B Transitioning OAM 11g from a Source to a Target Environment
This chapter describes creating a replica (target) Oracle Access Manager 11g environment from an existing, provisioned, Oracle Access Manager 11g (source) environment. You can use this approach for rolling out your tested upgrades.
This information applies whether your source is a test environment or a production environment. This chapter includes the following topics:
B.1 Prerequisites
Install and configure target components, as described in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Installation Guide for Oracle Identity Management.
See Also:
Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for complete details.
B.2 Introduction to Transitioning
This section provides the following topics:
B.2.1 About Deployment Types
Table B-1 describes the types of deployments that customers might have within their enterprise. Deployment types might be named differently in your enterprise.
| Deployment Type | Description |
|---|---|
|
Development Deployment |
Ideally a sandbox-type setting where the dependency on the overall deployment is minimal |
|
QA Deployment |
Typically a smaller shared deployment used for testing |
|
Pre-production Deployment |
Typically a shared deployment used for testing with a wider audience |
|
Production Deployment |
Fully shared and available within the enterprise on a daily basis |
B.2.2 About Oracle Access Manager Data
Within each deployment, Oracle Access Manager 11g configuration data is stored in files while Oracle Access Manager 11g policy data is stored in a database. The database in the target environment must be the same type of database as in the source environment.
On the policy configuration side, each application domain is constructed using the following shared components:
-
Authentication Module
-
Authentication Scheme (containing one authentication module)
-
Host-Identifiers
-
Resources
On the system configuration side are the agents, host resources, or partner applications that must be protected. An agent can be an OAM Agent (Webgate or Access Client) or an OSSO agent. Each agent must be registered with OAM 11g to protect hosted resources. Registering an agent occurs automatically during replication and:
-
Defines the agent and its specific configuration parameters
-
Creates an application domain for the specified resources
-
Creates an authentication policy with the default authentication scheme for the partner application
-
Creates an authorization policy for the specified resources
-
Generates the symmetric key for the partner application
Transitioning policy and partner information from the source environment to the target environment is accomplished with MBean registered on the AdminServer of the source environment. The client is used to fetch partner and policy information from the source server and apply this to the target server.
The following overview presents the general scope of tasks that must be performed to migrate policy and partner information from a source OAM server to the target.
Caveats:
-
Oracle Security Token Service: Only partners and policies are migrated. Other server artifacts (partner profiles, validation/issuance templates) are not migrated.
-
Oracle Access Manager and Oracle Security Token Service: Key store and trust anchor migration must be performed manually.
B.2.3 About Common Transition Tasks
The following tasks are generally involved in the transition from a source to a target. Task 1 is described in this chapter. Remaining topics, including the actual transition (Task 8), are described in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide.
Task overview: Transitioning to a Target Environment generally includes
-
Configuring Users, Groups, Security Polices, and Credential Stores for Components
-
Moving Oracle Fusion Middleware Components, including Oracle Access Manager with Oracle Security Token Service
B.2.4 About New versus Existing Target Environments
Oracle Access Manager and Oracle Identity Manager are components of Oracle Fusion Middleware 11g.
Transitioning Oracle Access Manager 11g is part of a larger operation. The differences in the scope of tasks required to move an entire Identity Management environment from a source to a target are described in Table B-2.
Table B-2 Differences when Transitioning Data to New versus Existing Target Environments
| New Target Environment | Existing Target Environment |
|---|---|
|
In this scenario you want to move existing Identity Management components in a source environment to a new target environment that does not yet exist. This requires the following tasks, (Task 1 is required while others are needed based on your deployment). All are described in detail the Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide. |
In this scenario you want to move one or more applications from the source to a target in an existing environment, while retaining the source security-related configuration. This requires migrating application-specific data and incremental changes from the source to the target, as described in detail in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide. |
|
|
B.3 Introduction to Transitioning Methods and Tools
This section provides a high-level overview of methods and tools for transitionin Oracle Access Manager 11g with Oracle Security Token Service.
See Also:
For specific details of Fusion Middleware replication tools and methods, see Task 5, "Move Oracle Access Manager 11g to a New Production Environment" of the procedure "Moving Identity Management to a New Production Environment" in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide.
-
About Methods to Propagate Oracle Access Manager Source Data
-
About Migrating OSSO Partners from One OAM Instance to Another
-
About Configuring the Target User Identity Store and Migrating Data
B.3.1 About Methods to Propagate Oracle Access Manager Source Data
To propagate source date you must export the data (users and groups, the identity and policy stores, and credentials from the source) and then import data to the target. You might also need to modify any information that is specific to the new environment (host name or ports, for instance).
Note:
Agents are re-registered during replication. You do not need to re-register agents.
When replicating data in a provisioned source Oracle Access Manager 11g environment, you can use one of the methods described here. These methods include Oracle Security Token Service partners and policies. Primary and secondary server lists of OAM partners and agents serve only delta migration scenarios:
Note:
In the full replication method, the source is cloned to create the target. If the target exists, it is completely erased during processing. To preserve the existing target environment, you must either create a fresh target environment (or do not use the full migration procedure).
