Tx Fr Ok : addr(0xd801006c): 0x00003de4
Tx Broadcast Fr Ok : addr(0xd8010070): 0x00000022
Tx Multic Fr Ok : addr(0xd8010074): 0x00000009
Tx Underrun Err : addr(0xd8010078): 0x00000000
Tx Cntl Fr Ok : addr(0xd801007c): 0x00000000
Tx Vlan Tag Fr Ok : addr(0xd8010080): 0x00003aa3
Tx Pause Fr Ok : addr(0xd8010084): 0x00000000
Rx Alignment Err : addr(0xd8010100): 0x003464f0
Rx_Cfg_Word0 : addr(0xd8010a00): 0x00000000
Rx_Cfg_Word1 : addr(0xd8010a40): 0x5a000000
Tx_Cfg : addr(0xd8010a80): 0x58000000
Flow_Ctl_Cfg : addr(0xd8010ac0): 0x00000000
Speed_Cfg : addr(0xd8010b00): 0x80000000
Mgt_Cfg : addr(0xd8010b40): 0x00000000
Uni_Addr_Word0 : addr(0xd8010b80): 0x00000000
Uni_Addr_Word1 : addr(0xd8010b84): 0x00000000
PHY Stats on ch0:
NA
Curtailed due to size…… Similar output for port 1 through 7
----------------- Port 1 -------------------------
----------------- Port 2 -------------------------
----------------- Port 3 -------------------------
----------------- Port 4 -------------------------
----------------- Port 5 -------------------------
----------------- Port 6 -------------------------
----------------- Port 7 -------------------------
Hyperchicken FPGA Internal MacPhy Stats Reg dump:
MAC Stats on ch7:
Tx Bytes : addr(0xd801e000): 0x00000c80
Rx Bytes : addr(0xd801e004): 0x00001410
Rx Undersz Fr : addr(0xd801e008): 0x00000000
Rx Frag Fr : addr(0xd801e00c): 0x00000000
Rx 64B Fr Ok : addr(0xd801e010): 0x0000002a
Rx 65-127B Fr Ok : addr(0xd801e014): 0x00000024
Rx 128-255B Fr Ok : addr(0xd801e018): 0x00000000
Rx 256-511B Fr Ok : addr(0xd801e01c): 0x00000000
Rx 512-1023B Fr Ok : addr(0xd801e020): 0x00000000
Rx 1024-Max Fr Ok : addr(0xd801e024): 0x00000000
Rx Oversz Fr : addr(0xd801e028): 0x00000000
Tx 64B Fr Ok : addr(0xd801e02c): 0x00000032
Tx 65-127B Fr Ok : addr(0xd801e030): 0x00000000
Tx 128-255B Fr Ok : addr(0xd801e034): 0x00000000
Tx 256-511B Fr Ok : addr(0xd801e038): 0x00000000
Tx 512-1023B Fr Ok : addr(0xd801e03c): 0x00000000
Tx 1024-Max Fr Ok : addr(0xd801e040): 0x00000000
Tx Oversz Fr : addr(0xd801e044): 0x00000000
Rx Fr Ok : addr(0xd801e048): 0x0000004e
Rx Fr ChkSeq Err : addr(0xd801e04c): 0x00000000
Rx Broadcast Fr Ok : addr(0xd801e050): 0x00000021
Rx Multic Fr Ok : addr(0xd801e054): 0x00000009
Rx Cntl Fr Ok : addr(0xd801e058): 0x00000000
Rx FrLen/Typ ooRng : addr(0xd801e05c): 0x00000000
Rx Vlan Tag Fr Ok : addr(0xd801e060): 0x0000004e
Rx Pause Fr Ok : addr(0xd801e064): 0x00000000
Rx CtlFr+uns opcode: addr(0xd801e068): 0x00000000
Tx Fr Ok : addr(0xd801e06c): 0x00000032
Tx Broadcast Fr Ok : addr(0xd801e070): 0x00000032
Tx Multic Fr Ok : addr(0xd801e074): 0x00000000
Tx Underrun Err : addr(0xd801e078): 0x00000000
Tx Cntl Fr Ok : addr(0xd801e07c): 0x00000000
