52 Configuring an XML Descriptor
This chapter explains how to configure descriptor options specific to an XML descriptor.
This chapter includes the following sections:
For information on how to configure descriptor options common to two or more descriptor types, see Chapter 119, "Configuring a Descriptor".
52.1 Introduction to XML Descriptor Configuration
Table 52-1 lists the default configurable options for an XML descriptor.
Table 52-1 Configuration Options for XML Descriptors
For more information, see Chapter 50, "Introduction to XML Descriptors".
52.2 Configuring Schema Context for an XML Descriptor
Oracle JDeveloper TopLink Editor and TopLink Workbench use the schema context to associate the XML descriptor reference class with a simple or complex type in one of the schemas associated with the XML project (see Section 5.6.4, "How to Configure an XML Schema Reference"). This allows Oracle JDeveloper TopLink Editor and TopLink Workbench to display the appropriate attributes available for mapping in that context.
You must configure the schema context for an XML descriptor regardless of whether or not you are using Oracle JDeveloper or TopLink Workbench.
The TopLink runtime uses the schema context to validate XML fragments.
52.2.1 How to Configure Schema Context for an XML Descriptor Using TopLink Workbench
To associate an XML descriptor with a specific schema complex type, use this procedure:
-
Select an XML descriptor in the Navigator. Its properties appear in the Editor.
-
Click the Descriptor Info tab. The Descriptor Info tab appears.
Figure 52-1 Descriptor Info Tab, Schema Context Option
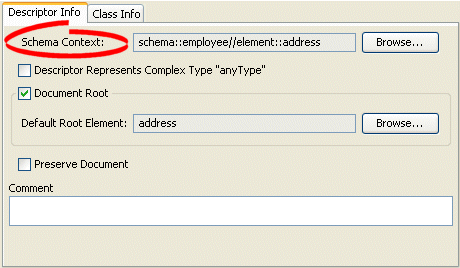
Description of "Figure 52-1 Descriptor Info Tab, Schema Context Option"
Click Browse to select the schema element to associate with this descriptor. For more information, see Section 52.2.1.1, "Choosing a Schema Context".
52.2.1.1 Choosing a Schema Context
Use the Choose Schema Context dialog box to select a specific schema element (such as when mapping an element).
Figure 52-2 Choose Schema Context Dialog Box
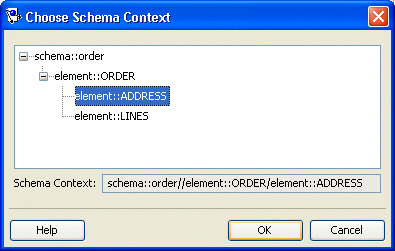
Description of "Figure 52-2 Choose Schema Context Dialog Box"
Select a schema element and click OK.
52.2.2 How to Configure Schema Context for an XML Descriptor Using Java
To configure an XML descriptor with a schema context using Java, create a descriptor amendment method (see Section 119.35, "Configuring Amendment Methods") that uses XMLSchemaReference method setSchemaContext, as Example 52-1 shows.
52.3 Configuring for Complex Type of anyType
This attribute applies only to TopLink Workbench. Use this option to solve "No schema context is specified" problems (see Section 5.3.5, "How to Use the Problems Window") for an XML descriptor that does not represent an element in your XML schema.
In general, TopLink Workbench assumes that every XML descriptor must have a schema context (see Section 52.2, "Configuring Schema Context for an XML Descriptor"). However, if a class in your project does not relate to an element in your schema, then it does not have a schema context.
For example, consider the schema that Example 52-2 shows.
Example 52-2 Schema Using xsd:anyType
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xsd:schema xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema">
<xsd:element name="customer" type="customer-type"/>
<xsd:complexType name="customer-type">
<xsd:sequence>
<xsd:element name="contact-method" type="xsd:anyType"/>
</xsd:sequence>
</xsd:complexType>
<xsd:element name="address">
<xsd:complexType>
<xsd:sequence>
<xsd:element name="street" type="xsd:string"/>
<xsd:element name="city" type="xsd:string"/>
</xsd:sequence>
</xsd:complexType>
</xsd:element>
<xsd:element name="phone-number" type="xsd:string"/>
</xsd:schema>
Because element contact-method is of type xsd:anyType, your project requires a class to represent that type, such as class AnyTypeImpl shown in Figure 52-3. Because this class does not relate to any complex type in your schema, it has no schema context. In this example, you would select this option for the AnyTypeImpl class.