Regardless of the method you choose:
-
Oracle Security Token Service: Only partners and policies are migrated. Other server artifacts (partner profiles, validation/issuance templates) are not migrated.
-
Oracle Access Manager and Oracle Security Token Service: Key store and trust anchor migration must be performed manually.
Table B-3 describes full data replication (partners and policies). By performing manual and automated tasks, you can replicate the Oracle Access Manager 11g source setup to a target. For complete setup (Oracle Fusion Middleware) replication, see the Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide.
| Requirements | Automated and Manual Tasks | Not Required or Processed |
|---|---|---|
|
The following WLST commands are used:
An Administrator must also:
|
|
Table B-4 describes requirements and processing for incremental transfer (known as delta replication). All incremental changes in the source are transferred to the target. Selective transfer is not required.
| Requirements | Tasks | Not Required or Processed |
|---|---|---|
|
The source OAM Server contains the "truth". Any conflicts between the source and the target are resolved based on the source. |
The Administrator runs the WLST command with the "MigrateAll" flag set to "false" to move only the changes from the source to the target system. |
Policy configuration that has not changed is not processed. |
B.3.2 About Migrating OSSO Partners from One OAM Instance to Another
Oracle Access Manager supports migrating partners across OAM Server instances. This is required in a GIT scenario where you must copy partner information from an internal to an external deployment.
When migrating a selected partner, you can retrieve the partner ID from the source system's oam-config.xml. For example, if the partner ID for the OSSO Agent with site name 'TEST_OSSO_AGENT2' is 998AF964144D39BC2F, as shown here:
<Setting Name="998AF964144D39BC2F" Type="htf:map"> <Setting Name="AdminId" Type="xsd:string"></Setting> <Setting Name="SiteName" Type="xsd:string">TEST_OSSO_AGENT2</Setting>
Then you could execute the following command from the WLST prompt:
exportSelectedPartners(pathTempOAMPartnerFile="<path where the temporary file need to be generated>",partnersNameList="998AF964144D39BC2F")
B.3.3 About Configuring the Target User Identity Store and Migrating Data
Whether you are moving to a new target, or to an existing target, Oracle provides the WebLogic Scripting Tool (WLST) commands that use an MBean on the Oracle Access Manager 11g AdminServer and enable administrators to:
-
Configure the target user identity store to match the source user identity store, when needed.
-
Replicate and move application domain and policy data (for all or for only selected domains and policies).
-
Provide a conflict resolution profile (automatically) that describes how ID conflicts between the source and target systems must be resolved.
Exporting replicates and exports application domains and partner information to a temporary dump file. To protect this sensitive information, a keystore is generated with the dump file. The key in this keystore is used to encrypt the dump file.
Table B-5 provides information on export mode commands, which you run on the source OAM Server that is hosting the partner to be exported.
Table B-5 Export Partner and Policy Commands
| Command | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
exportPartners() |
Exporting a partner creates an object with all partner information, along with the key for each of the partners. This command takes the path to the temporary oam-partners file as a parameter. |
exportPartners(pathTempOAMPartnerFile=' <pathTempOAMPartnerFile>) |
|
exportPolicy() |
Exports application domain and policy data from the source. OAM application domains are exported with all dependencies. This command takes the path to the temporary oam-policy file as a parameter. |
exportPolicy(pathTempOAMPolicyFile=' <pathTempOAMPolicyFile >') |
Importing decrypts the generated dump file using the key in the keystore and imports the dump file contents to the target OAM Server. You can import partners, policies, or policy differences, as described in Table B-6. Import commands are run on the target OAM Server.
Table B-6 Import Partners, Policy, and Delta Commands
| Command | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
importPartners() |
Decrypts and imports partner data using the key in the keystore. This command takes as input the path the temporary oam-partners file as a parameter that was created during the export operation. |
importPartners (pathTempOAMPartnerFile=' <pathTempOAMPartnerFile>') |
|
importPolicy() |
Decrypts and imports application domain and policy data. Caution: This command overwrites all policy data on the target. This command takes as input the path the temporary oam-policy file that was created during the export operation. |
importPolicy(pathTempOAMPolicyFile=' <pathTempOAMPolicyFile >') |
|
importPolicyDelta() |
Decrypts and only the changes from the source to the target OAM Server without overwriting unchanged policy data on the target. Note: This command writes only changed policy data to the target. This command takes as input the path the temporary oam-policy file that was created during the export operation. |
importPolicyDelta(pathTempOAMPolicyFile=' <pathTempOAMPolicyFile >' |
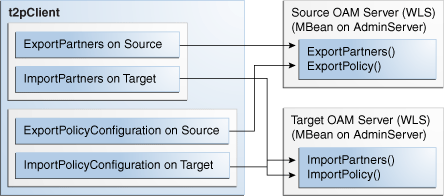
See Also:
Figure B-1 illustrates the processing that occurs between the source and target systems.