Tx Vlan Tag Fr Ok : addr(0xd801e080): 0x00000032
Tx Pause Fr Ok : addr(0xd801e084): 0x00000000
Rx Alignment Err : addr(0xd801e100): 0x00000c80
Rx_Cfg_Word0 : addr(0xd801ea00): 0xddccbbaa
Rx_Cfg_Word1 : addr(0xd801ea40): 0x5800ffee
Tx_Cfg : addr(0xd801ea80): 0x58000000
Flow_Ctl_Cfg : addr(0xd801eac0): 0x00000000
Speed_Cfg : addr(0xd801eb00): 0x8c000000
Mgt_Cfg : addr(0xd801eb40): 0x00000041
Uni_Addr_Word0 : addr(0xd801eb80): 0x00000041
Uni_Addr_Word1 : addr(0xd801eb84): 0x00000000
PHY Stats on ch7:
PHY Stats on ch7:
Ctl_Reg : addr(0xd801f000): 0x00001140
Status_Reg : addr(0xd801f004): 0x000001e8
Phy_Id1 : addr(0xd801f008): 0x00000028
Phy_Id2 : addr(0xd801f00c): 0x0000d400
Auto_Neg4 : addr(0xd801f010): 0x000001a0
Auto_Neg5 : addr(0xd801f014): 0x00004060
Auto_Neg6 : addr(0xd801f018): 0x00000006
Auto_Neg7 : addr(0xd801f01c): 0x00002001
Auto_Neg8 : addr(0xd801f020): 0x00000000
Ext_Status : addr(0xd801f03c): 0x00008000
AN_Intr_Ctl: addr(0xd801f040): 0x00000003
Lpbk_Ctl : addr(0xd801f044): 0x00000000
----------------- SPI ports -------------------------
Hyperchicken FPGA Internal SPI Stats Reg dump:
SPI Link Status : addr(0xd8000080): 0x000008b9
SPI Port 8 Status : addr(0xd8000084): 0x00028200
SPI Port 8 Rx Good Packet Count : addr(0xd8000088): 0x0000770e
SPI Port 8 Rx Bad Packet Count : addr(0xd800008c): 0x00000000
SPI Port 8 Tx Good Packet Count : addr(0xd8000090): 0x00007aa0
SPI Port 8 Tx Bad Packet Count : addr(0xd8000094): 0x00000000
SPI Port 9 Status : addr(0xd8000098): 0x00008000
SPI Port 9 Rx Good Packet Count : addr(0xd800009c): 0x00000000
SPI Port 9 Rx Bad Packet Count : addr(0xd80000a0): 0x00000000
SPI Port 9 Tx Good Packet Count : addr(0xd80000a4): 0x00000000
SPI Port 9 Tx Bad Packet Count : addr(0xd80000a8): 0x00000000
SPI Port 10 Status : addr(0xd80000ac): 0x00008200
SPI Port 10 Rx Good Packet Count : addr(0xd80000b0): 0x00000000
SPI Port 10 Rx Bad Packet Count : addr(0xd80000b4): 0x00000000
SPI Port 10 Tx Good Packet Count : addr(0xd80000b8): 0x00000000
SPI Port 10 Tx Bad Packet Count : addr(0xd80000bc): 0x00000000
------------------------ Octeon Debug Level---------------------------
Current Debug Flags: CVMX Debug: 0x20000 PPM Error: 0x0 PPM Debug: 0x0 PPM Bypass: 0x0
--------------------- Octeon Debug Statistics-------------------------
--- Total Debug Statistics ---
Debug:
normal_debug: 62845
pci_debug: 2
pkt_debug: 31422
ppm_debug: 61927
host_debug: 156
send_events: 913
Warnings:
Failures:
Errors:
PPMs:
ppmid_debug[2]: 33
ppmid_debug[3]: 23
ppmid_errors[4]: 30036
ppmid_debug[5]: 2737
Exceptions:
Interrupts:
----------------------------------
------------------- Octeon Command Statistics-----------------------
--- Command Statistics ---
flow_adds: 9