Figure 52-3 Class Representing xsd:anyType
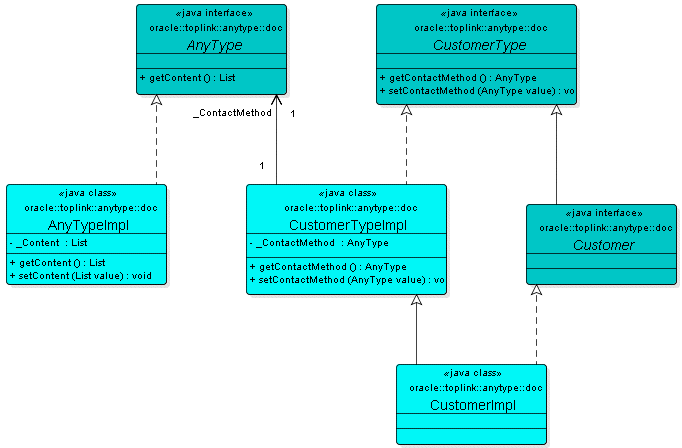
Description of "Figure 52-3 Class Representing xsd:anyType"
Note:
See also Section 54.4, "Configuring Maps to Wildcard".For more information, see Section 53.2.5, "xs:any and xs:anyType Support".
52.3.1 How to Configure Complex Type of anyType Using TopLink Workbench
To specify that the descriptor represents a complex type of anyType, use this procedure:
-
Select a descriptor in the Navigator. Its properties appear in the Editor.
-
Click the Descriptor Info tab. The Descriptor Info tab appears.
Figure 52-4 Descriptor Info Tab, Complex Type "anyType" Option
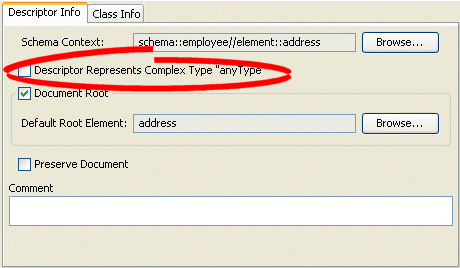
Description of "Figure 52-4 Descriptor Info Tab, Complex Type "anyType" Option"
Select the Descriptor Represents Complex Type "anyType" option to specify this descriptor as the root element.
52.4 Configuring Default Root Element
The default root element is the name that TopLink uses for the root element when marshalling objects for this descriptor to, and unmarshalling from, an XML document. Descriptors used only in composite relationship mappings do not require a default root element.
For more information, see Section 16.2.12, "Default Root Element".
52.4.1 How to Configure Default Root Element Using TopLink Workbench
To specify a schema element as the default root element for the descriptor, use this procedure:
-
Select a descriptor in the Navigator. Its properties appear in the Editor.
-
Click the Descriptor Info tab. The Descriptor Info tab appears.
Figure 52-5 Descriptor Info Tab, Default Root Option
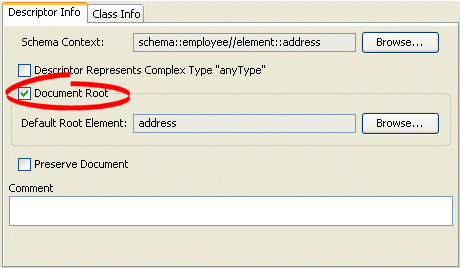
Description of "Figure 52-5 Descriptor Info Tab, Default Root Option"
Select the Default Root Element option to specify this descriptor as the root element.
Click Browse to select the schema element to identify as the root element for this descriptor. See Section 52.4.1.1, "Choosing a Root Element" for more information.
52.4.1.1 Choosing a Root Element
Use the Choose Root Element dialog box to select a specific root element.
Figure 52-6 Choose Root Element Dialog Box
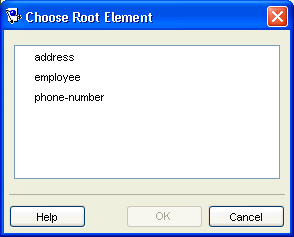
Description of "Figure 52-6 Choose Root Element Dialog Box"
Select the root element and click OK.
52.5 Configuring Document Preservation
TopLink lets you preserve any "extra" data in your XML source that is not required to map to an object model (such as comments, processing instructions, or unmapped elements).
This permits round-tripping from XML to objects and back to XML without losing any data.
52.5.1 How to Configure Document Preservation Using TopLink Workbench
To preserve the entire XML source document, use this procedure:
-
Select a descriptor in the Navigator. Its properties appear in the Editor.
-
Click the Descriptor Info tab. The Descriptor Info tab appears.
Figure 52-7 Descriptor Info Tab, Preserve Document Option
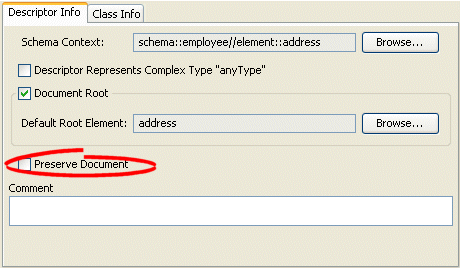
Description of "Figure 52-7 Descriptor Info Tab, Preserve Document Option"
Select the Preserve Document option to maintain any extra information from the source XML document that TopLink does not require (such as comments).
52.5.2 How to Configure Document Preservation Using Java
To configure an XML descriptor to maintain any extra information from the source XML document that TopLink does not require (such as comments) using Java, create a descriptor amendment method (see Section 119.35, "Configuring Amendment Methods") that configures the descriptor using XMLDescriptor method setShouldPreserveDocument.