B.3.3.1 About Policy Conflict Resolution
Policy conflicts are resolved automatically during processing. The source system is presumed to be the single source of truth during data migration. Any conflicts that are detected between the source system and the target system must be resolved during processing.
B.3.3.2 About Building a Dependency Tree for Each Application Domain
Before migrating an OAM 11g application domain, a dependency tree must be constructed for each of the application domains to be migrated.
The dependency tree can be represented as shown in Figure B-2.
Figure B-2 Dependency Tree for Each Application Domain

Description of "Figure B-2 Dependency Tree for Each Application Domain"
In the sample dependency tree shown in Figure B-2, the application domain consists of three authentication policies and two resources. Each authentication policy is configured with an authentication scheme and each of authentication scheme has an authentication module configured. This sample application domain applies to two resources (each resource is defined as a host identifier and a resource URL).
To migrate data for an application domain, the shared components (Modules, Schemes and Host-identifiers) must be migrated first, if they are not already migrated. Shared component data migration is followed by application domain data migration.
B.4 Planning Your Transition
Planning and preparation are key components of any successful strategy.
This section discusses the planning considerations and inventory items that you and your team need to create to ensure your success:
B.4.1 Choosing A Transitioning Method
Review details in "About Methods to Propagate Oracle Access Manager Source Data" and choose the method that best suits your needs.
See Also:
Task 5, "Move Oracle Access Manager 11g to a New Production Environment" of the procedure "Moving Identity Management to a New Production Environment" in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide.
B.4.2 Noting Differences Between Source and Target Environments
When transferring Oracle Access Manager configuration data from a source to a target, be sure to note the following types of differences between the two environments:
-
Names and implementation details of OAM Server instances
-
Names and implementation details of OAM Agents (Webgates, and Access Clients) including changing the OAM Server to which the Agent points.
-
Names and implementation details of OSSO Agents (mod_osso) including changing the OAM Server to which the Agent points
-
Definitions for Host Identifiers
-
Definitions for authentication schemes, including Challenge Redirect parameters.
-
Definitions for authorization policies, constraints, responses, and resources
-
Definitions for application domains, including all redirect URLs defined in authentication and authorization policies
B.4.3 Developing Deployment Inventories
Before starting any transfer activities, Oracle recommends that you take inventory of your existing Oracle Access Manager 11g Release 1 (11.1.1) deployment. You can gather details from existing installation records or you can gather fresh information directly from the deployment.
B.4.4 Developing Backup and Recovery Strategies
Oracle recommends that you back up data before transfer, and restore the backup after transfer, if needed.
B.4.5 Developing Tests
To help ensure data correctness before transfer, Oracle recommends that you develop specific tests that evaluate configuration in the source deployment.
After transfer, you can use these same tests in the target deployment to ensure that everything is working as expected.
B.4.6 Getting Familiar with Change Propagation
All changes are reflected in the Oracle Access Manager Console and are automatically propagated to every OAM Server in the cluster, including agent registrations.
When you have a single OAM Server and a single Oracle Access Manager Console running on different computers, changes are propagated to the managed run-time OAM Server.
B.4.7 Scheduling and Notifications
Before starting any move, Oracle strongly recommends that you and your team schedule specific transfer windows and that you notify other administrators about planned activities in any deployment for which they are responsible.
B.5 Migrating Oracle Access Manager 11g Data
This section is divided into the following topics, which are a part of a larger procedure to replicate a provisioned Oracle Access Manager 11g deployment:
B.5.1 Exporting Oracle Access Manager 11g Source Data
Use the following procedure as needed to export partner and policy data from the source environment.
See Also:
-
About Configuring the Target User Identity Store and Migrating Data
-
Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide
-
Export Partner Data: On the source OAM Server hosting the OAM 11g partner run the following command using the path to your own temporary OAM partners file. For example:
exportPartners(pathTempOAMPartnerFile=', <pathTempOAMPartnerFile>>')
-
Export Policy Data: On the source OAM Server hosting the OAM 11g policy data, run the following command using the path to your own temporary OAM policy file. For example:
exportPolicy(pathTempOAMPolicyFile=', <pathTempOAMPolicyFile >')
-
Repeat on each source OAM Server hosting partner and policy data.
B.5.2 Importing Oracle Access Manager Data to the Target
Use the following procedure as needed to import partner and policy data from the source environment.
Exporting Oracle Access Manager 11g Source Data
See Also:
-
About Configuring the Target User Identity Store and Migrating Data
-
Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide
-
Import Partner Data: On the target OAM Server, run the following command using the path to the temporary source partners file. For example:
importPartners(pathTempOAMPartnerFile=', <pathTempOAMPartnerFile>>')
-
Import Full Policy Data: On the target OAM Server, run the following command using the path to the temporary source policy file. For example:
importPolicy(pathTempOAMPolicyFile=', <pathTempOAMPolicyFile >')
-
Import Only the Policy Delta: On the target OAM Server, run the following command using the path to the temporary source policy file. For example:
importPolicyDelta(pathTempOAMPolicyFile=', <pathTempOAMPolicyFile >')
-
Repeat on each source OAM Server hosting partner and policy data.