flow_add_acks: 9
flow_modifys: 3
flow_modify_acks: 3
flow_querys: 6
flow_query_acks: 6
flow_deletes: 4
flow_delete_acks: 4
stat_cmds: 0
stat_cmd_acks: 0
reset_stat_cmds: 0
reset_stat_cmd_acks: 0
device_cmds: 0
device_cmd_acks: 0
print_cmds: 0
print_cmd_acks: 0
------------------ Octeon Core Statistics---------------------------
--- Core Statistics ---
Processing(usec) Usage %
Core input_packets output_packets status avg min max avg min max now
0 22 22 On 29 13 84 2 0 2 2
1 0 0 On 0 -1 0 2 0 2 2
2 29195 28329 On 4 5 23 2 0 2 2
3 722 699 On 4 5 9 2 0 2 2
4 500 490 On 4 5 9 2 0 2 2
5 260 255 On 4 5 9 2 0 2 2
6 88 87 On 5 5 10 2 0 2 2
7 47 46 On 5 5 9 2 0 2 2
8 8 6 On 5 5 8 2 0 2 2
9 36 35 On 4 5 9 2 0 2 2
10 3 2 On 5 6 10 2 0 2 2
11 10 10 On 5 5 10 2 0 2 2
12 37 36 On 5 5 10 2 0 2 2
13 1 1 On 10 10 10 2 0 3 2
14 14 14 On 5 5 10 2 0 2 2
15 31 30 On 5 5 10 2 0 3 2
--- --- ---
Total: 30974 30062 16
------------------- Octeon PPM Statistics----------------------------
--------------- SRTP_E stats -------------------
alloc-count: 50
dealloc-count: 16
init-requests: 4
init-success: 4
init-fail: 0
modify-request: 0
modify-success: 0
modify-fail: 0
delete-request: 2
delete-success: 2
delete-fail: 0
query-request: 0
query-success: 0
query-fail: 0
protect-fail: 0
unprotect-fail: 0
-----------------------------------------------
--------------- SRTP_D stats -------------------
alloc-count: 50
dealloc-count: 16
init-requests: 2
init-success: 2
init-fail: 0
modify-request: 1
modify-success: 1
modify-fail: 0
delete-request: 0
delete-success: 0
delete-fail: 0
query-request: 2
query-success: 2
query-fail: 0
protect-fail: 0
unprotect-fail: 0
-----------------------------------------------
--- Total IPT Statistics ---
input_packets: 912
output_packets: 912
------------------- Octeon Memory Stats----------------------------
--- Buffer Pool Statistics ---
pool size number available inuse
0 9216 81920 81812 (100) 8
1 128 102400 102348(50 ) 2
2 1024 81920 81905 (0 ) 15
3 128 81920 81920 (0 ) 0
4 9216 10240 10240 (0 ) 0
5 128 81920 81918 (0 ) 2
6 512 81920 81920 (0 ) 0
7 2048 81920 81920 (0 ) 0
Memory Details:
Memory Size: 4010 MB
FW Init Size: 1187 MB
PPMs Init Size: 192 MB
Memory Avail: 2631 MB (2694724 KB)
-------------------- Octeon Port Statistics--------------------------
--- Port Statistics ---
Total active ports: 11
| 0| 1| 2| 3| 4| 5| 6| 7| 32| 33|34|Totals
Raw packets | 15225| 228| 15224| 227| 0| 0| 0| 0| 22| 0| 0|30926
Octets |3421656|27756|3504819|27644| 0| 0| 0| 0|6724| 0| 0|6988599
Runt packets | 46| 37| 46| 37| 0| 0| 0| 0| 0| 0| 0|166
Multicast packets| 228| 228| 227| 227| 0| 0| 0| 0| 0| 0| 0|910
64B packets | 48| 37| 46| 37| 0| 0| 0| 0| 10| 0| 0|178
65B-127B packets| 229| 228| 515| 227| 0| 0| 0| 0| 5| 0| 0|1204
128B-255B packets| 14997| 0| 14997| 0| 0| 0| 0| 0| 0| 0| 0|29994
256B-511B packets| 2| 0| 0| 0| 0| 0| 0| 0| 0| 0| 0|2
512B-1023B packets| 1| 0| 2| 0| 0| 0| 0| 0| 7| 0| 0|10
1024B-1518B packets| 2| 0| 0| 0| 0| 0| 0| 0| 0| 0| 0|2
Rx errors | 46| 37| 46| 37| 0| 0| 0| 0| 0| 0| 0|166
Rx good | 15233| 228| 15514| 227| 0| 0| 0| 0| 22| 0| 0|31224
Rx octets |3421656|27756|3504819|27644| 0| 0| 0| 0|6724| 0| 0|6988599
Rx packets | 15279| 265| 15560| 264| 0| 0| 0| 0| 22| 0| 0|31390
Tx packets | 0| 0| 0| 0| 15051| 37| 15333| 37| 0| 911| 0|31369
Tx octets | 0| 0| 0| 0|3336132|2220|3299431|2220| 0|116544| 0|6756547
---------------------------- Host CVMX Statistics---------------------------------------
--- nPApp_cvmx_stats ---
flow_adds: 9
flow_add_acks: 9
flow_modifys: 3
flow_modify_acks: 3
flow_deletes: 4
flow_delete_acks: 4
flow_querys: 6
flow_query_acks: 6
---------------------------- Octeon Host Statistics-------------------------------------
Host Async stats:
Octeon Async Tx Packets: 0
Octeon Async Tx Data: 0
Octeon Async Tx Failed Packets: 0
Octeon Async Tx Empty Messages: 0
Octeon Async Rx Device: 0
Octeon Async Rx Event: 913
Octeon Async Rx Data: 0
Octeon Async Rx Error: 0
Octeon Droq Packets: 495
Octeon Command Tx Packets: 22
Octeon Command Tx Failed: 0
Octeon Tx MsgQ Tx Failed: 0
Octeon Tx MsgQ Rx Failed: 0
Octeon Tx MsgQ Delays: 0
Host DROQ 0 stats:
Dev stats:
interrupts: 935
poll_count: 396454
comp_tasklet_count: 0
droq_tasklet_count: 914
cntq_tasklet_count: 0
droq = 0x439AC40
host_read_index: 0
octeon_write_index: 0
host_refill_index: 0
pkts_pending: 0
max_count: 128
refill_count: 0
refill_threshold: 64
pkts_received: 0
bytes_received: 0
dropped_nodispatch: 0
dropped_nomem: 0
dropped_toomany: 0
Host DROQ 1 stats:
Dev stats:
interrupts: 935
poll_count: 396490
comp_tasklet_count: 0
droq_tasklet_count: 914
cntq_tasklet_count: 0
droq = 0x439AD40
host_read_index: 17
octeon_write_index: 0
host_refill_index: 0
pkts_pending: 0
max_count: 128
refill_count: 17
refill_threshold: 64
pkts_received: 913
bytes_received: 109496
dropped_nodispatch: 0
dropped_nomem: 0
dropped_toomany: 0
Host MBLK pool:
type number
--------- ------
FREE : 4999
DATA : 1
TOTAL : 5000
number of mbufs: 5000
number of times failed to find space: 0
number of times waited for space: 0
number of times drained protocols for space: 0
__________________
CLUSTER POOL TABLE
______________________________________________________________________
size clusters free usage minsize maxsize empty
----------------------------------------------------------------------
10172 5000 4999 913 10000 10000 0
----------------------------------------------------------------------
task done